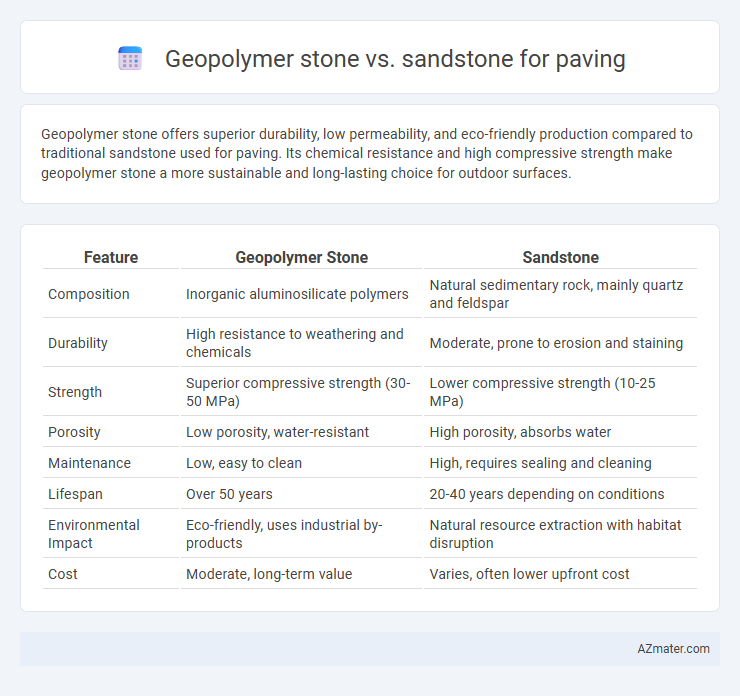
Geopolymer stone offers superior durability, low permeability, and eco-friendly production compared to traditional sandstone used for paving. Its chemical resistance and high compressive strength make geopolymer stone a more sustainable and long-lasting choice for outdoor surfaces.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Geopolymer Stone | Sandstone |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Inorganic aluminosilicate polymers | Natural sedimentary rock, mainly quartz and feldspar |
| Durability | High resistance to weathering and chemicals | Moderate, prone to erosion and staining |
| Strength | Superior compressive strength (30-50 MPa) | Lower compressive strength (10-25 MPa) |
| Porosity | Low porosity, water-resistant | High porosity, absorbs water |
| Maintenance | Low, easy to clean | High, requires sealing and cleaning |
| Lifespan | Over 50 years | 20-40 years depending on conditions |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, uses industrial by-products | Natural resource extraction with habitat disruption |
| Cost | Moderate, long-term value | Varies, often lower upfront cost |
Introduction to Paving Material Choices
Geopolymer stone offers a sustainable alternative to traditional sandstone for paving, combining high durability with eco-friendly manufacturing processes. Sandstone, renowned for its natural aesthetic and ease of workability, remains popular but often requires more maintenance due to weathering effects. Choosing between geopolymer stone and sandstone depends on factors such as longevity, environmental impact, and cost efficiency in paving applications.
What is Geopolymer Stone?
Geopolymer stone is an innovative, eco-friendly paving material made from industrial byproducts like fly ash and slag, offering high durability and resistance to weathering compared to natural sandstone. It features low porosity, enhanced compressive strength, and reduced maintenance requirements, making it ideal for high-traffic outdoor areas. Unlike traditional sandstone, geopolymer stone provides better sustainability by minimizing natural resource extraction and lowering carbon emissions during production.
Understanding Natural Sandstone
Natural sandstone, composed primarily of compacted sand grains bound by mineral cement, offers unique permeability and durability ideal for paving. Its porous texture facilitates water drainage and provides slip resistance, but variable hardness and susceptibility to weathering require careful maintenance. Compared to geopolymer stone, which mimics natural stone properties through synthetic binding agents, sandstone delivers authentic aesthetic appeal and natural thermal regulation benefits.
Key Material Properties Compared
Geopolymer stone exhibits superior compressive strength and enhanced chemical resistance compared to natural sandstone, making it highly durable for paving applications. Its low porosity reduces water absorption, minimizing freeze-thaw damage, unlike sandstone which often has higher porosity and susceptibility to weathering. Geopolymer stone's environmental benefits include lower carbon emissions during production, whereas quarrying and processing sandstone typically result in greater ecological impact.
Durability and Longevity Analysis
Geopolymer stone exhibits significantly higher durability and longevity compared to natural sandstone, resisting weathering, chemical erosion, and freeze-thaw cycles due to its synthetic aluminosilicate matrix. While sandstone is prone to surface wear and degradation over time, geopolymer paving withstands heavy traffic and environmental stress without significant loss of structural integrity. Studies indicate geopolymer stone retains over 90% of its mechanical strength after extensive aging tests, making it a superior choice for long-term paving solutions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Geopolymer stone offers significantly lower carbon emissions compared to traditional sandstone due to its manufacturing process, which uses industrial by-products like fly ash and slag, reducing reliance on quarried natural resources. The energy-efficient production and recyclability of geopolymer materials contribute to a smaller environmental footprint and enhanced sustainability in paving applications. In contrast, sandstone extraction often results in habitat disruption and higher energy consumption, making geopolymer stone a more eco-friendly choice for sustainable urban development.
Installation Process: Geopolymer vs Sandstone
The installation process for geopolymer stone involves precise mixing and curing of synthetic materials, allowing for custom shapes and faster setting times compared to natural sandstone. Geopolymer stone requires less excavation and foundation work due to its lightweight nature, simplifying handling and reducing labor costs. Sandstone paving demands careful selection and cutting of heavy natural slabs, longer drying periods, and more intensive groundwork to ensure durability and stability.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Geopolymer stone requires less maintenance than traditional sandstone due to its enhanced resistance to stains, weathering, and microbial growth, reducing the frequency of cleaning needed. Its non-porous surface prevents dirt and moisture absorption, making routine cleaning straightforward with just water and mild detergents. In contrast, sandstone's porous nature demands regular sealing and more intensive cleaning to avoid discoloration and erosion over time.
Cost Comparison for Paving Projects
Geopolymer stone typically offers a lower cost per square meter compared to natural sandstone due to its synthetic production process and use of industrial byproducts, reducing raw material expenses. Sandstone often incurs higher costs linked to quarrying, transportation, and variability in quality, which can increase installation and maintenance expenses over time. For large paving projects, choosing geopolymer stone can result in significant budget savings without compromising durability or aesthetic appeal.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Stone for Your Paving Needs
Geopolymer stone offers superior durability, resistance to weathering, and lower maintenance compared to traditional sandstone, making it ideal for high-traffic and harsh outdoor environments. Sandstone provides natural aesthetic appeal and is often preferred for its classic look and affordability in residential projects. Selecting the right stone depends on balancing budget, design preferences, and the specific durability demands of your paving application.
Infographic: Geopolymer stone vs Sandstone for Paving
 azmater.com
azmater.com