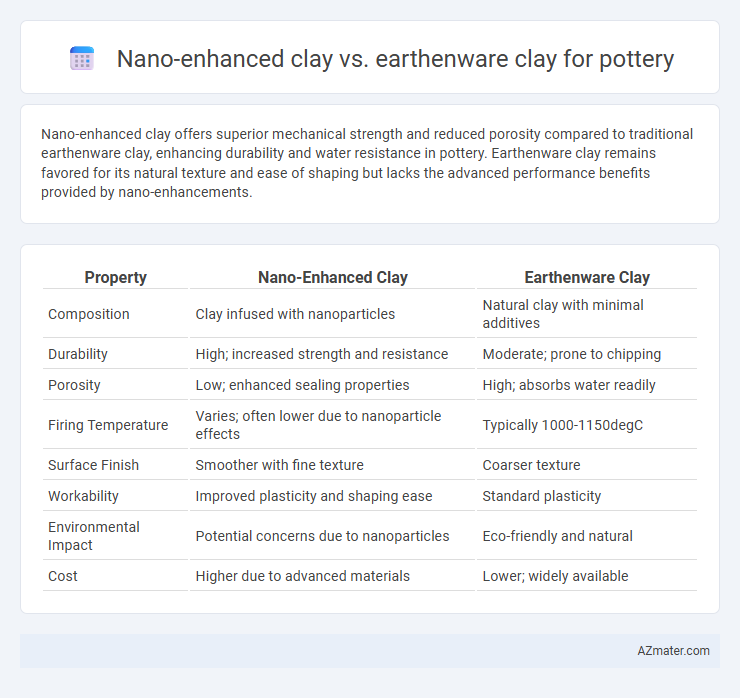
Nano-enhanced clay offers superior mechanical strength and reduced porosity compared to traditional earthenware clay, enhancing durability and water resistance in pottery. Earthenware clay remains favored for its natural texture and ease of shaping but lacks the advanced performance benefits provided by nano-enhancements.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nano-Enhanced Clay | Earthenware Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Clay infused with nanoparticles | Natural clay with minimal additives |
| Durability | High; increased strength and resistance | Moderate; prone to chipping |
| Porosity | Low; enhanced sealing properties | High; absorbs water readily |
| Firing Temperature | Varies; often lower due to nanoparticle effects | Typically 1000-1150degC |
| Surface Finish | Smoother with fine texture | Coarser texture |
| Workability | Improved plasticity and shaping ease | Standard plasticity |
| Environmental Impact | Potential concerns due to nanoparticles | Eco-friendly and natural |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced materials | Lower; widely available |
Introduction to Nano-Enhanced Clay and Earthenware Clay
Nano-enhanced clay integrates nanoscale particles into traditional clay matrices to improve mechanical strength, thermal stability, and surface smoothness, making it ideal for high-performance pottery applications. Earthenware clay, a classic ceramic material, consists primarily of natural clay minerals with lower firing temperatures and porous characteristics, offering a rustic and absorbent finish suitable for decorative and functional pottery. The introduction of nanotechnology in clay formulation enhances durability and aesthetic precision, contrasting with the organic and breathable qualities of earthenware clay.
Composition Differences: Nano-Enhanced vs. Traditional Earthenware
Nano-enhanced clay incorporates nanoparticles such as silica or alumina, which significantly improve the material's mechanical strength, thermal resistance, and plasticity compared to traditional earthenware clay. Traditional earthenware clay primarily consists of natural minerals like kaolinite and quartz, resulting in coarser texture and lower firing temperatures between 1000-1150degC. The nano-scale additives refine the microstructure by filling microscopic voids and enhancing particle bonding, leading to more durable and finely detailed pottery.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Nano-enhanced clay exhibits significantly higher mechanical strength compared to traditional earthenware clay, due to the incorporation of nanoparticles that improve particle bonding and reduce micro-cracks. This enhancement results in greater durability and resistance to wear, making nano-enhanced clay ideal for applications requiring robust structural integrity. Earthenware clay, while more porous and less strong, remains popular for decorative pottery but lacks the mechanical performance offered by nano-infused formulations.
Workability and Handling in Pottery Studios
Nano-enhanced clay offers significantly improved plasticity and smoother consistency compared to traditional earthenware clay, facilitating easier shaping and finer detail work in pottery studios. The incorporation of nanoparticles enhances the clay's cohesion, reducing cracking and enabling greater flexibility during the forming process. Potters benefit from reduced drying time and higher resistance to deformation, translating to more efficient handling and improved overall workability.
Firing Temperatures and Process Variations
Nano-enhanced clay exhibits improved thermal stability and lower firing temperatures, typically ranging between 900degC and 1100degC, compared to traditional earthenware clay which commonly fires between 1050degC and 1150degC. The inclusion of nanoparticles in nano-enhanced clay promotes more uniform sintering and reduces the risk of cracking or warping during the firing process. Variations in processing involve precise control of nanoparticle dispersion and firing schedules to optimize mechanical strength and surface finish in nano-enhanced pottery.
Surface Finish and Aesthetic Qualities
Nano-enhanced clay offers a significantly smoother surface finish compared to traditional earthenware clay, due to the integration of nanoparticles that fill microscopic pores and enhance plasticity. This results in finer detail retention and a more polished, glossy aesthetic ideal for high-end pottery and decorative pieces. Earthenware clay, while prized for its rustic texture and rich, natural color variations, typically exhibits a more porous surface and matte finish, appealing to artisans seeking a traditional, earthy appearance.
Porosity, Absorption, and Water Resistance
Nano-enhanced clay demonstrates significantly lower porosity compared to traditional earthenware clay, resulting in reduced water absorption rates that enhance the durability and water resistance of finished pottery. The incorporation of nanoparticles effectively fills micro-pores within the clay matrix, minimizing water penetration and improving the structural integrity of the ceramics. In contrast, earthenware clay typically exhibits higher porosity and absorption, making it more susceptible to water damage and less ideal for functional pottery requiring water resistance.
Environmental and Health Impacts
Nano-enhanced clay in pottery offers improved durability and reduced material waste, lowering environmental impact compared to traditional earthenware clay, which often requires more frequent replacement and higher energy consumption during firing. The use of nanoparticles raises health concerns due to potential inhalation risks during handling and firing, whereas earthenware clay poses fewer respiratory hazards but may release higher levels of dust and silica particles. Sustainable pottery practices increasingly favor nano-enhanced clay when proper safety measures are implemented to mitigate nanomaterial exposure while benefiting from its eco-friendly properties.
Cost and Accessibility for Potters
Nano-enhanced clay typically presents a higher cost due to advanced manufacturing processes and the inclusion of nano-materials that improve strength and durability, making it less accessible for hobbyist potters or those with limited budgets. Earthenware clay remains a more affordable and widely accessible option, favored for its ease of use and availability in art supply stores and local pottery centers. Cost-efficiency and accessibility make earthenware clay the practical choice for beginner potters and educational settings, while nano-enhanced clay suits professional studios seeking enhanced performance despite the higher investment.
Future Trends in Pottery: Nano-Enhanced vs. Earthenware Clay
Nano-enhanced clay incorporates nanoparticles to improve strength, durability, and thermal resistance compared to traditional earthenware clay, enabling innovative design possibilities in modern pottery. Future trends highlight increased use of nano-enhanced clays for functional ceramics with enhanced performance, including water resistance and lightweight structures, appealing to both artisanal and industrial markets. Earthenware clay remains popular for its natural aesthetic and ease of use but faces limitations in durability and precision that nanotechnology advancements aim to overcome.
Infographic: Nano-enhanced clay vs Earthenware clay for Pottery
 azmater.com
azmater.com