Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings offer superior thermal resistance and lightweight properties compared to traditional armor materials, while boron carbide provides exceptional hardness and ballistic protection due to its high density and tensile strength. Boron carbide's combination of low weight and high hardness makes it a preferred choice for advanced personal and vehicle armor systems over plasma-sprayed ceramic alternatives.
Table of Comparison
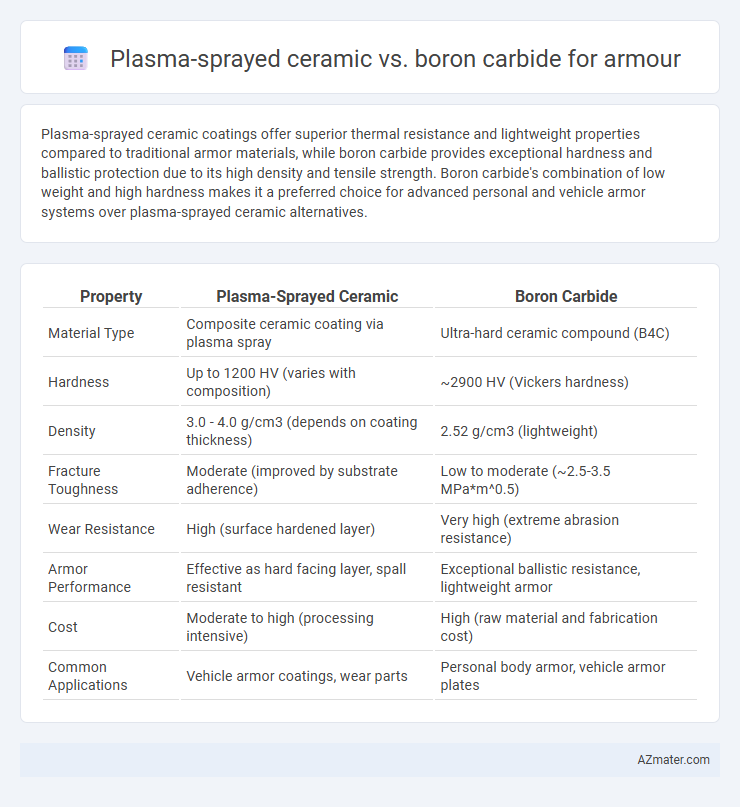
| Property | Plasma-Sprayed Ceramic | Boron Carbide |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Composite ceramic coating via plasma spray | Ultra-hard ceramic compound (B4C) |
| Hardness | Up to 1200 HV (varies with composition) | ~2900 HV (Vickers hardness) |
| Density | 3.0 - 4.0 g/cm3 (depends on coating thickness) | 2.52 g/cm3 (lightweight) |
| Fracture Toughness | Moderate (improved by substrate adherence) | Low to moderate (~2.5-3.5 MPa*m^0.5) |
| Wear Resistance | High (surface hardened layer) | Very high (extreme abrasion resistance) |
| Armor Performance | Effective as hard facing layer, spall resistant | Exceptional ballistic resistance, lightweight armor |
| Cost | Moderate to high (processing intensive) | High (raw material and fabrication cost) |
| Common Applications | Vehicle armor coatings, wear parts | Personal body armor, vehicle armor plates |
Introduction to Armour Materials
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings exhibit high hardness and thermal stability, offering effective resistance against high-velocity impacts in armor applications. Boron carbide is among the hardest known materials, providing exceptional ballistic protection with low density, making it ideal for lightweight armor solutions. Comparing these materials highlights the trade-offs between the protective efficiency of bulk boron carbide ceramics and the customizable, damage-tolerant properties of plasma-sprayed ceramic layers.
Overview of Plasma-Sprayed Ceramic Armour
Plasma-sprayed ceramic armour offers a lightweight, high-hardness barrier ideal for ballistic protection by applying molten ceramic particles onto substrates, resulting in a dense, adherent coating that enhances impact resistance. This technology excels in providing improved energy absorption and fragmentation control compared to traditional ceramics, with customizable microstructures tailored for specific threat levels. While boron carbide remains a top-tier ceramic for armour due to its exceptional hardness and low density, plasma-sprayed ceramics allow versatile fabrication and coating on complex geometries, optimizing tactical applications.
Understanding Boron Carbide Armour
Boron carbide armor exhibits exceptional hardness, lightweight properties, and superior ballistic resistance, making it preferable over plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings in critical military and personal protection applications. Unlike plasma-sprayed ceramics, which provide surface-level protection through thermal barrier coatings, boron carbide acts as a bulk armor material with high fracture toughness and excellent ability to absorb impact energy. The intrinsic material properties of boron carbide, such as a Mohs hardness of approximately 9.5 and a density around 2.52 g/cm3, position it as an optimal choice for lightweight, high-performance armor systems.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Hardness
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings exhibit high hardness levels, making them effective for surface protection, but often suffer from lower tensile strength and brittleness compared to bulk materials. Boron carbide, one of the hardest known ceramics, combines exceptional hardness with superior compressive strength, providing excellent ballistic resistance and structural integrity in armor applications. The mechanical performance of boron carbide outmatches plasma-sprayed ceramics in terms of impact resistance and durability under high-stress conditions, critical for effective armor protection.
Weight and Density Comparison
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings typically exhibit densities ranging from 2.5 to 3.5 g/cm3, offering significant weight savings compared to boron carbide, which has a higher density of approximately 2.52 g/cm3 but provides superior hardness and ballistic resistance. In armor applications, the lower density of plasma-sprayed ceramics enables lighter protective layers without compromising structural integrity, making them ideal for mobile platforms where weight reduction is critical. Boron carbide's intrinsic hardness and toughness, despite its slightly higher density, result in excellent stopping power, but plasma-sprayed ceramic systems allow customization of thickness and composition to optimize weight and performance balance.
Ballistic Performance Analysis
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings provide enhanced surface hardness and improved resistance to spallation, which contributes to effective shockwave dispersion during ballistic impacts. Boron carbide is known for its exceptional hardness and low density, delivering superior ballistic performance by efficiently blunting projectile penetration and minimizing weight. Ballistic performance analysis reveals that while plasma-sprayed ceramics offer customizable surface properties and good energy absorption, boron carbide remains the preferred material for lightweight, high-strength armor systems due to its proven multi-hit capability and superior ceramic toughness.
Resistance to Environmental Factors
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings offer superior resistance to high temperatures and oxidation, making them ideal for harsh thermal environments in armor applications. Boron carbide displays exceptional hardness and chemical stability, providing excellent resistance to corrosion and wear under diverse environmental conditions. Combining these materials can enhance overall armor durability by leveraging the thermal resilience of plasma-sprayed ceramics and the environmental toughness of boron carbide.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Plasma-sprayed ceramic armor offers a cost-effective manufacturing process due to lower raw material expenses and scalable coating techniques, making it suitable for large-area applications. Boron carbide, while providing superior hardness and ballistic protection, involves complex and energy-intensive sintering processes, resulting in higher production costs. Manufacturing considerations also include the slower production rate and tooling requirements for boron carbide, contrasted with the relatively rapid and flexible plasma spray deposition methods.
Applications in Military and Civilian Sectors
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings provide enhanced thermal resistance and wear protection, making them suitable for lightweight armor in military vehicles and personal protective equipment. Boron carbide, known for its exceptional hardness and low density, is extensively used in ballistic armor for both military personnel and civilian applications such as armored vehicles and security infrastructure. The combination of plasma-sprayed ceramic layers with boron carbide plates ultimately improves impact resistance and durability in diverse operational environments.
Summary: Choosing the Optimal Armour Material
Plasma-sprayed ceramic offers excellent hardness and thermal resistance, making it suitable for lightweight, high-performance armour applications. Boron carbide provides superior hardness-to-weight ratio and exceptional ballistic protection, widely preferred in military and personal armor systems. Selecting the optimal armour material depends on balancing factors like weight, cost, impact resistance, and specific threat levels for targeted protection needs.
Infographic: Plasma-sprayed ceramic vs Boron carbide for Armour
 azmater.com
azmater.com