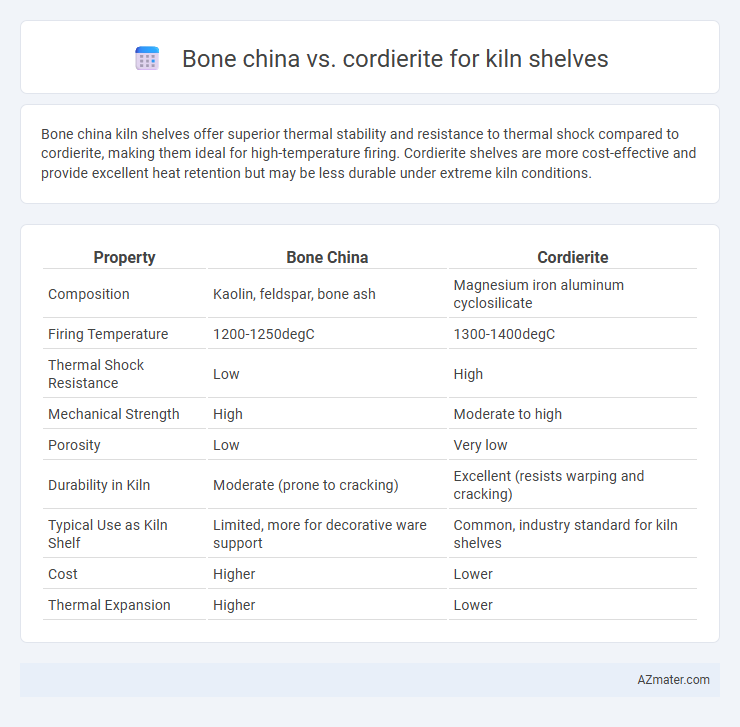
Bone china kiln shelves offer superior thermal stability and resistance to thermal shock compared to cordierite, making them ideal for high-temperature firing. Cordierite shelves are more cost-effective and provide excellent heat retention but may be less durable under extreme kiln conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bone China | Cordierite |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Kaolin, feldspar, bone ash | Magnesium iron aluminum cyclosilicate |
| Firing Temperature | 1200-1250degC | 1300-1400degC |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Low | High |
| Mechanical Strength | High | Moderate to high |
| Porosity | Low | Very low |
| Durability in Kiln | Moderate (prone to cracking) | Excellent (resists warping and cracking) |
| Typical Use as Kiln Shelf | Limited, more for decorative ware support | Common, industry standard for kiln shelves |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Thermal Expansion | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Kiln Shelf Materials
Kiln shelves are essential components in pottery and ceramics firing, designed to support wares inside the kiln while withstanding high temperatures. Bone china shelves offer smooth surfaces and thermal stability ideal for delicate porcelain pieces, while cordierite shelves provide exceptional thermal shock resistance and durability suited for high-temperature firings and heavier ceramic loads. Selecting the appropriate kiln shelf material depends on specific firing requirements, including maximum temperature and the type of ceramics being produced.
What is Bone China?
Bone china is a type of porcelain known for its high levels of whiteness, translucency, and strength, produced by adding bone ash to the traditional ceramic mixture. This material offers excellent thermal shock resistance but is generally less durable under extreme kiln temperatures compared to cordierite, making it less ideal for kiln shelves which require high heat tolerance. Cordierite shelves outperform bone china in thermal stability and longevity, essential for consistent firing without warping or cracking.
What is Cordierite?
Cordierite is a crystalline mineral commonly used in kiln shelves due to its superior thermal shock resistance and high-temperature stability, making it ideal for prolonged firing processes. Unlike bone china, which is a fine porcelain containing bone ash and favored for delicate tableware, cordierite kiln shelves offer exceptional durability and dimensional stability under rapid temperature changes. This mineral's low thermal expansion prevents warping or cracking during intense firing cycles, ensuring consistent performance in ceramics production.
Durability Comparison: Bone China vs Cordierite
Cordierite kiln shelves offer superior durability compared to bone china, exhibiting excellent thermal shock resistance and minimal warping under extreme temperatures. Bone china, while aesthetically appealing and strong for tableware, tends to be more brittle and less capable of withstanding repeated high-heat firing cycles used in kilns. Cordierite's robust composition makes it the preferred choice for kiln shelves, ensuring longevity and consistent performance during strenuous ceramic firing processes.
Thermal Shock Resistance in Kiln Shelves
Cordierite kiln shelves exhibit superior thermal shock resistance compared to bone china, making them ideal for repeated high-temperature firings and rapid cooling cycles in ceramic and glasswork. Bone china tends to be more porous and less durable under extreme temperature fluctuations, often leading to warping or cracking. Manufacturers favor cordierite for kiln shelves due to its low thermal expansion coefficient and enhanced structural integrity, ensuring longer lifespan and consistent performance.
Weight and Handling Differences
Bone china kiln shelves are significantly lighter than cordierite shelves, making them easier to handle during kiln loading and unloading. Cordierite shelves, known for their durability and thermal shock resistance, tend to be heavier and bulkier, which can affect maneuverability and require more effort when positioning within the kiln. The lightweight nature of bone china shelves reduces strain and improves efficiency but may sacrifice some robustness compared to the dense, heat-resistant cordierite material.
Performance at High Temperatures
Bone china kiln shelves offer excellent thermal stability but tend to have lower resistance to thermal shock compared to cordierite shelves. Cordierite shelves excel under high temperatures up to 1300degC due to their superior thermal shock resistance and dimensional stability, making them ideal for rapid heating and cooling cycles. Performance-wise, cordierite outperforms bone china in durability and longevity in demanding ceramic firing environments.
Cost Analysis: Bone China vs Cordierite
Bone china kiln shelves generally incur higher initial costs due to premium raw materials and intricate manufacturing processes, making them more expensive than cordierite shelves. Cordierite offers cost efficiency with lower material expenses and excellent thermal shock resistance, reducing replacement frequency and maintenance costs. When evaluating long-term expenses, cordierite provides better value for budget-conscious ceramicists seeking durable and affordable kiln shelf options.
Best Applications for Each Material
Bone china kiln shelves excel in low-temperature firings and are ideal for delicate ceramics and fine porcelain due to their smooth surface and thermal stability. Cordierite kiln shelves are better suited for high-temperature firings, such as stoneware and technical ceramics, because of their superior thermal shock resistance and durability. Choosing between Bone china and Cordierite depends on the firing temperature and the type of ceramic work being produced.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Kiln Shelf Material
Bone china kiln shelves offer excellent thermal shock resistance and smooth surfaces ideal for delicate ceramic firings, while cordierite shelves provide superior durability and high-temperature stability suited for heavy-duty or frequent firings. Selecting the right kiln shelf material depends on firing temperatures, load weight, and the type of ceramics being fired to optimize shelf lifespan and firing quality. Prioritizing cordierite improves longevity and heat retention in rigorous firing environments, whereas bone china benefits intricate, low to mid-range temperature firings with reduced risk of warping.
Infographic: Bone china vs Cordierite for Kiln shelf
 azmater.com
azmater.com