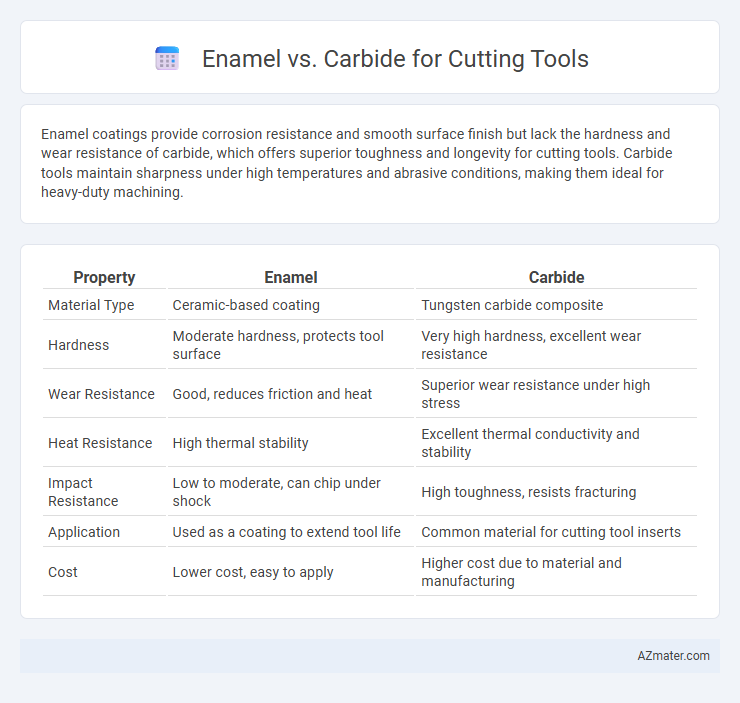
Enamel coatings provide corrosion resistance and smooth surface finish but lack the hardness and wear resistance of carbide, which offers superior toughness and longevity for cutting tools. Carbide tools maintain sharpness under high temperatures and abrasive conditions, making them ideal for heavy-duty machining.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Enamel | Carbide |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Ceramic-based coating | Tungsten carbide composite |
| Hardness | Moderate hardness, protects tool surface | Very high hardness, excellent wear resistance |
| Wear Resistance | Good, reduces friction and heat | Superior wear resistance under high stress |
| Heat Resistance | High thermal stability | Excellent thermal conductivity and stability |
| Impact Resistance | Low to moderate, can chip under shock | High toughness, resists fracturing |
| Application | Used as a coating to extend tool life | Common material for cutting tool inserts |
| Cost | Lower cost, easy to apply | Higher cost due to material and manufacturing |
Introduction to Cutting Tool Materials
Cutting tool materials such as enamel and carbide are critical in determining machining performance and tool longevity. Carbide, composed of tungsten carbide particles bonded with cobalt, offers superior hardness and wear resistance, making it ideal for high-speed cutting and abrasive materials. Enamel coatings, while enhancing corrosion resistance and reducing friction, are less durable under high-temperature and heavy-load conditions compared to carbide, influencing their application in specific cutting environments.
What is Enamel in Cutting Tools?
Enamel in cutting tools refers to a protective coating made from fused glass or ceramic materials applied to enhance tool durability and resistance to corrosion and wear. This coating provides a smooth, hard surface that reduces friction during cutting operations, leading to improved tool life and cutting performance. Enamel coatings are particularly effective in environments requiring high precision and surface finish quality.
What is Carbide in Cutting Tools?
Carbide in cutting tools refers to a composite material made primarily of tungsten carbide particles bonded with a metallic binder, usually cobalt, which provides exceptional hardness and wear resistance. This material enables cutting tools to maintain sharp edges and withstand high temperatures during metalworking operations, outperforming traditional steel or enamel-coated tools. Carbide's durability and precision make it ideal for applications requiring extended tool life and high-speed machining.
Key Properties: Enamel vs Carbide
Enamel cutting tools offer excellent corrosion resistance and a smooth, hard surface ideal for light-duty applications but lack the wear resistance and toughness of carbide tools. Carbide tools, composed of tungsten carbide particles bonded with cobalt, provide superior hardness, wear resistance, and heat resistance, making them suitable for high-speed, heavy-duty machining. The key distinction lies in carbide's ability to maintain cutting edge integrity under extreme conditions, whereas enamel tools excel in environments where chemical stability is critical.
Durability and Wear Resistance Comparison
Carbide cutting tools exhibit superior durability and wear resistance compared to enamel-coated tools due to their hardness and ability to maintain a sharp cutting edge under high temperatures. Enamel coatings provide a protective layer against corrosion and minor abrasion but tend to wear off faster under heavy machining conditions. Selecting carbide tools ensures prolonged tool life and consistent performance in demanding industrial applications.
Cutting Performance and Precision
Enamel-coated cutting tools offer superior corrosion resistance and smoother surface finish, enhancing cutting precision by reducing friction and heat buildup. Carbide tools exhibit exceptional hardness and wear resistance, enabling prolonged cutting performance and maintaining sharp edges for increased accuracy in high-speed machining. Selecting between enamel and carbide depends on material compatibility and required tolerance levels, with carbide favored for heavy-duty precision cutting tasks.
Cost Analysis: Enamel vs Carbide Tools
Enamel cutting tools generally present a lower initial cost compared to carbide tools, making them a budget-friendly option for less demanding applications. Carbide tools, despite higher upfront expenses, offer superior hardness and wear resistance, leading to longer tool life and reduced replacement frequency, which can offset the initial investment over time. When analyzing total cost of ownership, carbide tools often provide better cost efficiency due to enhanced durability and performance in high-speed or heavy-duty cutting operations.
Best Applications for Enamel Tools
Enamel cutting tools excel in applications requiring corrosion resistance and smooth finishes, particularly in woodworking and light metal fabrication where surface integrity is crucial. Their non-reactive surfaces prevent contamination and reduce friction, making them ideal for cutting softer materials such as plastics, composites, and delicate alloys. Enamel tools also perform well in environments with exposure to moisture or chemicals, maintaining durability without compromising precision.
Best Applications for Carbide Tools
Carbide cutting tools excel in high-speed machining and applications involving hard materials like stainless steel, titanium, and cast iron due to their superior hardness and wear resistance compared to enamel-coated tools. These tools maintain sharpness longer and withstand extreme temperatures, making them ideal for CNC milling, turning, and drilling in demanding industrial environments. Enamel coatings provide corrosion resistance but lack the durability required for precision cutting and heavy-duty metalworking tasks.
Choosing the Right Cutting Tool Material
When selecting the right cutting tool material, enamel offers excellent corrosion resistance and is ideal for light-duty applications where surface finish is critical, while carbide provides superior hardness, wear resistance, and high-temperature performance, making it suitable for heavy-duty machining and high-speed operations. Carbide tools typically extend tool life and improve efficiency in cutting tougher materials such as hardened steel, whereas enamel-coated tools are preferred for delicate or precision cutting tasks requiring minimal tool abrasion. Understanding the workpiece material and machining conditions is crucial in optimizing tool selection for durability and cutting performance.
Infographic: Enamel vs Carbide for Cutting Tool
 azmater.com
azmater.com