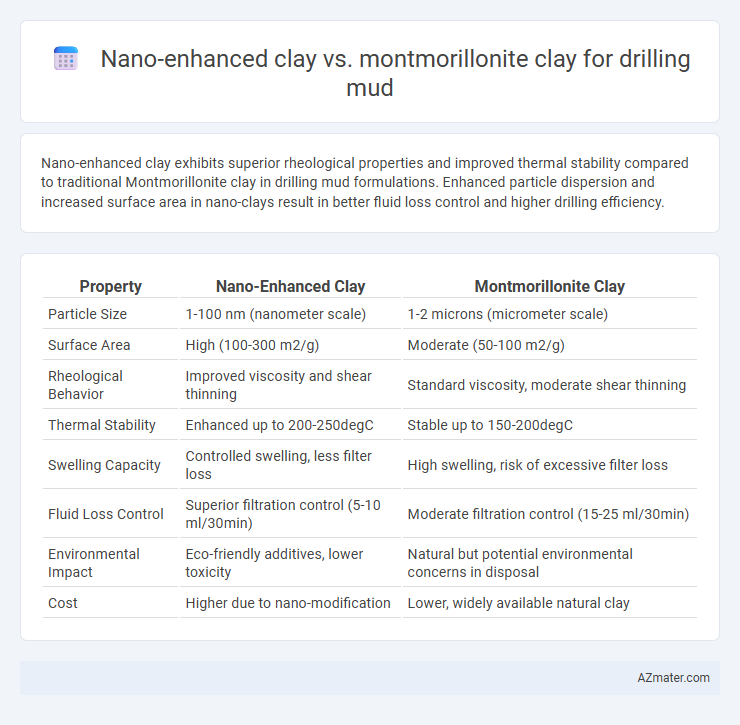
Nano-enhanced clay exhibits superior rheological properties and improved thermal stability compared to traditional Montmorillonite clay in drilling mud formulations. Enhanced particle dispersion and increased surface area in nano-clays result in better fluid loss control and higher drilling efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nano-Enhanced Clay | Montmorillonite Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Size | 1-100 nm (nanometer scale) | 1-2 microns (micrometer scale) |
| Surface Area | High (100-300 m2/g) | Moderate (50-100 m2/g) |
| Rheological Behavior | Improved viscosity and shear thinning | Standard viscosity, moderate shear thinning |
| Thermal Stability | Enhanced up to 200-250degC | Stable up to 150-200degC |
| Swelling Capacity | Controlled swelling, less filter loss | High swelling, risk of excessive filter loss |
| Fluid Loss Control | Superior filtration control (5-10 ml/30min) | Moderate filtration control (15-25 ml/30min) |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly additives, lower toxicity | Natural but potential environmental concerns in disposal |
| Cost | Higher due to nano-modification | Lower, widely available natural clay |
Introduction to Drilling Mud Technologies
Nano-enhanced clay exhibits superior rheological properties and thermal stability compared to traditional Montmorillonite clay, making it highly effective in drilling mud formulations. Montmorillonite, a type of smectite clay, is widely used for its swelling capacity and ability to form thixotropic suspensions, essential for wellbore stability. Innovations in nano-enhanced clays improve viscosity control and filtration loss, optimizing drilling performance in challenging subsurface conditions.
Overview of Montmorillonite Clay in Drilling Fluids
Montmorillonite clay is a key component in drilling fluids due to its exceptional swelling properties, high cation exchange capacity, and excellent rheological control. It forms a stable, viscous gel that effectively suspends drill cuttings, prevents fluid loss, and maintains wellbore stability under high temperature and pressure conditions. The unique layered structure of Montmorillonite enables superior hydration and dispersion, making it essential for effective water-based drilling mud formulations.
Emergence of Nano-Enhanced Clay Additives
Nano-enhanced clay additives in drilling mud demonstrate superior rheological properties and increased thermal stability compared to conventional montmorillonite clay, enabling more efficient drilling operations in harsh environments. The incorporation of nanoparticles improves the clay's particle packing and water retention, reducing fluid loss and enhancing wellbore stability. Advances in nanotechnology have accelerated the emergence of these modified clays as preferred additives in drilling fluids, offering enhanced performance in deep and ultra-deep well applications.
Comparative Rheological Properties
Nano-enhanced clay exhibits superior rheological properties compared to Montmorillonite clay in drilling mud formulations, including higher yield stress and better shear thinning behavior. The incorporation of nanoparticles significantly improves the viscosity stability under high temperature and pressure conditions, enhancing the mud's cuttings suspension and carrying capacity. Montmorillonite clay, while effective, tends to show decreased fluid loss control and lower thermal stability, impacting overall drilling efficiency and wellbore stability.
Filtration Control: Nano-Clay vs Montmorillonite
Nano-enhanced clay exhibits superior filtration control compared to traditional Montmorillonite clay in drilling mud applications, reducing fluid loss and filter cake thickness more effectively. Its nanoparticles create a denser, more impermeable mud cake, enhancing borehole stability and minimizing formation damage. Montmorillonite clay, while effective in swelling and viscosity control, lacks the fine particle size and surface area of nano-clays necessary for optimal filtration performance.
Thermal Stability and Performance Under Pressure
Nano-enhanced clay exhibits superior thermal stability compared to traditional Montmorillonite clay, maintaining structural integrity and rheological properties at temperatures exceeding 300degC. Under high-pressure conditions typical in deep drilling environments, nano-enhanced clay demonstrates enhanced viscosity retention and improved filtration control, resulting in more efficient borehole stability and reduced fluid loss. Montmorillonite clay, while effective at moderate temperatures and pressures, tends to degrade more rapidly, limiting its performance in ultra-deep or high-temperature wells.
Environmental Impact and Toxicity Assessment
Nano-enhanced clay in drilling mud demonstrates improved environmental compatibility by reducing toxic leachates compared to conventional Montmorillonite clay, which often releases harmful heavy metals under drilling conditions. Studies highlight that nano-modification enhances adsorption capacity, minimizing contaminant migration and promoting safer waste management. Toxicity assessments reveal lower bioaccumulation and cytotoxic effects in ecosystems exposed to nano-enhanced clays, offering a sustainable alternative for drilling operations.
Economic Feasibility and Cost-Benefit Analysis
Nano-enhanced clay in drilling mud offers superior rheological properties and improved filtration control compared to traditional Montmorillonite clay, resulting in enhanced wellbore stability and reduced non-productive time. Although the initial cost of nano-enhanced clay is higher, its ability to decrease mud volumes and improve drilling efficiency often leads to significant long-term cost savings. Economic feasibility studies highlight that the increased upfront investment is offset by reduced operational risks and overall lower total drilling expenses, providing a favorable cost-benefit ratio in complex drilling environments.
Field Applications and Case Studies
Nano-enhanced clay improves drilling mud performance by significantly increasing thermal stability and rheological properties compared to conventional Montmorillonite clay, enhancing wellbore stability in high-pressure, high-temperature (HPHT) wells. Field applications in deepwater drilling demonstrate nano-clay's ability to reduce fluid loss and maintain viscosity under extreme conditions, resulting in fewer stuck pipe incidents and improved rate of penetration. Case studies reveal that integrating nano-enhanced clays in drilling mud formulations contributes to cost efficiency and operational reliability in complex geological formations.
Future Trends in Drilling Mud Innovations
Nano-enhanced clay exhibits superior rheological properties and improved thermal stability compared to traditional Montmorillonite clay, making it a promising material for next-generation drilling mud formulations. Research focuses on integrating nanomaterials to enhance fluid loss control and increase wellbore stability under extreme downhole conditions. Future trends emphasize the development of multifunctional drilling fluids leveraging nano-enhanced clays to improve drilling efficiency and reduce environmental impact in unconventional reservoirs.
Infographic: Nano-enhanced clay vs Montmorillonite clay for Drilling mud
 azmater.com
azmater.com