Fire clay offers high heat resistance and durability, making it ideal for sculpting models exposed to firing processes. Paper clay, enhanced with cellulose fibers, provides lightweight, flexible, and crack-resistant properties suitable for detailed and delicate model construction.
Table of Comparison
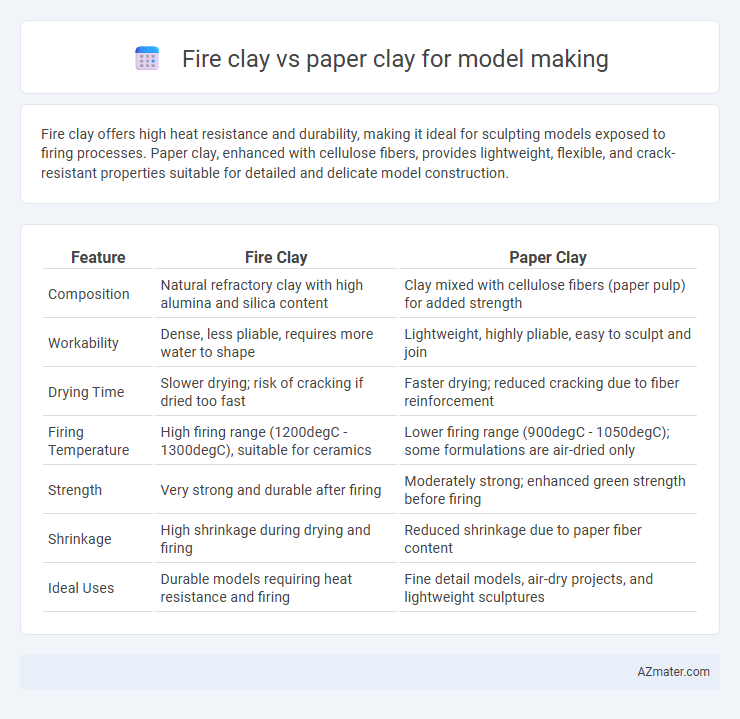
| Feature | Fire Clay | Paper Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Natural refractory clay with high alumina and silica content | Clay mixed with cellulose fibers (paper pulp) for added strength |
| Workability | Dense, less pliable, requires more water to shape | Lightweight, highly pliable, easy to sculpt and join |
| Drying Time | Slower drying; risk of cracking if dried too fast | Faster drying; reduced cracking due to fiber reinforcement |
| Firing Temperature | High firing range (1200degC - 1300degC), suitable for ceramics | Lower firing range (900degC - 1050degC); some formulations are air-dried only |
| Strength | Very strong and durable after firing | Moderately strong; enhanced green strength before firing |
| Shrinkage | High shrinkage during drying and firing | Reduced shrinkage due to paper fiber content |
| Ideal Uses | Durable models requiring heat resistance and firing | Fine detail models, air-dry projects, and lightweight sculptures |
Introduction to Fire Clay and Paper Clay
Fire clay is a type of refractory clay known for its ability to withstand high temperatures without melting or deforming, making it ideal for kiln shelves, molds, and sculptural model bases that require heat resistance. Paper clay combines traditional clay with cellulose fibers, enhancing its tensile strength, drying flexibility, and crack resistance, which benefits detailed sculpting and lightweight model construction. Both materials serve distinct purposes in model making, with fire clay excelling in heat durability and paper clay providing superior workability and surface detail.
Composition Differences: Fire Clay vs Paper Clay
Fire clay consists primarily of refractory alumina and silica, providing high-temperature resistance and structural strength ideal for kiln-fired models. Paper clay incorporates cellulose fibers into traditional clay bodies, enhancing pliability, drying strength, and reducing shrinkage, which benefits hand modeling and lightweight sculptures. The key composition difference lies in fire clay's mineral-based refractory nature versus paper clay's organic fiber reinforcement, influencing their performance and drying behavior in model making.
Workability and Sculpting Characteristics
Fire clay offers excellent heat resistance and durability, making it ideal for functional model making that requires strength and stability during firing. Paper clay is renowned for its superior workability, lightweight structure, and enhanced bonding properties due to the paper fibers, allowing for easier sculpting, finer detail, and extended drying time without cracking. Sculptors prioritize paper clay for intricate and delicate models, while fire clay suits robust forms needing high thermal stability.
Drying Time and Shrinkage Comparison
Fire clay exhibits slower drying time and minimal shrinkage, making it ideal for durable model making where stability is crucial. Paper clay dries faster due to its fiber content, reducing cracking but increasing shrinkage compared to fire clay. Model makers often prefer fire clay for intricate details requiring dimensional accuracy and paper clay for rapid prototyping with moderate shrinkage tolerance.
Strength and Durability After Firing
Fire clay offers superior strength and durability after firing due to its high alumina content and fire resistance, making it ideal for functional pottery and heat-exposed models. Paper clay, while easier to sculpt and lightweight before firing, tends to be less robust and can be more fragile after firing because the paper fibers burn out, leaving a porous structure. For models requiring long-lasting structural integrity and resistance to mechanical stress, fire clay is the preferred choice.
Surface Texture and Finish Quality
Fire clay offers a dense, coarse surface texture ideal for creating durable, rough-edged models with a natural clay finish, typically requiring firing to achieve hardness. Paper clay provides a smoother, more refined surface texture due to its fiber composition, allowing for easier sanding and detailed finishing without the need for kiln firing. Models made with paper clay exhibit higher finish quality with fewer cracks and finer detail retention compared to the traditionally textured fire clay.
Compatibility with Additives and Glazes
Fire clay exhibits excellent compatibility with traditional ceramic additives and high-temperature glazes due to its refractory properties, ensuring minimal shrinkage and warping during firing. Paper clay incorporates cellulose fibers that improve workability and surface texture but can alter glaze adherence, often requiring specialized glaze formulations tailored to the organic content. Understanding the chemical interactions between these clays and specific additives or glazes is crucial for achieving optimal durability and finish in model making.
Cost and Availability Factors
Fire clay offers a cost-effective option for model making due to its abundant natural deposits and widespread availability in bulk, making it ideal for large-scale projects. Paper clay tends to be more expensive because it incorporates cellulose fiber, which enhances workability but limits availability primarily to specialty art stores. Budget-conscious model makers often choose fire clay for its affordability and easy procurement, while paper clay is preferred when finer detail and texture are required despite the higher price.
Suitability for Detailed Model Making
Fire clay offers high heat resistance and durability but is less pliable for intricate detailing compared to paper clay, which contains fiber additives that enhance flexibility and allow for finer, more precise sculpting. Paper clay's lightweight composition enables easier manipulation of delicate features and smoother texturing, making it ideal for detailed model making. The choice depends on the balance between durability needs and the complexity of the model's fine details.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Fire clay, a natural material derived from kaolin, is locally sourced and often mined with minimal environmental disturbance, making it a more sustainable option for model making due to its biodegradability and low carbon footprint. Paper clay incorporates recycled paper fibers, reducing waste and promoting circular economy principles, while its lightweight properties lower transportation emissions. Both clays offer eco-friendly benefits, but paper clay's use of recycled content and potential for reduced energy consumption in drying can enhance environmental sustainability in creative modeling projects.
Infographic: Fire clay vs Paper clay for Model making
 azmater.com
azmater.com