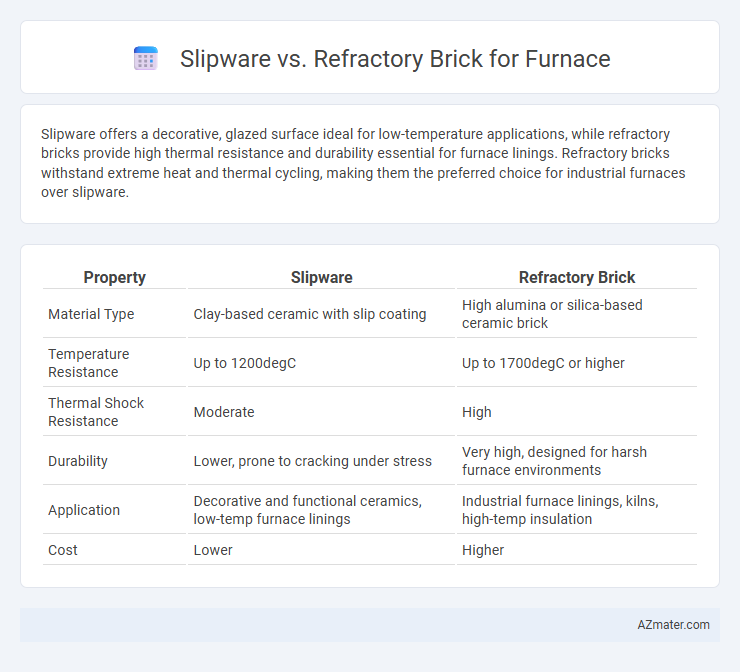
Slipware offers a decorative, glazed surface ideal for low-temperature applications, while refractory bricks provide high thermal resistance and durability essential for furnace linings. Refractory bricks withstand extreme heat and thermal cycling, making them the preferred choice for industrial furnaces over slipware.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Slipware | Refractory Brick |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Clay-based ceramic with slip coating | High alumina or silica-based ceramic brick |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 1200degC | Up to 1700degC or higher |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Durability | Lower, prone to cracking under stress | Very high, designed for harsh furnace environments |
| Application | Decorative and functional ceramics, low-temp furnace linings | Industrial furnace linings, kilns, high-temp insulation |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Slipware and Refractory Brick
Slipware is a type of pottery coated with a liquid clay slip, typically used for decorative or functional ceramic items rather than high-temperature applications. Refractory bricks, made from fireclay, alumina, silica, or other heat-resistant materials, are engineered to withstand extreme furnace temperatures, providing essential insulation and structural support. Understanding the fundamental differences between slipware's artistic use and refractory brick's thermal durability is crucial for selecting appropriate materials in furnace construction.
Understanding Slipware: Composition and Properties
Slipware consists of ceramic vessels coated with slip, a liquid clay mixture primarily made from refined clay and water, which allows for smooth surface finishes and decorative glazing. Its porous nature and lower thermal resistance make slipware unsuitable for high-temperature applications like furnace linings. In contrast, refractory bricks are engineered from alumina, silica, and fireclay mixtures, providing exceptional heat resistance and structural integrity for furnace use.
What Are Refractory Bricks? Key Characteristics
Refractory bricks, also known as firebricks, are ceramic materials specifically designed to withstand extreme temperatures in furnaces and kilns, featuring high thermal stability and resistance to chemical corrosion. These bricks are composed primarily of alumina and silica, which provide exceptional heat retention and durability under intense thermal cycling. Key characteristics include low thermal conductivity, high compressive strength, and excellent resistance to thermal shock, making them ideal for lining the interior of industrial furnaces.
Heat Resistance: Slipware vs Refractory Brick
Slipware offers moderate heat resistance suitable for decorative or low-temperature furnace linings, but lacks the durability required for intense thermal cycles. Refractory bricks are engineered from high-grade alumina, silica, or fireclay materials, providing exceptional heat resistance up to 1800degC and superior thermal shock resistance. This makes refractory bricks the preferred choice for furnace applications demanding sustained high-temperature endurance and structural stability.
Durability and Longevity in Furnace Applications
Slipware, a traditional ceramic coating, offers moderate durability but tends to degrade faster under high-temperature furnace conditions due to its porous nature. Refractory bricks, composed of dense, heat-resistant materials like alumina and silica, provide superior longevity and maintain structural integrity in extreme thermal cycles. Their high thermal mass and resistance to chemical corrosion make refractory bricks the preferred choice for long-term furnace durability.
Installation Process: Comparing Ease and Complexity
Slipware offers a quicker and more flexible installation process for furnaces due to its moldable consistency and faster setting time, reducing labor costs and downtime. Refractory bricks require precise stacking, skilled labor, and curing time to ensure durability and heat resistance, making the installation more complex and time-intensive. Choosing slipware or refractory brick depends largely on the furnace design requirements and installation timeline priorities.
Cost Effectiveness: Price and Value Analysis
Slipware furnaces typically offer lower initial material costs compared to refractory bricks, making them a budget-friendly option for smaller-scale or hobby applications. Refractory bricks, though more expensive upfront, provide superior durability and heat resistance, resulting in lower maintenance and replacement costs over time. Evaluating long-term value, refractory bricks deliver enhanced cost-effectiveness through extended lifespan and improved thermal efficiency, justifying higher initial investment in industrial furnace settings.
Maintenance and Repair Considerations
Slipware coatings on furnaces offer easier surface repairs due to their smooth, ceramic-based layer that resists cracking and spalling, reducing downtime during maintenance. Refractory bricks require periodic inspection for thermal cracking and erosion but provide enhanced durability under high thermal stress, making replacement more labor-intensive and costly. Proper maintenance scheduling and repair techniques optimize furnace longevity, with slipware favored for quick touch-ups and refractory bricks preferred for structural integrity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Slipware, composed primarily of clay mixed with water and organic materials, generally exhibits lower embodied energy and produces fewer emissions during production compared to refractory bricks, which require high-temperature kilns and energy-intensive manufacturing. Refractory bricks, often made from alumina, silica, and other minerals, offer superior thermal resistance and longer lifespan, reducing the frequency of replacement and associated waste, thus enhancing sustainability in long-term furnace operation. Selecting between slipware and refractory bricks depends on balancing immediate environmental impacts with durability and efficiency, as slipware may be more eco-friendly initially, while refractory bricks minimize overall resource consumption through extended service life.
Best Uses: Choosing the Right Material for Your Furnace
Slipware is best suited for decorative furnace components and lower-temperature applications due to its glazed surface that enhances aesthetic appeal but lacks high thermal resistance. Refractory brick excels in high-temperature environments, providing superior heat retention and durability, making it ideal for furnace linings and industrial kilns. Selecting the right material depends on the furnace's operating temperature and structural requirements, with refractory brick preferred for intense heat exposure and slipware for ornamental or moderate-heat uses.
Infographic: Slipware vs Refractory Brick for Furnace
 azmater.com
azmater.com