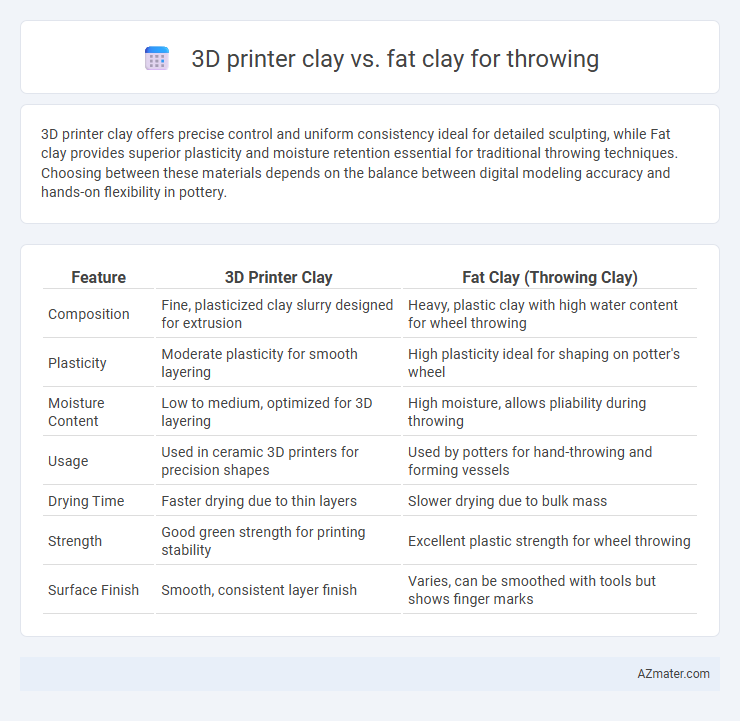
3D printer clay offers precise control and uniform consistency ideal for detailed sculpting, while Fat clay provides superior plasticity and moisture retention essential for traditional throwing techniques. Choosing between these materials depends on the balance between digital modeling accuracy and hands-on flexibility in pottery.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | 3D Printer Clay | Fat Clay (Throwing Clay) |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Fine, plasticized clay slurry designed for extrusion | Heavy, plastic clay with high water content for wheel throwing |
| Plasticity | Moderate plasticity for smooth layering | High plasticity ideal for shaping on potter's wheel |
| Moisture Content | Low to medium, optimized for 3D layering | High moisture, allows pliability during throwing |
| Usage | Used in ceramic 3D printers for precision shapes | Used by potters for hand-throwing and forming vessels |
| Drying Time | Faster drying due to thin layers | Slower drying due to bulk mass |
| Strength | Good green strength for printing stability | Excellent plastic strength for wheel throwing |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, consistent layer finish | Varies, can be smoothed with tools but shows finger marks |
Introduction to 3D Printer Clay and Fat Clay
3D printer clay is a specialized, highly plastic material designed for additive manufacturing processes, enabling intricate and precise ceramic parts through layer-by-layer deposition. Fat clay, known for its high plasticity and moisture content, is traditionally used for hand-throwing techniques on a potter's wheel, providing excellent workability and smooth shaping. While 3D printer clay optimizes digital ceramic fabrication, fat clay remains preferred for tactile, experimental pottery forms in wheel throwing.
Composition Differences: 3D Printer Clay vs Fat Clay
3D printer clay typically consists of fine, homogenous ceramic powders mixed with binders and additives optimized for precise extrusion and layer adhesion in additive manufacturing. Fat clay, commonly used for throwing, features a higher water content and plasticity due to its natural composition of clay minerals, organic matter, and fluxes, enhancing workability on the wheel. The key difference lies in 3D printer clay's engineered consistency for rigidity and printability versus fat clay's natural softness and elasticity suited for hand shaping and throwing.
Workability and Handling: Which Clay Is Easier to Use?
3D printer clay offers consistent texture and moisture content, making it highly manageable for precise shaping and detailed models, while traditional fat clay boasts superior plasticity and elasticity, allowing for smoother throwing and shaping on the wheel. Fat clay's pliability enhances workability by adapting easily to hand pressure, ideal for dynamic forms and quick adjustments, whereas 3D printer clay may be less forgiving due to its firmer consistency tailored for additive manufacturing processes. For potters prioritizing ease of handling and tactile responsiveness, fat clay is generally easier to use, but those requiring uniformity and fine detail might prefer 3D printer clay despite its comparatively rigid nature.
Plasticity and Forming Techniques for Each Clay Type
3D printer clay exhibits lower plasticity compared to fat clay, making it better suited for precise, layered forming techniques rather than traditional handbuilding or throwing on a wheel. Fat clay offers superior plasticity, allowing potters to easily manipulate and shape it through throwing due to its high moisture content and smooth consistency. While 3D printer clay is ideal for digital sculpting and additive manufacturing, fat clay remains the preferred choice for craftspeople focusing on fluid, dynamic forms requiring extensive hand manipulation.
Surface Texture: Smoothness and Finish Comparison
3D printer clay typically offers a uniform surface texture with high smoothness, making it ideal for detailed, precise finishes and modern design applications. Fat clay, known for its higher plasticity and thicker consistency, tends to produce a more textured surface with natural, hand-formed imperfections, enhancing tactile qualities ideal for traditional throwing techniques. The smoothness of 3D printer clay allows for cleaner, sharper edges, while fat clay provides a richer, organic finish favored in artisanal pottery.
Suitability for Throwing vs 3D Printing Applications
3D printer clay, formulated for precision and layering in additive manufacturing, offers fine granularity and consistent moisture content, making it less ideal for traditional throwing on a wheel due to reduced plasticity and flexibility. Fat clay, with higher plasticity and cohesive properties, excels in throwing applications, allowing potters to shape and manipulate the clay easily on a wheel, but it lacks the fine particle size and drying characteristics necessary for detailed 3D printing processes. The suitability hinges on the intended use: fat clay is optimal for wheel throwing due to workability, while 3D printer clay is engineered for intricate, controlled layering in ceramic 3D printing.
Drying and Shrinkage Characteristics
3D printer clay typically exhibits controlled drying rates and minimal shrinkage due to its engineered composition, making it ideal for detailed, dimensionally stable prints. Fat clay, known for its high plasticity and moisture content, dries slower and undergoes more significant shrinkage, which can lead to warping or cracking if not managed carefully during the throwing and drying process. Understanding these differences in drying behavior and shrinkage is critical for potters aiming for precision and durability in their 3D-printed or traditionally thrown ceramic pieces.
Firing Results: Strength and Color Outcomes
3D printer clay typically yields more uniform firing results with consistent strength and color due to its controlled composition, making it ideal for precision work. Fat clay, rich in plasticity and moisture, often produces stronger, more durable pieces after firing but may show varied color outcomes based on firing temperature and atmosphere. Both clays require careful kiln management to optimize firing strength and achieve desired color intensities.
Cost and Availability of 3D Printer Clay vs Fat Clay
3D printer clay generally has a higher cost due to its specialized formulation and limited suppliers compared to fat clay, which is widely available and more affordable for ceramic artists and potters. Fat clay is commonly stocked in art supply stores and pottery studios, making bulk purchases easier and less expensive. The accessibility and pricing of fat clay make it the preferred choice for traditional throwing, whereas 3D printer clay is more niche and costly for similar applications.
Choosing the Right Clay: Recommendations for Artists
3D printer clay offers precise layering and fine details ideal for sculptors focusing on intricate designs, while fat clay boasts excellent plasticity and moisture retention perfect for traditional throwing techniques. Artists should consider the work process and desired texture; 3D printer clay suits experimental and digital fabrication, whereas fat clay supports hands-on wheel throwing with consistent elasticity. Selecting the right clay depends on compatibility with the artist's technique, whether precision modeling or fluid hand-building.
Infographic: 3D printer clay vs Fat clay for Throwing
 azmater.com
azmater.com