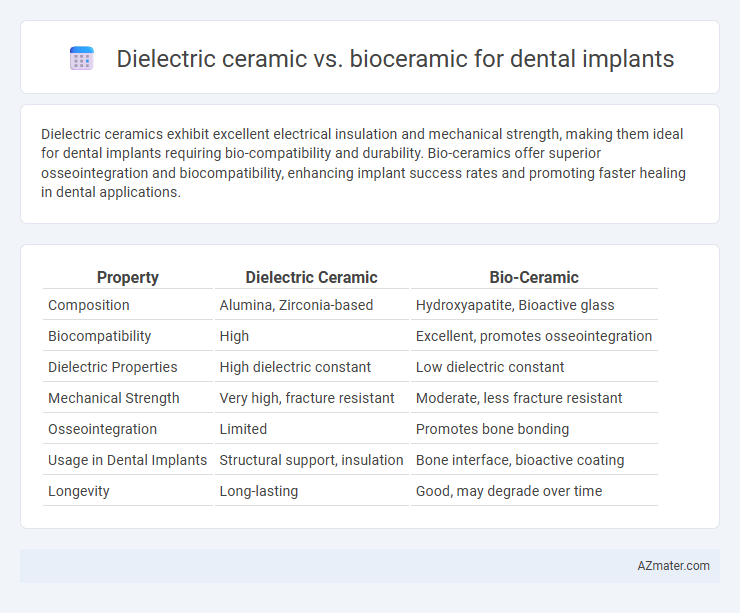
Dielectric ceramics exhibit excellent electrical insulation and mechanical strength, making them ideal for dental implants requiring bio-compatibility and durability. Bio-ceramics offer superior osseointegration and biocompatibility, enhancing implant success rates and promoting faster healing in dental applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Dielectric Ceramic | Bio-Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Alumina, Zirconia-based | Hydroxyapatite, Bioactive glass |
| Biocompatibility | High | Excellent, promotes osseointegration |
| Dielectric Properties | High dielectric constant | Low dielectric constant |
| Mechanical Strength | Very high, fracture resistant | Moderate, less fracture resistant |
| Osseointegration | Limited | Promotes bone bonding |
| Usage in Dental Implants | Structural support, insulation | Bone interface, bioactive coating |
| Longevity | Long-lasting | Good, may degrade over time |
Introduction to Dental Implant Materials
Dielectric ceramics and bio-ceramics are prominent materials in dental implantology, each offering unique properties that influence implant performance and biocompatibility. Dielectric ceramics, known for their excellent electrical insulation and mechanical strength, provide durability but may lack the optimal bioactivity necessary for osseointegration. Bio-ceramics, such as zirconia and hydroxyapatite, exhibit superior biocompatibility and promote bone integration, making them increasingly preferred for long-term dental implant success.
What Are Dielectric Ceramics?
Dielectric ceramics are insulating materials that exhibit high electrical resistance and strong dielectric properties, making them ideal for use in dental implants to enhance biocompatibility and reduce electrical conductivity within oral tissues. Unlike bio-ceramics, which are specifically designed to bond with bone and promote osseointegration, dielectric ceramics primarily serve to improve implant insulation and stability. Their unique electrical characteristics contribute to minimizing inflammation and ensuring long-term implant success in dental applications.
Overview of Bio-ceramics in Dentistry
Bio-ceramics in dentistry, such as zirconia and alumina, offer superior biocompatibility and osseointegration compared to traditional dielectric ceramics. These materials exhibit excellent chemical stability, resistance to corrosion, and minimal inflammatory response, making them ideal for dental implants and restorations. Their enhanced mechanical strength and bioactivity contribute to improved long-term success rates in implantology and restorative dental procedures.
Mechanical Properties: Dielectric vs. Bio-ceramic
Dielectric ceramics used in dental implants exhibit high dielectric strength and stability but generally possess lower fracture toughness compared to bio-ceramics. Bio-ceramics, such as zirconia, provide superior mechanical properties including enhanced toughness, wear resistance, and biocompatibility, making them more suitable for load-bearing dental applications. The mechanical reliability of bio-ceramics ensures better long-term performance under masticatory forces compared to dielectric ceramics.
Biocompatibility and Osseointegration
Dielectric ceramics exhibit excellent biocompatibility due to their inert chemical nature, minimizing inflammatory responses, while bio-ceramics like hydroxyapatite actively promote osseointegration by chemically bonding with bone tissue. Bio-ceramics provide superior osteoconductivity, enhancing the stability and longevity of dental implants through accelerated bone remodeling. Both materials resist corrosion and wear; however, bio-ceramics' bioactive surface significantly improves implant integration compared to the passive interface of dielectric ceramics.
Corrosion Resistance and Longevity
Dielectric ceramics used in dental implants exhibit excellent corrosion resistance due to their stable oxide layer, minimizing ion release and implant degradation over time. Bio-ceramics, particularly zirconia-based materials, offer superior biocompatibility combined with high corrosion resistance, enhancing implant longevity by preventing inflammatory responses and maintaining structural integrity. Comparative studies indicate that bio-ceramics tend to outperform traditional dielectric ceramics in long-term durability and resistance to oral environmental stressors.
Aesthetic Outcomes in Dental Implants
Dielectric ceramics offer superior aesthetic outcomes in dental implants due to their high translucency and color-matching capabilities, closely mimicking natural tooth enamel. Bio-ceramics, while biocompatible and promoting osseointegration, often lack the translucency required for optimal aesthetic integration in the anterior dental region. The choice between dielectric ceramic and bio-ceramic materials significantly impacts the visual appeal of dental implants, with dielectric ceramics providing a more lifelike and natural appearance.
Clinical Applications and Case Studies
Dielectric ceramics, primarily composed of alumina and zirconia, offer excellent biocompatibility and electrical insulation, making them suitable for dental implants requiring high mechanical strength and wear resistance in clinical practice. Bio-ceramics, such as hydroxyapatite and bioglass, promote osseointegration and bone regeneration, enhancing healing outcomes and implant stability in challenging cases like compromised bone quality. Clinical case studies demonstrate dielectric ceramics' durability in load-bearing implants, while bio-ceramics excel in enhancing biological integration and reducing infection risks post-implantation.
Cost and Accessibility Comparison
Dielectric ceramic dental implants generally offer a lower cost option due to more established manufacturing processes and availability, making them accessible in a wider range of markets and dental clinics. Bio-ceramic implants, often comprising advanced materials like zirconia, tend to have higher production costs, impacting their overall price and limiting accessibility mainly to specialized practices or regions with advanced dental care infrastructure. The cost disparity reflects material properties and demand, influencing patient choice based on budget constraints and implant performance expectations.
Future Trends in Dental Implant Materials
Dielectric ceramics in dental implants offer excellent electrical insulation and biocompatibility, enhancing osseointegration and reducing corrosion risks, while bio-ceramics provide superior bioactivity and mimic natural bone structure closely, promoting faster healing and tissue integration. Emerging future trends focus on hybrid materials combining dielectric and bio-ceramic properties to optimize mechanical strength and biological performance. Advanced surface modifications and nanotechnology integration are driving innovations that improve implant longevity and patient outcomes in dental treatments.
Infographic: Dielectric ceramic vs Bio-ceramic for Dental implant
 azmater.com
azmater.com