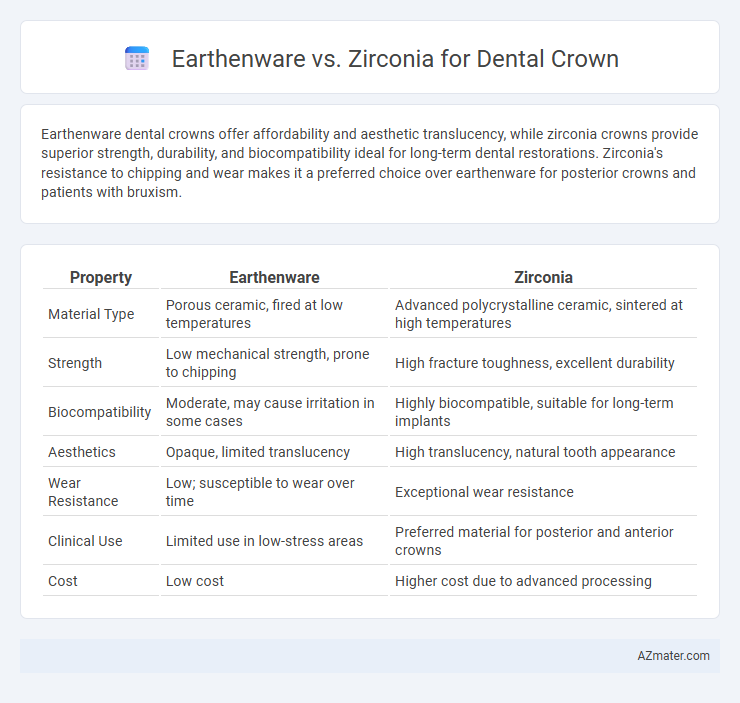
Earthenware dental crowns offer affordability and aesthetic translucency, while zirconia crowns provide superior strength, durability, and biocompatibility ideal for long-term dental restorations. Zirconia's resistance to chipping and wear makes it a preferred choice over earthenware for posterior crowns and patients with bruxism.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Earthenware | Zirconia |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Porous ceramic, fired at low temperatures | Advanced polycrystalline ceramic, sintered at high temperatures |
| Strength | Low mechanical strength, prone to chipping | High fracture toughness, excellent durability |
| Biocompatibility | Moderate, may cause irritation in some cases | Highly biocompatible, suitable for long-term implants |
| Aesthetics | Opaque, limited translucency | High translucency, natural tooth appearance |
| Wear Resistance | Low; susceptible to wear over time | Exceptional wear resistance |
| Clinical Use | Limited use in low-stress areas | Preferred material for posterior and anterior crowns |
| Cost | Low cost | Higher cost due to advanced processing |
Understanding Dental Crowns: Purpose and Material Choices
Dental crowns restore tooth structure and function, offering protection and aesthetic improvement for damaged teeth. Earthenware crowns, typically made from porcelain or ceramics, provide natural appearance but can lack durability compared to zirconia crowns. Zirconia crowns, crafted from zirconium dioxide, offer superior strength, biocompatibility, and long-lasting performance, making them ideal for both anterior and posterior restorations.
What is Earthenware? Properties and Dental Applications
Earthenware is a type of ceramic material made from natural clay that is fired at lower temperatures, resulting in a porous and less dense structure compared to zirconia. Its key properties include good aesthetic qualities with a warm, opaque appearance and ease of shaping, making it suitable for custom dental crowns and veneers where natural tooth color replication is important. In dental applications, earthenware crowns are preferred for their affordability and aesthetic appeal but lack the high strength and durability of zirconia, limiting their use in high-stress areas like molars.
Introduction to Zirconia Crowns: Strength and Aesthetics
Zirconia crowns offer exceptional strength and durability, making them ideal for withstanding the high biting forces in molars. Their biocompatibility and resistance to chipping surpass traditional earthenware crowns, ensuring longevity in dental restorations. Advanced manufacturing techniques allow zirconia crowns to mimic natural tooth translucency, providing superior aesthetics compared to conventional earthenware options.
Durability Comparison: Earthenware vs Zirconia
Zirconia crowns exhibit significantly higher durability compared to earthenware crowns, with superior resistance to fractures and wear due to their dense, crystalline structure. Earthenware crowns, often more brittle and prone to chipping, lack the mechanical strength necessary to withstand high occlusal forces over time. Clinical studies demonstrate zirconia's longevity, making it a preferred choice for patients requiring long-lasting dental restorations.
Aesthetic Considerations: Color, Translucency, and Fit
Earthenware dental crowns offer excellent color matching and translucency, closely mimicking natural teeth but may lack the precision fit compared to zirconia. Zirconia crowns provide superior strength and an exceptionally accurate fit due to advanced CAD/CAM manufacturing, though their translucency and color gradation can be less natural without specialized layering techniques. For optimal aesthetics, earthenware excels in lifelike appearance, while zirconia balances durability with acceptable esthetics when enhanced by layered ceramics.
Biocompatibility and Patient Safety: Material Reactions
Earthenware dental crowns, primarily made from feldspathic porcelain, are prone to microcracks and may cause minor allergic reactions due to their composition, impacting biocompatibility and patient safety. Zirconia crowns exhibit superior biocompatibility with minimal inflammatory response, resisting bacterial adhesion and demonstrating high strength, making them safer for long-term oral health. Clinical studies highlight zirconia's lower risk of adverse tissue reactions and higher patient acceptance compared to earthenware materials.
Cost Analysis: Budgeting for Earthenware vs Zirconia Crowns
Earthenware dental crowns typically cost between $300 and $700 per tooth, making them a more budget-friendly option compared to zirconia crowns, which range from $800 to $2,500 per tooth due to their superior durability and aesthetics. Insurance plans often cover a larger portion of earthenware crown expenses, reducing out-of-pocket costs for patients prioritizing affordability. When budgeting for dental crowns, it's essential to consider the long-term value of zirconia crowns, which may require fewer replacements, potentially offsetting the higher upfront investment.
Procedure Differences: Preparation and Placement
Earthenware dental crowns require more extensive tooth reduction to accommodate their thicker structure, whereas zirconia crowns demand minimal tooth preparation due to their strength and thinner profile. Placement of earthenware crowns often involves a multi-step cementation process to ensure a secure fit, while zirconia crowns can be placed using resin cements that offer superior bonding and durability. The precision in zirconia crown placement benefits from CAD/CAM technology, enabling a more accurate fit compared to the traditional manual techniques used for earthenware crowns.
Longevity and Maintenance: What to Expect
Earthenware dental crowns, while aesthetically pleasing, typically have a shorter lifespan of around 5-7 years due to their brittleness and higher susceptibility to chipping and wear. Zirconia crowns offer superior longevity, often lasting 10-15 years or more, owing to their exceptional strength, durability, and resistance to fractures. Maintenance for earthenware crowns involves careful avoidance of hard foods and regular dental check-ups, whereas zirconia crowns require less intensive upkeep, making them a more practical choice for long-term dental restoration.
Choosing the Right Material: Dentists’ Recommendations
Dentists recommend zirconia crowns for their superior strength, durability, and biocompatibility, making them ideal for molars and patients with bruxism. Earthenware crowns, while aesthetically pleasing with natural translucency, are best suited for front teeth due to their lower fracture resistance. Selecting the right material involves balancing durability requirements with aesthetic goals, considering patient-specific factors like bite force and gum sensitivity.
Infographic: Earthenware vs Zirconia for Dental Crown
 azmater.com
azmater.com