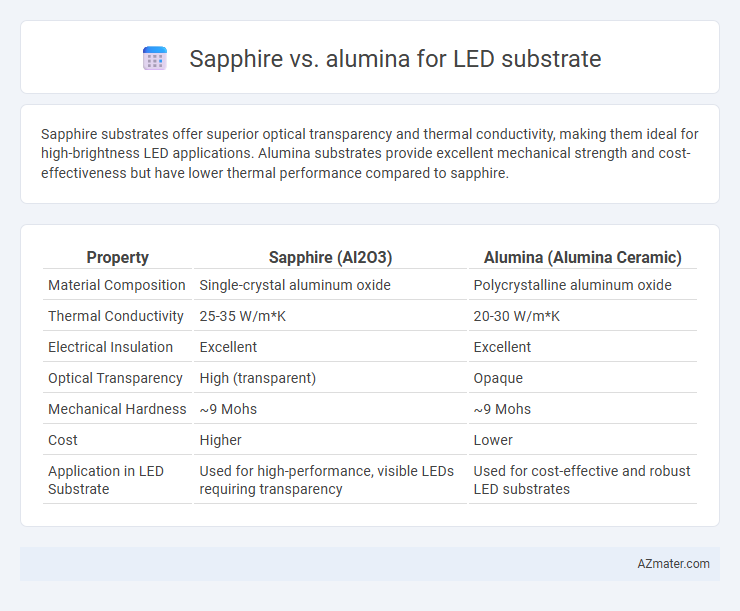
Sapphire substrates offer superior optical transparency and thermal conductivity, making them ideal for high-brightness LED applications. Alumina substrates provide excellent mechanical strength and cost-effectiveness but have lower thermal performance compared to sapphire.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Sapphire (Al2O3) | Alumina (Alumina Ceramic) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Single-crystal aluminum oxide | Polycrystalline aluminum oxide |
| Thermal Conductivity | 25-35 W/m*K | 20-30 W/m*K |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent | Excellent |
| Optical Transparency | High (transparent) | Opaque |
| Mechanical Hardness | ~9 Mohs | ~9 Mohs |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Application in LED Substrate | Used for high-performance, visible LEDs requiring transparency | Used for cost-effective and robust LED substrates |
Introduction to LED Substrate Materials
Sapphire and alumina are widely used LED substrate materials, each offering distinct advantages based on thermal conductivity and lattice matching properties essential for epitaxial growth. Sapphire provides excellent optical transparency and lattice compatibility with gallium nitride (GaN), promoting high-quality LED performance and efficiency. Alumina offers superior thermal conductivity and mechanical strength, making it suitable for high-power LEDs that require efficient heat dissipation and durability.
Overview of Sapphire and Alumina Properties
Sapphire substrates offer excellent thermal conductivity of approximately 35 W/m*K and high chemical stability, making them ideal for high-power LED applications requiring efficient heat dissipation. Alumina substrates provide superior dielectric strength and mechanical robustness with thermal conductivity around 25 W/m*K, favored for cost-effective, low to medium power LEDs. Both materials exhibit high electrical insulation, but sapphire's crystalline structure enhances lattice matching with gallium nitride (GaN), improving LED efficiency and lifespan.
Thermal Conductivity Comparison
Alumina substrates exhibit higher thermal conductivity, typically ranging from 20 to 30 W/m*K, significantly outperforming sapphire substrates, which have thermal conductivity around 35 W/m*K. This improved heat dissipation in alumina substrates enhances LED performance by reducing junction temperature and extending device lifespan. Selecting alumina for LED substrates supports efficient thermal management in high-power LED applications.
Optical Transparency and Performance
Sapphire substrates offer excellent optical transparency in the ultraviolet to visible spectrum, making them ideal for high-performance LED applications requiring efficient light transmission. Alumina substrates exhibit lower optical transparency but provide superior thermal conductivity and mechanical stability, enhancing overall device durability. Choosing between sapphire and alumina depends on the specific LED performance requirements, where sapphire excels in optical clarity and alumina in heat dissipation.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Alumina substrates exhibit higher mechanical strength and superior thermal shock resistance compared to sapphire, making them more durable under extreme operating conditions. Sapphire substrates, while offering excellent optical transparency and thermal conductivity, tend to be more brittle and susceptible to cracking during high-stress manufacturing processes. The enhanced toughness of alumina ensures better longevity and reliability in LED applications subjected to mechanical and thermal stress.
Chemical Stability and Corrosion Resistance
Sapphire exhibits superior chemical stability and corrosion resistance compared to alumina when used as an LED substrate, making it highly resistant to acidic and alkaline environments during LED fabrication. Alumina, while mechanically strong, is more susceptible to chemical degradation and surface corrosion under harsh processing conditions. The enhanced durability of sapphire substrates contributes to longer-lasting, higher-performance LED devices in chemically aggressive manufacturing processes.
Cost-Effectiveness and Manufacturing Scalability
Sapphire substrates offer lower material costs and widespread availability, making them more cost-effective for high-volume LED production compared to alumina. Alumina substrates provide superior thermal conductivity and mechanical strength but involve higher manufacturing expenses and limited scalability. Choosing sapphire supports cost-efficient large-scale manufacturing, while alumina benefits specialized applications requiring enhanced performance despite elevated costs.
Compatibility with LED Epitaxy Processes
Sapphire substrates offer excellent lattice matching and thermal stability, making them highly compatible with gallium nitride (GaN) LED epitaxy processes commonly used in LED manufacturing. Alumina substrates exhibit lower lattice compatibility but provide superior mechanical strength and thermal conductivity for high-power LED applications. Selecting between sapphire and alumina depends on optimizing epitaxial layer quality, defect density, and thermal management requirements in LED device fabrication.
Application Suitability in LED Technologies
Sapphire substrates offer excellent optical transparency and thermal conductivity, making them ideal for high-brightness LED applications, particularly in blue and white LEDs. Alumina substrates provide superior electrical insulation and mechanical strength, suitable for high-power and high-frequency LED devices where thermal management and durability are critical. Choosing between sapphire and alumina depends on the specific LED technology requirements, including wavelength, heat dissipation, and device lifespan.
Future Trends in LED Substrate Material Selection
Emerging trends in LED substrate material selection emphasize the shift towards alumina due to its superior thermal conductivity and cost-effectiveness compared to sapphire, enhancing LED performance and reliability. Innovations in composite materials and nano-engineered alumina substrates are driving improvements in light extraction efficiency and thermal management, crucial for next-generation high-power LEDs. The industry increasingly favors substrates that balance scalability and thermal dissipation, positioning alumina as a promising alternative to sapphire in future LED manufacturing.
Infographic: Sapphire vs Alumina for LED substrate
 azmater.com
azmater.com