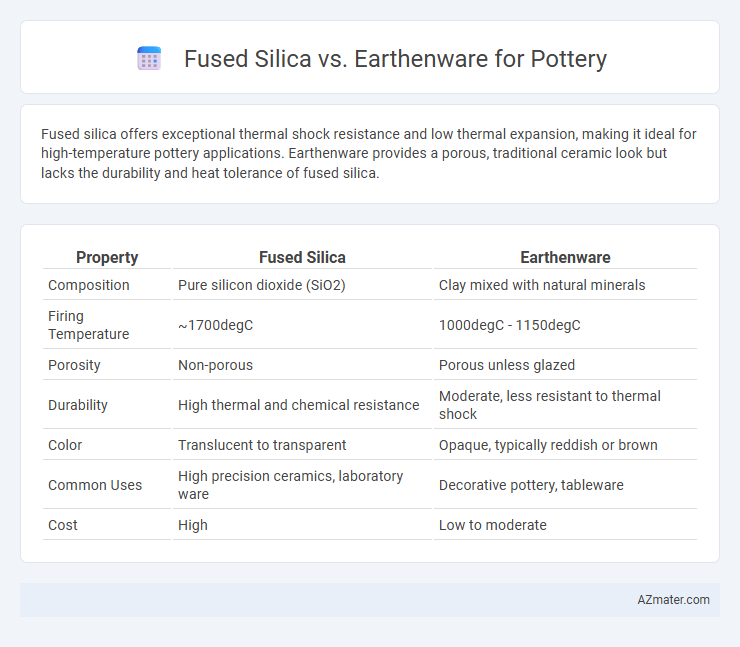
Fused silica offers exceptional thermal shock resistance and low thermal expansion, making it ideal for high-temperature pottery applications. Earthenware provides a porous, traditional ceramic look but lacks the durability and heat tolerance of fused silica.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fused Silica | Earthenware |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Pure silicon dioxide (SiO2) | Clay mixed with natural minerals |
| Firing Temperature | ~1700degC | 1000degC - 1150degC |
| Porosity | Non-porous | Porous unless glazed |
| Durability | High thermal and chemical resistance | Moderate, less resistant to thermal shock |
| Color | Translucent to transparent | Opaque, typically reddish or brown |
| Common Uses | High precision ceramics, laboratory ware | Decorative pottery, tableware |
| Cost | High | Low to moderate |
Introduction to Fused Silica and Earthenware
Fused silica is a high-purity silica glass known for its exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and low thermal expansion, making it ideal for precision applications including advanced pottery techniques requiring durability at high temperatures. Earthenware, a traditional pottery material, consists of porous, natural clay fired at relatively low temperatures, resulting in a more fragile and absorbent ceramic suitable for decorative or utilitarian objects. Understanding the distinct thermal properties and composition of fused silica and earthenware is crucial for selecting the appropriate material based on the desired strength, finish, and functionality in pottery.
Material Composition: Fused Silica vs Earthenware
Fused silica is composed primarily of high-purity silicon dioxide (SiO2) in an amorphous glass form, offering exceptional thermal stability and chemical inertness for pottery applications. Earthenware consists mainly of clay minerals such as kaolinite combined with various natural sesquioxides and fluxes, resulting in a porous and less dense ceramic material after firing. The distinct material compositions influence their thermal shock resistance, durability, and suitability for different pottery techniques, with fused silica providing greater resilience to extreme temperature changes.
Thermal Properties and Heat Resistance
Fused silica exhibits exceptional thermal stability with a melting point around 1,710degC and a low coefficient of thermal expansion (0.5 x 10^-6 /degC), making it highly resistant to thermal shock and ideal for high-temperature applications. Earthenware, in contrast, typically withstands temperatures up to 1,100degC but has a higher coefficient of thermal expansion, resulting in lower thermal shock resistance and increased susceptibility to cracking under rapid temperature changes. The superior heat resistance and thermal endurance of fused silica significantly surpass earthenware's capabilities, rendering it preferable for advanced thermal insulation and kiln components.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Fused silica offers exceptional durability and strength due to its high thermal shock resistance and low thermal expansion, making it ideal for precision pottery applications where durability under heat stress is critical. Earthenware, while aesthetically versatile and easier to mold, is more porous and less durable, prone to chipping and cracking under mechanical stress or thermal changes. The superior mechanical properties of fused silica provide longer-lasting pottery, especially in environments exposed to rapid temperature fluctuations or heavy use.
Aesthetic Qualities and Surface Finish
Fused silica offers a sleek, glass-like surface with exceptional smoothness and a subtle translucency that enhances modern pottery aesthetics, while earthenware presents a warm, rustic texture characterized by natural earthy tones and a matte to slightly textured finish. The surface finish of fused silica is highly polished and resistant to staining, making it ideal for minimalist, contemporary designs, whereas earthenware's porous surface readily accepts glazes that create rich color variations and tactile interest. Potters seeking refined elegance often choose fused silica for its uniformity and brilliance, contrasting with earthenware's organic charm and versatility in traditional or rustic pottery styles.
Workability and Crafting Techniques
Fused silica offers exceptional workability for pottery due to its high thermal resistance and low thermal expansion, allowing craftsmen to achieve fine detail without risk of cracking during firing. Earthenware, with its porous nature and lower firing temperature, provides a more forgiving medium for hand-building and sculptural techniques but requires careful glazing to ensure durability. The choice between fused silica and earthenware depends on the desired finish and firing conditions, with fused silica suited for precision techniques and earthenware favored for traditional, tactile crafting methods.
Firing Temperatures and Kiln Requirements
Fused silica requires extremely high firing temperatures above 1700degC, demanding advanced kilns with precise temperature control and often electric or gas heating elements resistant to thermal shock. Earthenware, on the other hand, fires at much lower temperatures between 1000degC and 1150degC, compatible with standard pit or electric kilns commonly used in traditional pottery. The significant difference in kiln requirements makes fused silica suitable for industrial applications, while earthenware remains ideal for artisanal and everyday ceramics.
Cost Considerations and Availability
Fused silica offers exceptional thermal stability and durability but comes at a higher cost compared to earthenware, impacting budget-sensitive pottery projects. Earthenware clay is widely available and affordable, making it a popular choice for beginners and large-scale productions. Availability of fused silica is more limited and often sourced from specialized suppliers, whereas earthenware is commonly accessible in craft stores and local suppliers.
Typical Uses in Pottery and Ceramic Art
Fused silica is prized in pottery and ceramic art for its exceptional thermal shock resistance and stability, making it ideal for kiln shelves and high-temperature applications. Earthenware, known for its porous nature and lower firing temperatures, is commonly used for decorative pottery, flower pots, and traditional ceramics due to its rustic appearance and ease of glazing. Both materials serve distinct roles, with fused silica supporting technical and industrial ceramic needs while earthenware caters to artistic and functional pottery.
Choosing the Right Material: Key Considerations
Fused silica offers exceptional thermal shock resistance and durability, making it ideal for high-temperature pottery applications and precision crafts. Earthenware, composed of natural clay minerals, provides a porous, rustic finish suited for decorative or traditional pottery but requires careful glazing to prevent water absorption. Choosing between fused silica and earthenware hinges on factors like firing temperature, desired aesthetic, mechanical strength, and intended use of the pottery piece.
Infographic: Fused silica vs Earthenware for Pottery
 azmater.com
azmater.com