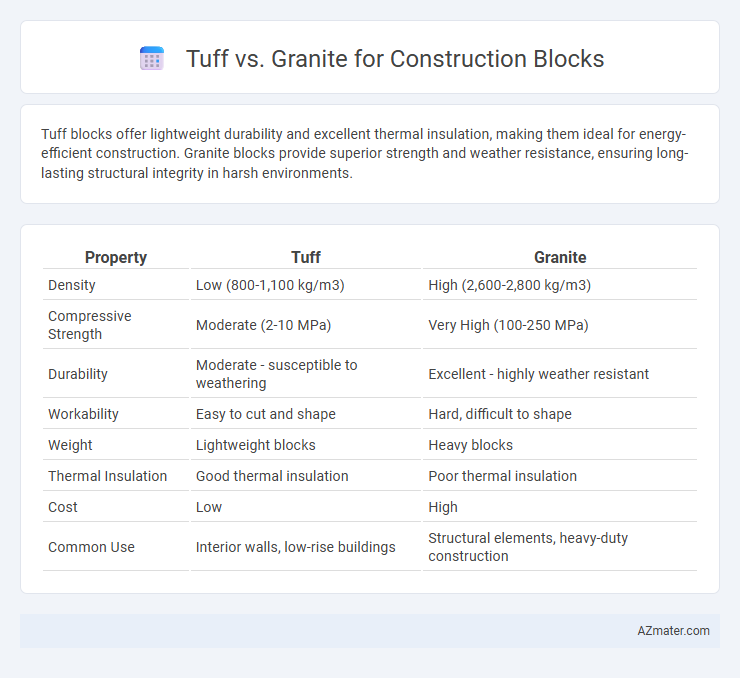
Tuff blocks offer lightweight durability and excellent thermal insulation, making them ideal for energy-efficient construction. Granite blocks provide superior strength and weather resistance, ensuring long-lasting structural integrity in harsh environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tuff | Granite |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Low (800-1,100 kg/m3) | High (2,600-2,800 kg/m3) |
| Compressive Strength | Moderate (2-10 MPa) | Very High (100-250 MPa) |
| Durability | Moderate - susceptible to weathering | Excellent - highly weather resistant |
| Workability | Easy to cut and shape | Hard, difficult to shape |
| Weight | Lightweight blocks | Heavy blocks |
| Thermal Insulation | Good thermal insulation | Poor thermal insulation |
| Cost | Low | High |
| Common Use | Interior walls, low-rise buildings | Structural elements, heavy-duty construction |
Introduction to Tuff and Granite as Construction Materials
Tuff, a porous volcanic rock, offers lightweight and insulating properties ideal for construction blocks, making it suitable for energy-efficient buildings. Granite, a dense and durable igneous rock, provides exceptional strength and resistance to weathering, commonly used in structural and decorative applications. Both materials differ significantly in density, strength, and thermal conductivity, influencing their selection based on specific building requirements.
Geological Formation and Composition
Tuff, a volcanic rock formed from consolidated volcanic ash, primarily consists of pumice, volcanic glass, and mineral fragments, making it lightweight and porous compared to granite. Granite is an intrusive igneous rock composed mainly of quartz, feldspar, and mica, forming deep within the Earth's crust through slow crystallization, resulting in a dense and durable structure. The contrasting geological formations influence their physical properties, with tuff offering ease of cutting and insulation, while granite provides superior strength and resistance for construction blocks.
Physical Properties: Strength and Durability
Tuff blocks exhibit moderate compressive strength ranging from 5 to 15 MPa, making them suitable for non-load-bearing walls, while granite blocks offer superior strength exceeding 100 MPa, ideal for high-load structural applications. Granite's exceptional durability stems from its dense, interlocking crystal structure, providing excellent resistance to weathering and abrasion, whereas tuff's porous nature can lead to quicker degradation in harsh environmental conditions. Selecting granite ensures long-term structural integrity and minimal maintenance, whereas tuff offers lightweight and cost-effective advantages primarily in less demanding construction scenarios.
Aesthetic Differences and Appearance
Tuff blocks exhibit a natural, porous texture with earthy tones ranging from light beige to reddish-brown, offering a rustic and warm aesthetic ideal for decorative facades. Granite blocks display a dense, fine-grained surface with a polished finish that highlights their speckled patterns in shades of grey, black, and white, providing a sleek and modern look. The choice between tuff and granite significantly influences the visual appeal of construction projects, balancing natural ruggedness against refined sophistication.
Workability and Ease of Cutting
Tuff exhibits superior workability compared to granite due to its softer and porous nature, allowing for easier shaping and cutting with standard masonry tools. Granite's hardness, measured at 6-7 on the Mohs scale, makes it significantly more challenging to cut, often requiring diamond-tipped blades and specialized equipment. The ease of cutting tuff not only reduces labor costs but also accelerates construction timelines, making it a practical choice for block manufacturing where precision and efficiency are critical.
Weather Resistance and Longevity
Tuff offers excellent weather resistance due to its porous structure, which allows for better moisture regulation, reducing freeze-thaw damage in varying climates. Granite, known for its dense, non-porous composition, provides superior durability and longevity by resisting erosion, abrasion, and chemical weathering over extended periods. Choosing between tuff and granite for construction blocks involves balancing tuff's natural insulation properties with granite's unmatched strength and resistance to environmental degradation.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Qualities
Tuff blocks exhibit superior thermal insulation due to their porous structure, which reduces heat transfer and maintains indoor temperature stability compared to dense granite blocks. Acoustic insulation is also more effective in tuff because its natural pore spaces absorb sound waves better than granite's solid, less porous composition. These qualities make tuff an optimal choice for energy-efficient and noise-reducing construction blocks.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Tuff, a volcanic rock, offers lower embodied energy compared to granite, making it a more sustainable option for construction blocks due to its easier extraction and reduced processing requirements. Granite, though highly durable, involves intensive quarrying and energy consumption, resulting in a larger carbon footprint and greater environmental disturbance. Choosing tuff supports eco-friendly building practices by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and minimizing ecological degradation.
Cost Comparison: Tuff vs Granite
Tuff blocks generally offer a more cost-effective solution compared to granite due to their lower extraction and processing expenses, making them ideal for budget-conscious construction projects. Granite, while significantly more durable and visually appealing, incurs higher costs linked to quarrying, cutting, and transportation. Choosing between tuff and granite affects overall project budgets, with tuff reducing upfront material costs but granite providing long-term value through enhanced strength and lifespan.
Choosing the Best Stone for Construction Blocks
Tuff offers excellent thermal insulation and lightweight properties, making it suitable for energy-efficient construction blocks, while granite provides superior strength, durability, and resistance to weathering, ideal for high-load-bearing structures. The choice between tuff and granite depends on project requirements: tuff is preferred for cost-effective, lightweight applications, whereas granite is favored for longevity and structural integrity. Assessing factors like compressive strength, local availability, and environmental conditions ensures the selected stone aligns with the building's performance and budget goals.
Infographic: Tuff vs Granite for Construction Block
 azmater.com
azmater.com