Lustreware offers superior thermal shock resistance and aesthetic appeal, making it ideal for decorative furnace linings, while Refractory materials provide exceptional heat insulation and structural durability essential for high-temperature industrial furnace linings. Choosing between Lustreware and Refractory depends on the balance between thermal performance and design requirements in furnace applications.
Table of Comparison
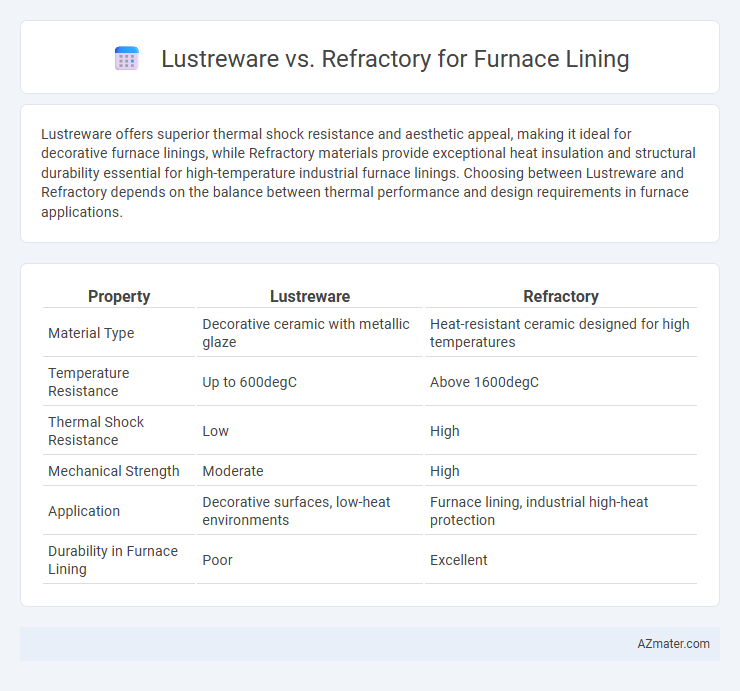
| Property | Lustreware | Refractory |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Decorative ceramic with metallic glaze | Heat-resistant ceramic designed for high temperatures |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 600degC | Above 1600degC |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Low | High |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate | High |
| Application | Decorative surfaces, low-heat environments | Furnace lining, industrial high-heat protection |
| Durability in Furnace Lining | Poor | Excellent |
Introduction to Furnace Lining Materials
Furnace lining materials like lustreware and refractory serve critical roles in heat containment and thermal insulation within high-temperature furnaces. Lustreware, often characterized by its decorative and reflective ceramic coating, offers moderate thermal resistance but is less durable under extreme heat compared to refractory materials engineered from alumina, silica, or fireclay compounds. Refractory linings are specifically formulated to withstand high thermal stresses, chemical corrosion, and mechanical wear, making them the preferred choice for industrial furnace applications demanding prolonged exposure to intense heat.
What is Lustreware?
Lustreware is a ceramic material known for its iridescent, metallic glaze achieved through applying metal oxides and firing them at low temperatures, enhancing both aesthetic appeal and surface durability. In furnace lining, lustreware offers moderate heat resistance but is primarily valued for decorative purposes rather than high thermal performance. Compared to refractory materials, which are engineered to withstand extreme temperatures and thermal stress, lustreware is less durable and not suitable for intense furnace environments.
What are Refractory Materials?
Refractory materials are heat-resistant substances specifically engineered to withstand extremely high temperatures in industrial furnaces, kilns, and reactors. These materials, including fireclay, silica, alumina, and magnesite, provide essential thermal insulation, chemical inertness, and mechanical strength to protect furnace linings from thermal shock and corrosion. Their ability to maintain structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 1700degC makes them critical for efficient and safe furnace operation compared to lustreware, which is primarily decorative and not designed for such thermal performance.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Lustreware furnace linings consist primarily of ceramic materials enriched with metallic oxides that enhance thermal radiation properties, while refractory linings are typically composed of alumina, silica, and magnesia, designed to withstand higher temperatures and corrosive environments. Lustreware production involves glazing and firing techniques that create a reflective surface, optimizing heat retention, whereas refractory manufacturing employs sintering and casting processes to achieve dense, durable structures capable of enduring thermal shock. The compositional focus on lustrous oxides versus the robust mineral matrix in refractories dictates their specific performance characteristics in industrial furnace applications.
Thermal Resistance: Lustreware vs Refractory
Lustreware offers moderate thermal resistance suitable for decorative furnace liners but lacks the high-temperature tolerance required for industrial furnace linings. Refractory materials, composed of ceramics and specialized clays, provide superior thermal resistance, enduring temperatures above 1600degC without structural degradation. This makes refractory a preferred choice for furnace linings demanding robust heat insulation and prolonged operational durability.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Lustreware furnace lining exhibits moderate mechanical strength suitable for low to medium temperature applications, while refractory linings provide superior mechanical durability under extreme thermal stress. Refractory materials like alumina and silica-based bricks resist deformation, spalling, and abrasion, ensuring longevity in high-temperature furnaces above 1500degC. Lustreware's ceramic composition offers aesthetic appeal but falls short in mechanical resilience compared to dense, engineered refractory linings optimized for industrial furnace durability.
Chemical Stability and Corrosion Resistance
Lustreware furnace linings exhibit superior chemical stability, maintaining structural integrity in highly alkaline and acidic environments due to their specialized glaze composition. Refractory linings offer excellent corrosion resistance against molten slags and metal slags, attributed to their dense microstructure and mineral composition such as alumina and silica. For high-temperature furnace applications, choosing Lustreware improves chemical resistance while refractory materials ensure enhanced durability against mechanical and chemical wear.
Cost-Effectiveness and Lifecycle
Lustreware furnace linings offer moderate initial costs but generally require more frequent maintenance and replacement due to lower wear resistance compared to refractory materials. Refractory linings, though initially more expensive, provide superior durability and thermal stability, resulting in longer lifecycle performance and reduced downtime. Evaluating total cost of ownership, refractory linings tend to deliver better cost-effectiveness through enhanced longevity and lower operational disruptions.
Applications in Modern Furnaces
Lustreware coatings provide enhanced thermal shock resistance and aesthetic appeal in modern furnace linings, making them ideal for decorative or specialty glass furnaces. Refractory materials, composed of high-alumina or silica-based compounds, offer superior durability and chemical stability, essential for industrial furnaces operating at extreme temperatures and aggressive environments. Applications in steelmaking, petrochemical processing, and high-temperature ceramics manufacturing predominantly utilize refractory linings due to their structural integrity and longevity.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Furnace
Choosing the right material for your furnace lining is crucial for optimal performance and durability. Lustreware offers excellent thermal shock resistance and aesthetic appeal, making it ideal for furnaces that require frequent temperature cycling and decorative finishes. Refractory materials provide superior heat resistance and structural integrity at extremely high temperatures, ensuring long-term protection and stability in industrial furnace applications.
Infographic: Lustreware vs Refractory for Furnace lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com