Nano-ceramic dinnerware offers enhanced durability and resistance to scratches and heat due to its advanced nanotechnology-infused composition. Bone china dinnerware is known for its lightweight, translucency, and elegant appearance, made from a blend of bone ash, feldspathic material, and kaolin, providing superior strength compared to traditional ceramics.
Table of Comparison
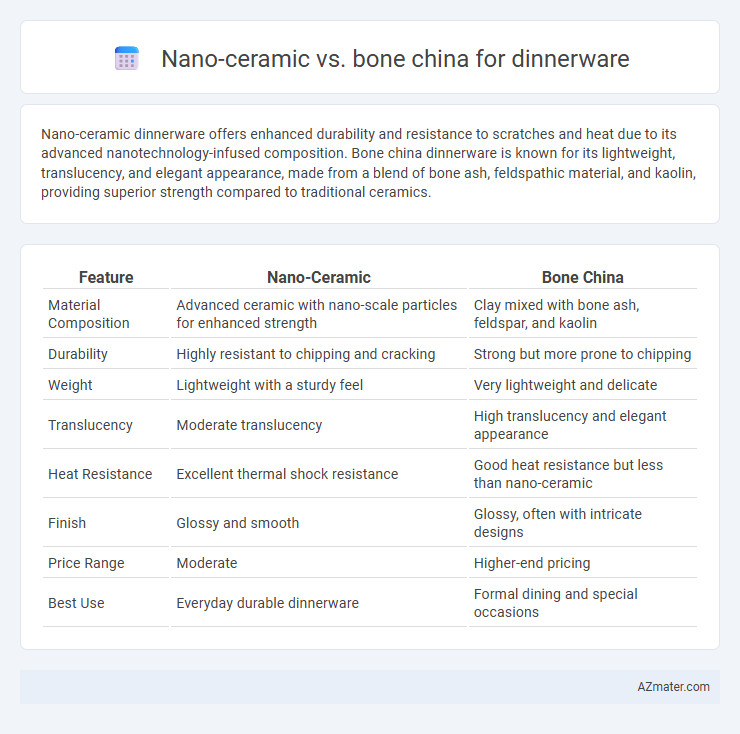
| Feature | Nano-Ceramic | Bone China |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Advanced ceramic with nano-scale particles for enhanced strength | Clay mixed with bone ash, feldspar, and kaolin |
| Durability | Highly resistant to chipping and cracking | Strong but more prone to chipping |
| Weight | Lightweight with a sturdy feel | Very lightweight and delicate |
| Translucency | Moderate translucency | High translucency and elegant appearance |
| Heat Resistance | Excellent thermal shock resistance | Good heat resistance but less than nano-ceramic |
| Finish | Glossy and smooth | Glossy, often with intricate designs |
| Price Range | Moderate | Higher-end pricing |
| Best Use | Everyday durable dinnerware | Formal dining and special occasions |
Introduction to Nano-Ceramic and Bone China Dinnerware
Nano-ceramic dinnerware incorporates advanced nanotechnology to enhance durability, scratch resistance, and heat retention, making it ideal for daily use. Bone china, composed of bone ash, feldspathic material, and kaolin, is renowned for its translucency, lightweight structure, and elegant appearance favored in formal dining. Comparing material composition and performance highlights nano-ceramic's strength and practicality against bone china's refined aesthetics and delicate craftsmanship.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Nano-ceramic dinnerware incorporates ultra-fine ceramic particles fused at low temperatures using advanced nanotechnology, resulting in enhanced strength, scratch resistance, and a smooth, non-porous surface. Bone china is produced by combining bone ash, kaolin, and feldspar, then firing at high temperatures, which embeds calcium phosphate from the bone ash to create a lightweight yet durable and translucent material. The key difference lies in nano-ceramic's modern particle engineering for durability and bone china's traditional mineral and bone ash composition for elegance and resilience.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Nano-ceramic dinnerware offers exceptional durability due to its advanced nanotechnology composition, making it highly resistant to chipping and cracking under daily use. Bone china, known for its high strength-to-weight ratio, combines bone ash with porcelain to create a delicate yet remarkably strong material that withstands thermal shock better than traditional ceramics. While bone china exhibits superior translucency and elegance, nano-ceramic dinnerware generally surpasses it in overall toughness and resistance to wear over time.
Weight and Handling Experience
Nano-ceramic dinnerware is significantly lighter than bone china, offering enhanced ease of handling and reduced strain during use, making it ideal for everyday meals and frequent handling. Bone china, while heavier, provides a sturdy and balanced feel that many users associate with premium dining experiences and greater durability despite the added weight. The weight difference directly influences comfort and usability; nano-ceramics excel in lightweight practicality, whereas bone china imparts a classic, substantial presence on the table.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Versatility
Nano-ceramic dinnerware showcases a sleek, modern aesthetic with a smooth, durable surface that enhances vibrant glazes and intricate patterns, offering high resistance to scratches and chipping. Bone china, known for its translucent quality and delicate, refined texture, provides an elegant and classic appeal ideal for formal settings and intricate hand-painted designs. Both materials exhibit exceptional design versatility, but nano-ceramic allows for bolder, contemporary styles while bone china excels in timeless, sophisticated motifs.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Performance
Nano-ceramic dinnerware offers superior heat resistance, withstanding temperatures up to 1,200degC, making it ideal for both high-heat cooking and serving applications. Bone china typically has a lower heat tolerance, around 1,000degC, and may experience thermal shock if exposed to sudden temperature changes. The enhanced thermal performance of nano-ceramics ensures better durability and retention of heat without cracking, outperforming bone china in intense thermal environments.
Stain, Chip, and Scratch Resistance
Nano-ceramic dinnerware offers superior stain resistance due to its non-porous surface, preventing discoloration from food and beverages, while bone china is more prone to staining over time. In terms of chip resistance, nano-ceramic is highly durable and resistant to impact, whereas bone china, although elegant, is more delicate and susceptible to chipping. Nano-ceramic materials also excel in scratch resistance, maintaining a smooth, unmarred finish after prolonged use, contrasting with bone china which can develop fine scratches more easily.
Safety and Food Compatibility
Nano-ceramic dinnerware features a non-porous surface resistant to bacteria and stains, ensuring high safety levels for food contact. Bone china contains natural bone ash, providing durability and a non-toxic, lead-free composition suitable for everyday use. Both materials offer excellent food compatibility, but nano-ceramic's enhanced resistance to scratches and chemical absorption improves long-term hygiene.
Cost and Long-Term Value
Nano-ceramic dinnerware generally offers a lower upfront cost compared to bone china, making it a budget-friendly option for everyday use. While bone china is more expensive initially, its superior durability, chip resistance, and timeless elegance provide enhanced long-term value and a better investment for formal dining occasions. Consideration of usage frequency and aesthetic preferences is crucial when balancing cost and lasting value between these two materials.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Nano-ceramic dinnerware features high durability and stain resistance with lower firing temperatures, reducing energy consumption and carbon emissions during production. Bone china, traditionally made from bone ash, offers biodegradability but relies on finite animal resources and higher energy use in kiln firing, increasing its environmental footprint. Choosing nano-ceramic can lead to less waste and improved recyclability, supporting sustainability goals in modern tableware manufacturing.
Infographic: Nano-ceramic vs Bone china for Dinnerware
 azmater.com
azmater.com