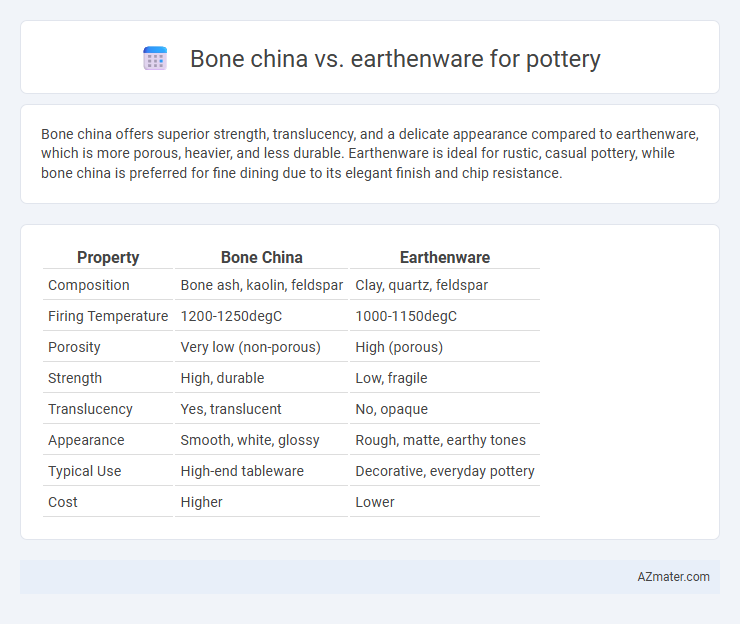
Bone china offers superior strength, translucency, and a delicate appearance compared to earthenware, which is more porous, heavier, and less durable. Earthenware is ideal for rustic, casual pottery, while bone china is preferred for fine dining due to its elegant finish and chip resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bone China | Earthenware |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Bone ash, kaolin, feldspar | Clay, quartz, feldspar |
| Firing Temperature | 1200-1250degC | 1000-1150degC |
| Porosity | Very low (non-porous) | High (porous) |
| Strength | High, durable | Low, fragile |
| Translucency | Yes, translucent | No, opaque |
| Appearance | Smooth, white, glossy | Rough, matte, earthy tones |
| Typical Use | High-end tableware | Decorative, everyday pottery |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Bone China and Earthenware
Bone china is a type of porcelain known for its high level of whiteness, translucency, and strength, made from a mixture of bone ash, feldspar, and kaolin. Earthenware is a porous ceramic fired at lower temperatures, characterized by its higher absorbency and typically opaque finish, often glazed to enhance durability. Both materials serve distinct purposes in pottery, with bone china favored for fine tableware and earthenware common in rustic or decorative pieces.
Historical Origins and Development
Bone china originated in 18th-century England, developed by Josiah Spode who incorporated bone ash to create a strong, translucent porcelain prized for its durability and refined appearance. Earthenware dates back to ancient civilizations such as Mesopotamia and Egypt, characterized by its porous nature, fired at lower temperatures, and often used for everyday pottery and decorative items. The development of bone china represented a technological advancement in pottery, combining strength and elegance, while earthenware maintained its role as an accessible, functional ceramic throughout history.
Composition and Raw Materials
Bone china is composed primarily of bone ash, feldspathic material, and kaolin, giving it a translucent and lightweight quality with high strength. Earthenware is made from natural clay mixed with quartz and feldspar, resulting in a porous and less durable ceramic fired at lower temperatures. The high bone ash content in bone china distinguishes it from the more porous and coarser earthenware in terms of raw materials and final composition.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Bone china is crafted using a refined mixture of bone ash, feldspar, and kaolin fired at high temperatures around 1,200degC to 1,300degC, resulting in a translucent, durable, and lightweight ceramic. Earthenware is made from porous clay fired at lower temperatures between 1,000degC and 1,150degC, which produces a denser, more porous material requiring glazing to hold liquids. The key manufacturing difference lies in firing temperature and raw material composition, influencing the strength, translucency, and water resistance of the final pottery product.
Physical Properties: Strength and Durability
Bone china exhibits superior strength and durability due to its high calcium phosphate content derived from bone ash, resulting in a translucent yet resilient ceramic. Earthenware, composed of clay fired at lower temperatures, tends to be more porous and less durable, making it prone to chipping and cracking under stress. The vitrification process in bone china enhances its mechanical strength, whereas earthenware's porous nature limits its overall durability in everyday use.
Aesthetic Qualities: Color and Finish
Bone china exhibits a translucent, smooth finish with a bright white color that enhances intricate designs and fine details, making it highly prized for elegant and delicate pottery. Earthenware features a more rustic, porous surface with earthy tones ranging from tan to reddish-brown, often showcasing a matte or slightly textured finish that emphasizes handcrafted, traditional aesthetics. The color and finish differences between bone china and earthenware significantly influence their visual appeal and suitability for different artistic and functional pottery uses.
Weight and Thinness Differences
Bone china is renowned for its lightweight and thin structure, often measuring around 0.4 to 0.6 mm in thickness, providing a delicate yet durable quality. In contrast, earthenware is generally thicker and heavier, ranging from 2 to 5 mm, which contributes to its sturdier but less refined feel. This weight and thinness difference significantly influences the tactile experience and visual elegance between the two pottery types.
Common Uses and Applications
Bone china is prized for its strength, translucency, and delicate appearance, making it ideal for fine dinnerware, tea sets, and decorative pieces used in formal dining settings. Earthenware, characterized by its porous nature and heavier weight, is commonly employed for everyday pottery such as plates, bowls, and garden pots due to its durability and affordability. While bone china excels in elegance and sophistication, earthenware offers practicality and versatility for casual, rustic, and functional applications.
Pros and Cons of Bone China vs Earthenware
Bone china offers superior durability, translucency, and a refined, smooth finish, making it ideal for elegant tableware and fine dining. In contrast, earthenware is more porous, less durable, and often heavier but provides a rustic charm and affordability suited for casual use and decorative pottery. Bone china's higher firing temperature and bone ash composition contribute to its strength and whiteness, whereas earthenware's lower firing temperature results in a more absorbent and fragile product that requires glazing.
Choosing the Right Pottery for Your Needs
Bone china offers superior strength, translucency, and elegance, making it ideal for formal dining and decorative purposes, while earthenware is more porous, heavier, and less durable, suitable for casual use and rustic aesthetics. Consider factors such as durability, appearance, and intended use when choosing; bone china resists chipping and stains better, whereas earthenware requires careful handling and is prone to absorbing moisture. Selecting the right pottery depends on balancing functional needs with style preferences, where bone china suits refined settings and earthenware fits everyday practicality.
Infographic: Bone china vs Earthenware for Pottery
 azmater.com
azmater.com