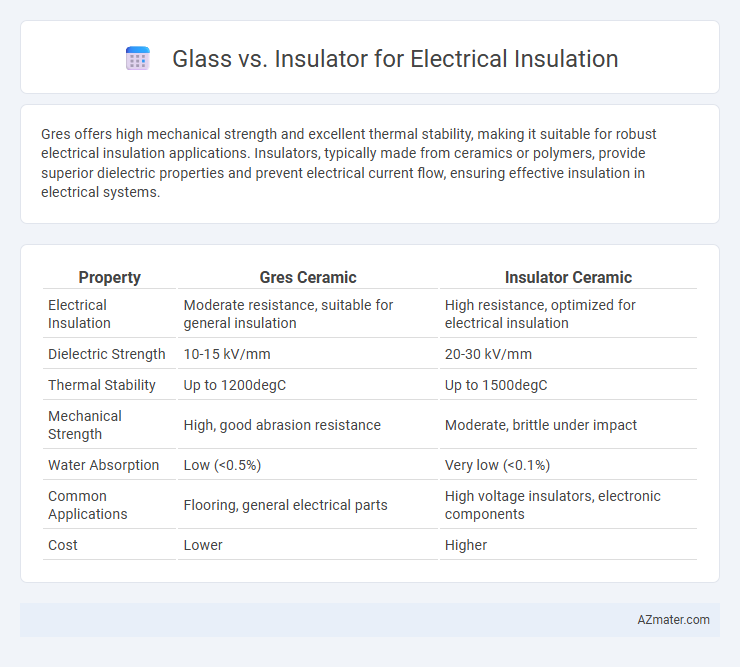
Gres offers high mechanical strength and excellent thermal stability, making it suitable for robust electrical insulation applications. Insulators, typically made from ceramics or polymers, provide superior dielectric properties and prevent electrical current flow, ensuring effective insulation in electrical systems.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Gres Ceramic | Insulator Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Insulation | Moderate resistance, suitable for general insulation | High resistance, optimized for electrical insulation |
| Dielectric Strength | 10-15 kV/mm | 20-30 kV/mm |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 1200degC | Up to 1500degC |
| Mechanical Strength | High, good abrasion resistance | Moderate, brittle under impact |
| Water Absorption | Low (<0.5%) | Very low (<0.1%) |
| Common Applications | Flooring, general electrical parts | High voltage insulators, electronic components |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Electrical Insulation Materials
Electrical insulation materials such as gres and insulators play a crucial role in preventing electrical current leakage and ensuring safety in electrical systems. Gres, a type of ceramic material, offers high mechanical strength and excellent thermal stability, making it suitable for high-voltage applications. Insulators, typically made from porcelain, glass, or polymer composites, provide superior dielectric properties and resist environmental degradation, optimizing electrical performance and reliability.
What is Gres? Properties and Applications
Gres, a high-strength ceramic material, is widely used for electrical insulation due to its excellent dielectric properties, high thermal resistance, and mechanical robustness. It features low electrical conductivity, superior heat resistance up to 1300degC, and exceptional chemical stability, making it ideal for insulators in high-voltage power systems and electronic devices. Common applications include insulator components in transformers, switchgears, and high-voltage transmission lines where durability and electrical insulation are critical.
Understanding Electrical Insulators
Electrical insulators, such as gres and traditional materials, play a critical role in preventing the flow of electrical current by providing high resistance and maintaining safety in electrical systems. Gres, a type of ceramic insulator made from feldspathic clay fired at high temperatures, offers superior mechanical strength and excellent dielectric properties compared to conventional materials, making it ideal for high-voltage applications. Understanding the electrical insulation properties of gres versus other insulators is essential for selecting appropriate materials in power transmission and distribution networks to minimize energy loss and prevent electrical hazards.
Key Differences Between Gres and Insulators
Gres, a type of dense porcelain material, offers mechanical strength and thermal stability, making it suitable for high-voltage electrical insulation applications. Insulators, primarily made from ceramic, glass, or polymer materials, prevent electrical current flow and provide crucial protection in power systems. Key differences lie in Gres's enhanced durability and heat resistance compared to standard insulators, which are optimized for electrical conductivity prevention and environmental resilience.
Comparative Electrical Performance: Gres vs Traditional Insulators
Gres offers superior electrical insulation performance compared to traditional insulators due to its higher dielectric strength and lower electrical conductivity, minimizing leakage currents in high-voltage applications. The dense, non-porous structure of gres enhances its resistance to moisture absorption, significantly improving insulation reliability under varying environmental conditions. Traditional insulators, often made from porcelain or glass, may exhibit lower durability and higher susceptibility to electrical degradation over time, especially in polluted or humid environments.
Thermal Stability: Gres Compared to Other Insulators
Gres exhibits superior thermal stability compared to many traditional electrical insulators, maintaining integrity under high-temperature conditions exceeding 1000degC. Its dense, fine-grained structure minimizes thermal expansion and prevents deformation, ensuring reliable insulation performance in demanding applications. Compared to polymer-based insulators, gres offers enhanced resistance to thermal aging and chemical degradation, making it ideal for industrial electrical systems exposed to extreme heat.
Mechanical Strength: Gres vs Insulator Materials
Gres, a type of ceramic material, exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to conventional electrical insulators, making it ideal for high-stress applications. Its high compressive strength and resistance to thermal shock enhance durability in demanding electrical environments. In contrast, traditional insulator materials like porcelain or polymer composites often have lower mechanical strength and may degrade faster under mechanical stresses.
Cost Analysis: Gres Versus Conventional Insulators
Gres insulators typically offer lower production and maintenance costs compared to conventional ceramic and glass insulators due to simpler manufacturing processes and improved durability. Cost analysis reveals gres insulators reduce long-term expenses by minimizing replacement frequency and enhancing resistance to environmental degradation. Conventional insulators may have a higher initial price but often incur greater lifecycle costs due to fragility and susceptibility to weather-induced damage.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Gres materials exhibit lower environmental impact due to their natural composition and recyclability, reducing waste and toxic emissions during production compared to synthetic insulators. Insulators made from non-biodegradable polymers often involve energy-intensive manufacturing and pose disposal challenges, contributing to long-term environmental pollution. Prioritizing gres-based insulation supports sustainability by minimizing carbon footprint and promoting eco-friendly lifecycle management.
Choosing the Right Material: Gres or Standard Insulator?
Choosing between gres and standard insulators for electrical insulation depends on factors like mechanical strength, thermal stability, and cost-effectiveness. Gres, a type of high-strength ceramic material, offers superior resistance to thermal shock and mechanical stress, making it ideal for high-voltage and harsh environments. Standard insulators, typically made from porcelain or glass, provide reliable insulation with lower manufacturing costs and sufficient performance for less demanding electrical applications.
Infographic: Gres vs Insulator for Electrical Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com