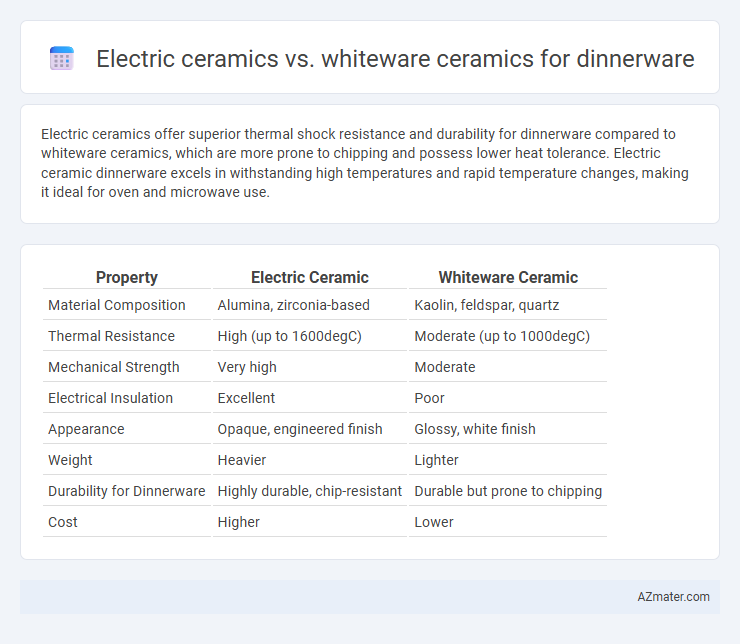
Electric ceramics offer superior thermal shock resistance and durability for dinnerware compared to whiteware ceramics, which are more prone to chipping and possess lower heat tolerance. Electric ceramic dinnerware excels in withstanding high temperatures and rapid temperature changes, making it ideal for oven and microwave use.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Electric Ceramic | Whiteware Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Alumina, zirconia-based | Kaolin, feldspar, quartz |
| Thermal Resistance | High (up to 1600degC) | Moderate (up to 1000degC) |
| Mechanical Strength | Very high | Moderate |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent | Poor |
| Appearance | Opaque, engineered finish | Glossy, white finish |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Durability for Dinnerware | Highly durable, chip-resistant | Durable but prone to chipping |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Electric Ceramic and Whiteware Ceramic
Electric ceramic, known for its high thermal shock resistance and durability, is often used in dinnerware requiring enhanced heat retention and resilience. Whiteware ceramic, composed primarily of kaolin and feldspar, offers a smooth, white finish ideal for aesthetic appeal and everyday use in table settings. Both materials provide unique benefits, with electric ceramic excelling in performance under thermal stress, while whiteware ceramic is favored for its classic appearance and cost-effectiveness.
Composition Differences between Electric and Whiteware Ceramics
Electric ceramics typically consist of high-purity alumina and zirconia, allowing them to withstand high temperatures and thermal shock for electrical insulation purposes. Whiteware ceramics are mainly composed of kaolin, feldspar, and quartz, designed for durability, whiteness, and smooth surfaces in dinnerware applications. The differing compositions reflect their functional requirements, with electric ceramics prioritizing electrical and thermal properties, while whiteware ceramics emphasize aesthetic appeal and mechanical strength.
Manufacturing Processes: Electric vs Whiteware Ceramic
Electric ceramic dinnerware is manufactured using advanced electro-firing techniques that enhance durability and create a smoother, more uniform glaze, while whiteware ceramic relies on traditional kiln-firing methods at high temperatures to achieve its hardness and whiteness. The electric firing process allows precise temperature control, reducing defects and improving material consistency, whereas whiteware ceramics undergo multiple firings and glazing steps to ensure strength and aesthetic appeal. Differences in raw materials also affect manufacturing; electric ceramics often incorporate engineered clays for enhanced electrical properties, whereas whiteware uses natural kaolin, feldspar, and quartz blends optimized for whiteness and chip resistance.
Durability and Strength in Everyday Use
Electric ceramic dinnerware, often made from advanced materials designed to withstand high heat, offers superior durability and resistance to cracking compared to traditional whiteware ceramics. Whiteware ceramic, while aesthetically pleasing and suitable for standard use, tends to be more prone to chipping and breakage under heavy or frequent use. The enhanced durability and thermal shock resistance of electric ceramics make them ideal for everyday use, especially in environments requiring frequent heating and cooling cycles.
Aesthetic Appeal: Color, Texture, and Finishes
Electric ceramic dinnerware exhibits a sleek, glossy finish with vibrant, uniform color tones due to high-temperature glazing techniques, enhancing modern aesthetic appeal. Whiteware ceramic offers a classic, matte or semi-matte texture with subtle variations in color and finish, providing a timeless and handcrafted look. Both materials accommodate diverse glazing options, but electric ceramics tend to emphasize contemporary brilliance, while whiteware emphasizes traditional, rustic charm.
Heat and Chemical Resistance Comparison
Electric ceramic exhibits superior heat resistance, withstanding temperatures up to 1400degC, making it ideal for high-heat cooking and serving applications. Whiteware ceramic typically tolerates heat up to 1200degC and offers excellent chemical resistance, preventing reactions with acidic or alkaline foods. The higher sintering temperature of electric ceramic enhances its structural integrity and chemical stability, resulting in longer-lasting, durable dinnerware.
Food Safety and Non-Toxicity Considerations
Electric ceramics often feature advanced glazing and firing techniques that enhance their non-toxicity and food safety by minimizing leaching of harmful substances. Whiteware ceramics, commonly used for traditional dinnerware, are generally safe when finished with lead-free and cadmium-free glazes, ensuring compliance with food safety standards. Both materials require proper manufacturing and certification to guarantee they are free from toxic elements and safe for daily food contact.
Cost and Affordability for Consumers
Electric ceramic dinnerware typically falls on the higher end of the price spectrum due to advanced manufacturing processes and enhanced durability features, making it less affordable for budget-conscious consumers. Whiteware ceramic, produced using traditional methods with widespread availability, offers a more cost-effective option, appealing to a broader market seeking functional and stylish dinnerware. Consumers prioritizing affordability often choose whiteware ceramic as it combines reasonable price points with acceptable quality and aesthetic versatility.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Electric ceramic dinnerware typically involves advanced manufacturing processes with higher energy consumption and carbon emissions compared to traditional whiteware ceramics. Whiteware ceramics, made from natural clay materials and kiln-fired at moderate temperatures, offer a more sustainable option with lower environmental impact and greater biodegradability. Choosing whiteware ceramics supports eco-friendly production practices and reduces the overall carbon footprint associated with dinnerware manufacturing.
Which Ceramic Is Best for Your Dinnerware Needs?
Electric ceramics offer superior heat resistance and durability, making them ideal for frequent use in microwave ovens and electric cooktops. Whiteware ceramics, known for their classic aesthetic and affordability, provide excellent resistance to chipping and are dishwasher safe, suiting everyday dining needs. Choosing between electric and whiteware ceramic depends on your emphasis on heat performance or traditional style for your dinnerware.
Infographic: Electric ceramic vs Whiteware ceramic for Dinnerware
 azmater.com
azmater.com