Refractory materials offer high heat resistance and durability, ideal for industrial applications, while sanitaryware is specifically designed with ceramic or porcelain for hygiene, ease of cleaning, and aesthetic appeal in toilets. Choosing sanitaryware ensures water resistance and smooth finishes essential for bathroom fixtures, unlike refractory materials which prioritize thermal stability.
Table of Comparison
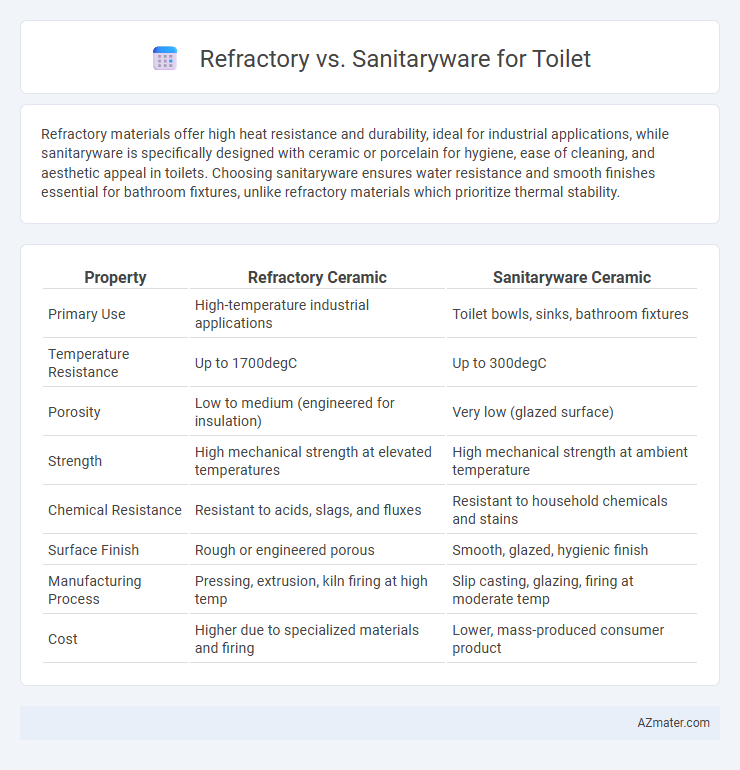
| Property | Refractory Ceramic | Sanitaryware Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | High-temperature industrial applications | Toilet bowls, sinks, bathroom fixtures |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 1700degC | Up to 300degC |
| Porosity | Low to medium (engineered for insulation) | Very low (glazed surface) |
| Strength | High mechanical strength at elevated temperatures | High mechanical strength at ambient temperature |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to acids, slags, and fluxes | Resistant to household chemicals and stains |
| Surface Finish | Rough or engineered porous | Smooth, glazed, hygienic finish |
| Manufacturing Process | Pressing, extrusion, kiln firing at high temp | Slip casting, glazing, firing at moderate temp |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized materials and firing | Lower, mass-produced consumer product |
Introduction to Refractory and Sanitaryware
Refractory materials are designed to withstand high temperatures, providing exceptional heat resistance and durability in industrial applications such as furnace linings and kilns. Sanitaryware includes bathroom fixtures like toilets, sinks, and urinals manufactured primarily from vitreous china or ceramic materials, emphasizing hygiene, smooth surfaces, and water resistance. The fundamental distinction lies in refractory's thermal resistance properties contrasted with sanitaryware's focus on cleanliness and aesthetic appeal in domestic and commercial sanitation environments.
Definition of Refractory Materials
Refractory materials are heat-resistant substances designed to withstand high temperatures without melting or deforming, making them ideal for industrial applications like kilns and furnaces. In toilet manufacturing, refractory materials contribute to the durability and heat resistance of components exposed to extreme conditions during firing processes. Unlike sanitaryware, which primarily focuses on aesthetics and hygiene, refractory materials prioritize thermal stability and structural integrity.
What is Sanitaryware?
Sanitaryware refers to glazed ceramic products designed for bathroom use, including toilets, sinks, and bidets, providing hygiene and aesthetic appeal. Made from materials such as vitreous china and porcelain, sanitaryware offers smooth, non-porous surfaces that resist stains and bacteria, ensuring easy cleaning and durability. Unlike refractory materials, sanitaryware prioritizes comfort, design, and sanitation in residential and commercial restroom environments.
Key Differences Between Refractory and Sanitaryware
Refractory materials are designed to withstand high temperatures and harsh chemical environments, making them essential in industrial applications, whereas sanitaryware is manufactured for bathroom fixtures emphasizing hygiene, aesthetics, and water resistance. The key differences lie in their composition, with refractory materials typically made from fireclay, alumina, and silica, while sanitaryware consists mainly of vitreous china or porcelain. Functionally, refractory products prioritize thermal durability, whereas sanitaryware prioritizes smooth surfaces and water-tightness for sanitary use.
Material Composition: Refractory vs. Sanitaryware
Refractory materials used in toilets primarily consist of alumina, silica, and fireclay, which provide high heat resistance and durability for industrial and high-temperature environments. Sanitaryware is typically composed of vitreous china or ceramic materials like porcelain, incorporating kaolin, quartz, and feldspar to ensure smooth surfaces, water resistance, and easy cleaning. The key difference lies in the thermal and mechanical properties, where refractory materials withstand extreme heat while sanitaryware emphasizes hygiene and aesthetic finish.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
Refractory materials for toilets involve high-temperature kiln firing processes that enhance heat resistance and durability through dense ceramic vitrification. Sanitaryware manufacturing typically includes slip casting, pressing, and glazing steps followed by controlled firing cycles to achieve smooth, waterproof surfaces with aesthetic finishes. The refractory process emphasizes thermal stability and structural integrity, while sanitaryware focuses on surface quality and hygiene standards.
Application of Refractory in Toilets
Refractory materials in toilets are primarily used in high-temperature components such as incinerating toilet combustion chambers due to their heat-resistant properties. These materials withstand extreme thermal stress, ensuring durability and safety in waste treatment processes. Unlike sanitaryware, which is designed for hygiene and aesthetics in standard toilets, refractories provide crucial thermal insulation and structural integrity in specialized toilet systems.
Sanitaryware Usage in Modern Toilets
Sanitaryware in modern toilets includes ceramic items such as bowls, sinks, and urinals designed for hygiene and easy maintenance, offering resistance to stains, odors, and microbial growth. Unlike refractory materials used for high-temperature applications, sanitaryware is optimized for consistent water exposure and everyday use, enhancing user comfort and functionality. The widespread adaptation of advanced glazing techniques further improves durability and cleanliness, making sanitaryware essential in contemporary restroom designs.
Durability and Performance Analysis
Refractory materials used in toilets exhibit superior durability due to their high resistance to heat, chemical corrosion, and mechanical stress, making them ideal for heavy-use or industrial environments. Sanitaryware, typically made from vitreous china or ceramic, offers excellent performance in terms of water efficiency and smooth surface finish but may be more prone to chipping or cracking under impact. Performance analysis reveals refractory toilets sustain prolonged operational integrity under extreme conditions, while sanitaryware remains preferred for residential applications due to aesthetic appeal and cost-effectiveness.
Choosing the Right Material for Toilets
Refractory materials, known for their high heat resistance and durability, are rarely used for toilets due to their rough texture and difficulty in cleaning, making sanitaryware the preferred choice. Sanitaryware, typically made from vitreous china or porcelain, offers smooth surfaces, resistance to stains, and ease of maintenance, ensuring hygiene in bathroom environments. Selecting sanitaryware with high vitrification levels guarantees durability, water resistance, and a polished finish ideal for long-term use.
Infographic: Refractory vs Sanitaryware for Toilet
 azmater.com
azmater.com