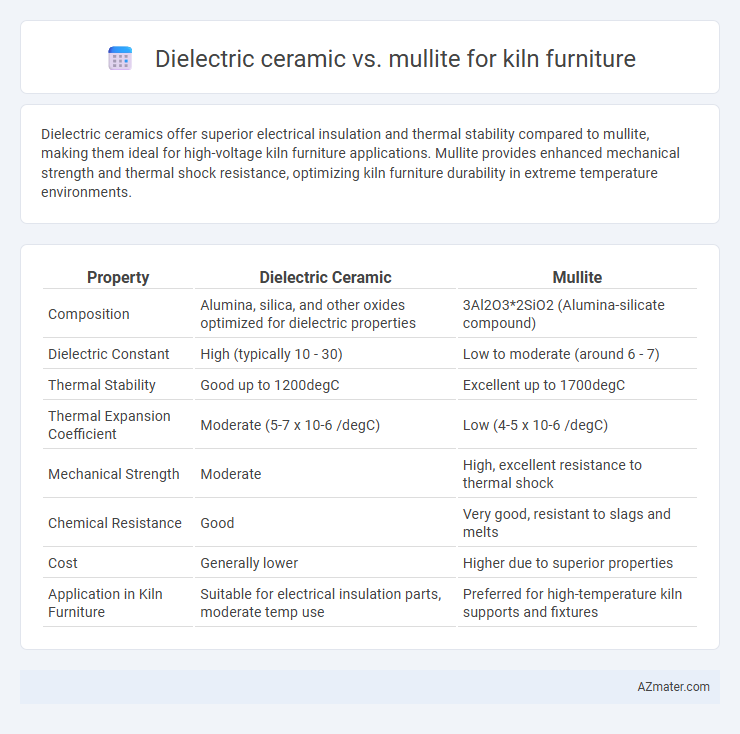
Dielectric ceramics offer superior electrical insulation and thermal stability compared to mullite, making them ideal for high-voltage kiln furniture applications. Mullite provides enhanced mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance, optimizing kiln furniture durability in extreme temperature environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Dielectric Ceramic | Mullite |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Alumina, silica, and other oxides optimized for dielectric properties | 3Al2O3*2SiO2 (Alumina-silicate compound) |
| Dielectric Constant | High (typically 10 - 30) | Low to moderate (around 6 - 7) |
| Thermal Stability | Good up to 1200degC | Excellent up to 1700degC |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | Moderate (5-7 x 10-6 /degC) | Low (4-5 x 10-6 /degC) |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate | High, excellent resistance to thermal shock |
| Chemical Resistance | Good | Very good, resistant to slags and melts |
| Cost | Generally lower | Higher due to superior properties |
| Application in Kiln Furniture | Suitable for electrical insulation parts, moderate temp use | Preferred for high-temperature kiln supports and fixtures |
Introduction: Understanding Kiln Furniture Materials
Dielectric ceramic and mullite are essential materials for kiln furniture, selected for their high thermal stability and resistance to thermal shock. Dielectric ceramics offer excellent electrical insulation and maintain structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 1400degC, making them ideal for specialty applications requiring minimal electrical conductivity. Mullite, with a melting point above 1840degC and superior creep resistance, provides robustness and longevity in high-temperature kiln environments commonly used in ceramics and metallurgy industries.
Overview of Dielectric Ceramic
Dielectric ceramics used in kiln furniture exhibit exceptional electrical insulation properties, high thermal stability, and resistance to thermal shock, making them ideal for high-temperature applications. These ceramics typically consist of alumina or zirconia-based materials that maintain structural integrity while minimizing heat conduction, optimizing energy efficiency in kilns. Compared to mullite, dielectric ceramics offer superior dielectric strength and tailored electrical characteristics for advanced kiln processes.
Overview of Mullite
Mullite, a robust ceramic material composed primarily of 3Al2O3*2SiO2, offers excellent thermal stability and low thermal expansion, making it ideal for kiln furniture applications exposed to extreme temperatures. Its high refractoriness and resistance to thermal shock outperform many dielectric ceramics, ensuring longevity and structural integrity during prolonged firing cycles. Mullite's mechanical strength and chemical inertness are critical for supporting heavy loads without deformation, enhancing kiln efficiency and lifespan.
Key Material Properties: Dielectric Ceramic vs Mullite
Dielectric ceramics exhibit high dielectric strength, excellent thermal shock resistance, and low dielectric loss, making them ideal for insulating and supporting components in high-frequency kiln applications. Mullite offers superior refractoriness with a melting point above 1840degC, low thermal expansion, and good mechanical strength, ensuring durability under extreme kiln temperatures and reducing deformation risks. The choice between dielectric ceramics and mullite hinges on specific kiln conditions, with dielectric ceramics favored for electrical insulation and mullite preferred for structural stability in high-temperature environments.
Thermal Resistance and Stability Comparison
Dielectric ceramic exhibits superior thermal resistance withstanding temperatures up to 1600degC, making it highly suitable for high-temperature kiln furniture applications. Mullite offers excellent thermal stability, maintaining structural integrity under prolonged exposure to temperatures around 1400degC while resisting thermal shock and chemical corrosion. Comparing the two, dielectric ceramic provides higher maximum temperature tolerance, whereas mullite excels in durability and stability during cyclic heating processes.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Dielectric ceramic exhibits superior mechanical strength with high resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for kiln furniture exposed to rapid temperature changes. Mullite offers excellent thermal stability and durability due to its low thermal expansion and high refractoriness, which enhances long-term structural integrity in high-temperature kiln environments. The choice between dielectric ceramic and mullite depends on specific kiln operating conditions, where mechanical robustness and lifespan requirements are critical factors.
Weight and Design Flexibility
Dielectric ceramic kiln furniture is significantly lighter than mullite, enabling easier handling and reduced load on kiln structures. Its high design flexibility allows for complex shapes and precise customizations, optimizing the support and thermal insulation in kilns. Mullite, while robust and thermally stable, is heavier and less adaptable to intricate designs, limiting its use where lightweight and tailored shapes are critical.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Dielectric ceramics generally exhibit higher raw material and manufacturing costs compared to mullite, which is more economically produced due to its abundant availability and simpler processing. Mullite kiln furniture offers excellent thermal stability and mechanical strength at a lower price point, making it a cost-effective choice for high-temperature applications. When optimizing for long-term operational expenses, mullite's durability and lower initial investment contribute to improved overall economic efficiency.
Application Suitability in Kiln Operations
Dielectric ceramic offers superior electrical insulation and thermal stability, making it ideal for applications requiring resistance to high-voltage electrical currents and rapid temperature changes in kiln operations. Mullite provides excellent thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength, supporting heavy loads and prolonged exposure to high temperatures without deformation. While dielectric ceramics excel in insulating heating elements, mullite is more suitable for structural kiln furniture components subject to mechanical stress and extreme thermal cycling.
Conclusion: Selecting the Optimal Kiln Furniture Material
Dielectric ceramics offer superior electrical insulation and thermal shock resistance, making them ideal for advanced kiln applications requiring precise temperature control. Mullite provides excellent mechanical strength and thermal stability at high temperatures, preferred for heavy-duty kiln furniture exposed to prolonged thermal cycles. Selecting the optimal kiln furniture material depends on balancing the specific operational requirements, where dielectric ceramics excel in electrical insulation and Mullite stands out in mechanical durability.
Infographic: Dielectric ceramic vs Mullite for Kiln furniture
 azmater.com
azmater.com