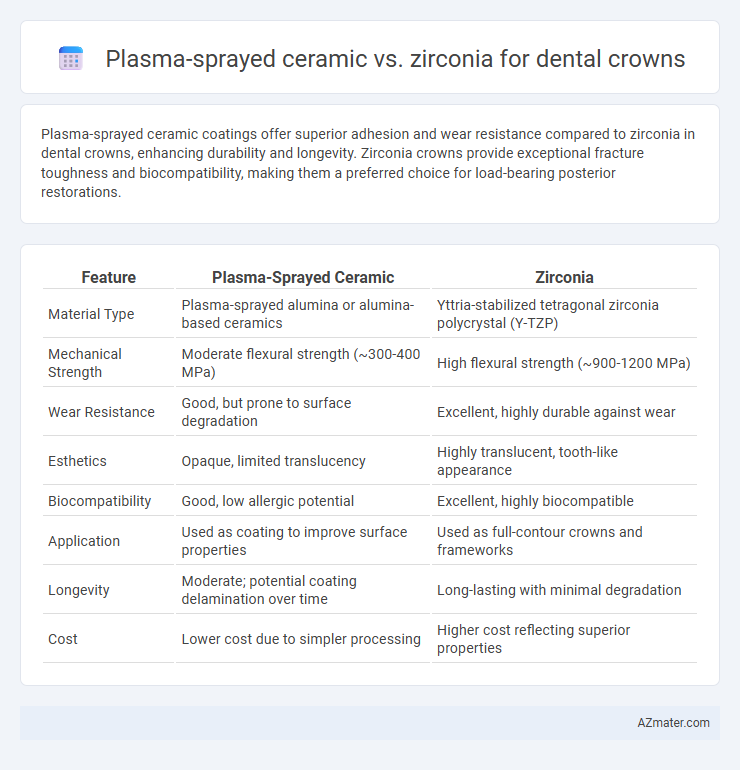
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings offer superior adhesion and wear resistance compared to zirconia in dental crowns, enhancing durability and longevity. Zirconia crowns provide exceptional fracture toughness and biocompatibility, making them a preferred choice for load-bearing posterior restorations.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Plasma-Sprayed Ceramic | Zirconia |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Plasma-sprayed alumina or alumina-based ceramics | Yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal (Y-TZP) |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate flexural strength (~300-400 MPa) | High flexural strength (~900-1200 MPa) |
| Wear Resistance | Good, but prone to surface degradation | Excellent, highly durable against wear |
| Esthetics | Opaque, limited translucency | Highly translucent, tooth-like appearance |
| Biocompatibility | Good, low allergic potential | Excellent, highly biocompatible |
| Application | Used as coating to improve surface properties | Used as full-contour crowns and frameworks |
| Longevity | Moderate; potential coating delamination over time | Long-lasting with minimal degradation |
| Cost | Lower cost due to simpler processing | Higher cost reflecting superior properties |
Introduction to Dental Crown Materials
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings offer enhanced surface durability and improved bonding strength compared to traditional zirconia used in dental crowns. Zirconia is renowned for its high fracture toughness and biocompatibility, making it a popular choice in restorative dentistry. Advances in plasma spray technology enable the customization of ceramic surfaces, optimizing wear resistance and aesthetics for long-lasting dental restorations.
Overview of Plasma-Sprayed Ceramic Crowns
Plasma-sprayed ceramic crowns utilize a high-velocity thermal spray process to deposit finely melted ceramic particles onto the crown substrate, creating a dense, strong, and wear-resistant surface. This technique enhances the adhesion and durability of the ceramic layer compared to traditional methods, making plasma-sprayed crowns highly resistant to chipping and fracture. Plasma-sprayed ceramics exhibit superior mechanical properties and esthetics, positioning them as a competitive alternative to zirconia crowns in restorative dentistry.
Understanding Zirconia Dental Crowns
Zirconia dental crowns offer exceptional strength and biocompatibility, making them highly suitable for long-lasting dental restorations. Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings on crowns can improve surface hardness and wear resistance, but Zirconia's inherent properties provide superior fracture toughness and resistance to chipping. Understanding Zirconia crowns involves recognizing their ability to withstand high bite forces and their aesthetic versatility, which closely mimics natural tooth enamel.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Plasma-sprayed ceramic dental crowns exhibit enhanced surface hardness and adhesion due to the rapid solidification process, contributing to improved wear resistance compared to traditional zirconia crowns. Zirconia crowns, known for their high flexural strength (typically 900-1200 MPa), offer superior fracture toughness and long-term durability under occlusal forces. While plasma-sprayed ceramics can provide tailored surface properties, zirconia remains the gold standard in dental restorations for optimal strength and longevity.
Esthetics and Color Matching
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings on dental crowns provide a smooth, highly durable surface with excellent color stability, enhancing long-term esthetics. Zirconia crowns offer superior translucency and lifelike color gradients, closely mimicking natural teeth, which allows for precise color matching in diverse dental restorations. While plasma-sprayed ceramics excel in maintaining brightness and gloss, zirconia's intrinsic optical properties contribute to more natural appearance and seamless integration with adjacent teeth.
Biocompatibility and Patient Safety
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings exhibit excellent biocompatibility with minimal cytotoxicity, promoting healthy gingival response and reducing inflammation risks in dental crowns. Zirconia, known for its superior biocompatibility, offers high fracture toughness and low plaque accumulation, enhancing patient safety by minimizing allergic reactions and providing long-term stability. Both materials ensure optimal integration with oral tissues, though zirconia's established clinical track record often makes it the preferred choice for patients requiring durable and safe dental restorations.
Wear Resistance and Longevity
Plasma-sprayed ceramic dental crowns exhibit enhanced wear resistance due to their dense microstructure and strong adhesion to the substrate, resulting in prolonged durability under occlusal forces. Zirconia crowns demonstrate superior longevity attributed to their high fracture toughness and resistance to low-temperature degradation, maintaining structural integrity over extended periods. Comparative studies indicate zirconia's better performance in preventing wear and chipping, making it preferable for long-lasting dental restorations.
Clinical Performance and Case Studies
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings on dental crowns demonstrate enhanced wear resistance and improved adhesion compared to traditional zirconia, contributing to prolonged clinical performance in high-stress occlusal environments. Clinical case studies reveal plasma-sprayed ceramics maintain superior marginal integrity and reduced chipping rates over a 5-year period, especially in posterior restorations. Zirconia crowns, while widely used for their strength and biocompatibility, may exhibit higher fracture incidence under cyclic loading, highlighting plasma-sprayed ceramics as a promising alternative for durable dental restorations.
Cost Considerations and Accessibility
Plasma-sprayed ceramic dental crowns offer a cost-effective alternative to zirconia crowns, primarily due to lower production expenses and simplified manufacturing processes. Zirconia crowns, while more expensive upfront, provide superior durability and aesthetic qualities, often justifying the higher investment for long-term use. Accessibility to plasma-sprayed ceramic crowns tends to be higher in regions with limited dental technology infrastructure, making them a practical choice for budget-conscious patients and clinics.
Choosing the Right Material: Factors for Dentists and Patients
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings offer enhanced adhesion and wear resistance for dental crowns, while zirconia provides superior strength and biocompatibility, making it a preferred choice for load-bearing restorations. Dentists should consider factors such as fracture toughness, esthetic requirements, and patient-specific oral conditions when selecting between plasma-sprayed ceramics and zirconia crowns. Patients benefit from zirconia's natural translucency and durability, but plasma-sprayed ceramics may be advantageous in cases requiring customized surface properties or improved bonding to the tooth structure.
Infographic: Plasma-sprayed ceramic vs Zirconia for Dental crown
 azmater.com
azmater.com