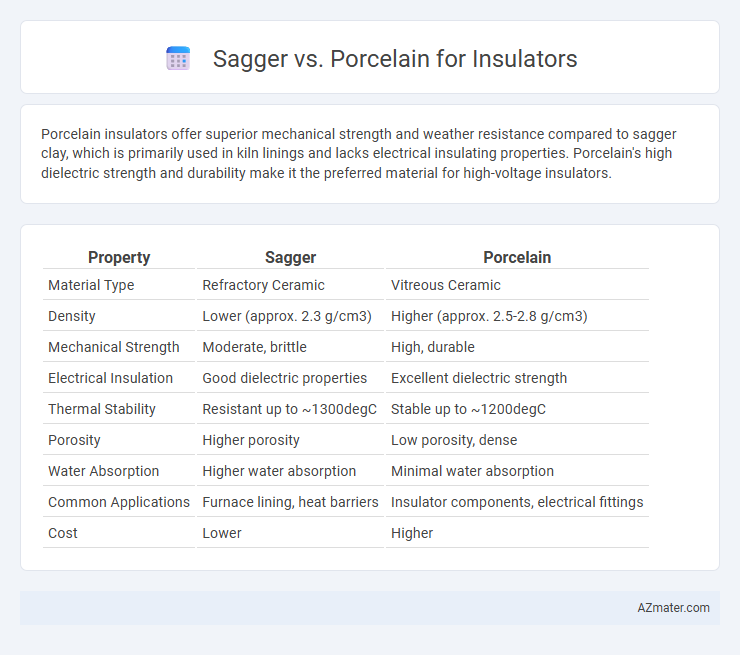
Porcelain insulators offer superior mechanical strength and weather resistance compared to sagger clay, which is primarily used in kiln linings and lacks electrical insulating properties. Porcelain's high dielectric strength and durability make it the preferred material for high-voltage insulators.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Sagger | Porcelain |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Refractory Ceramic | Vitreous Ceramic |
| Density | Lower (approx. 2.3 g/cm3) | Higher (approx. 2.5-2.8 g/cm3) |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate, brittle | High, durable |
| Electrical Insulation | Good dielectric properties | Excellent dielectric strength |
| Thermal Stability | Resistant up to ~1300degC | Stable up to ~1200degC |
| Porosity | Higher porosity | Low porosity, dense |
| Water Absorption | Higher water absorption | Minimal water absorption |
| Common Applications | Furnace lining, heat barriers | Insulator components, electrical fittings |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Sagger and Porcelain Insulators
Sagger insulators, typically made from high-purity refractory ceramics, are designed to withstand extreme temperatures and harsh chemical environments during kiln firing processes. Porcelain insulators consist of a ceramic material known for its excellent electrical insulation properties, mechanical strength, and resistance to weathering, making them ideal for power transmission and distribution. Both sagger and porcelain insulators serve critical roles in industrial and electrical applications, optimized for durability and performance under specific operational conditions.
Material Composition: Sagger vs Porcelain
Sagger insulators are typically made from high-quality ceramic clay mixed with alumina and silica, providing excellent thermal resistance and durability under high-temperature conditions during kiln firing. Porcelain insulators consist of a dense, vitrified ceramic material composed mainly of kaolin, feldspar, and quartz, known for their superior electrical insulation properties and mechanical strength. The key difference lies in the firing process and material purity, where sagger material prioritizes thermal insulation in extreme heat, while porcelain offers enhanced electrical performance and longevity in electrical applications.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Sagger insulators are produced by placing ceramic material inside a protective container called a sagger during the firing process, which helps prevent direct contact with the kiln atmosphere, ensuring uniform heat distribution and reducing defects. Porcelain insulators undergo a shaping process followed by a high-temperature vitrification firing, resulting in a dense, glass-like surface that provides superior mechanical strength and electrical insulation. The key manufacturing difference lies in the sagger's role as a protective barrier during firing, while porcelain insulators rely on vitrification to enhance durability and performance.
Mechanical and Thermal Strength Comparison
Porcelain insulators exhibit superior mechanical strength with high resistance to impact and compressive forces, making them ideal for heavy-load applications. Sagger materials generally offer enhanced thermal stability, withstanding higher operating temperatures without deformation or loss of insulating properties. In terms of thermal shock resistance, porcelain also performs well, but saggers maintain consistent insulation under extreme heat variations, providing reliability in high-temperature environments.
Electrical Insulation Performance
Porcelain insulators exhibit superior electrical insulation performance due to their high dielectric strength and resistance to surface contamination, making them ideal for high-voltage applications. Sagger insulators, typically used as protective containers during firing processes, have limited electrical insulation properties and are less suitable for electrical insulation purposes. The porosity and mechanical robustness of porcelain result in enhanced insulation reliability under electrical stress compared to saggers.
Durability and Lifespan of Insulators
Porcelain insulators exhibit superior durability due to their high mechanical strength and resistance to environmental factors such as UV radiation, moisture, and temperature fluctuations. Sagger insulators, typically made from composite materials, offer good flexibility and resistance to impact but may degrade faster under prolonged exposure to harsh conditions. Overall, porcelain insulators tend to have a longer lifespan, often exceeding 30 years in outdoor applications, whereas sagger insulators may require more frequent replacement depending on usage and environmental stress.
Cost Analysis: Sagger vs Porcelain
Sagger insulators generally offer lower initial costs due to simpler manufacturing processes and cheaper raw materials compared to porcelain insulators, which require extensive firing and glazing techniques, increasing production expenses. Porcelain insulators provide higher durability and longer service life, potentially reducing long-term maintenance and replacement costs despite the higher upfront investment. Evaluating total cost of ownership shows sagger insulators are cost-effective for short-term applications, while porcelain insulators yield better economic value for high-performance, long-term electrical insulation projects.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Sagger insulators, typically made from clay or ceramic materials, have lower environmental impact due to their natural composition and recyclability, reducing waste and energy consumption during production. Porcelain insulators, while durable and resistant to weathering, involve higher energy-intensive manufacturing processes and may contribute more to carbon emissions. Sustainable choices favor sagger insulators for their reduced ecological footprint and potential for easier end-of-life recycling.
Applications and Industry Use Cases
Porcelain insulators are widely used in high-voltage power transmission and distribution systems due to their excellent mechanical strength and weather resistance, making them ideal for outdoor applications such as overhead lines and substations. Sagger insulators, often utilized in manufacturing and industrial furnace environments, provide superior thermal insulation and durability at high temperatures, essential for processes like ceramics firing and metal heat treatment. While porcelain insulators dominate electrical infrastructure industries, saggers find specialized use in industrial processing sectors requiring heat containment and protection.
Choosing the Right Insulator: Key Considerations
Choosing the right insulator between Sagger and Porcelain involves evaluating factors like thermal stability, mechanical strength, and environmental resistance. Porcelain insulators offer superior durability and excellent resistance to weathering, making them ideal for outdoor electrical applications, whereas Sagger insulators provide better thermal shock resistance suited for high-temperature industrial settings. Key considerations include application-specific temperature ranges, mechanical load requirements, and long-term reliability under varying environmental conditions.
Infographic: Sagger vs Porcelain for Insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com