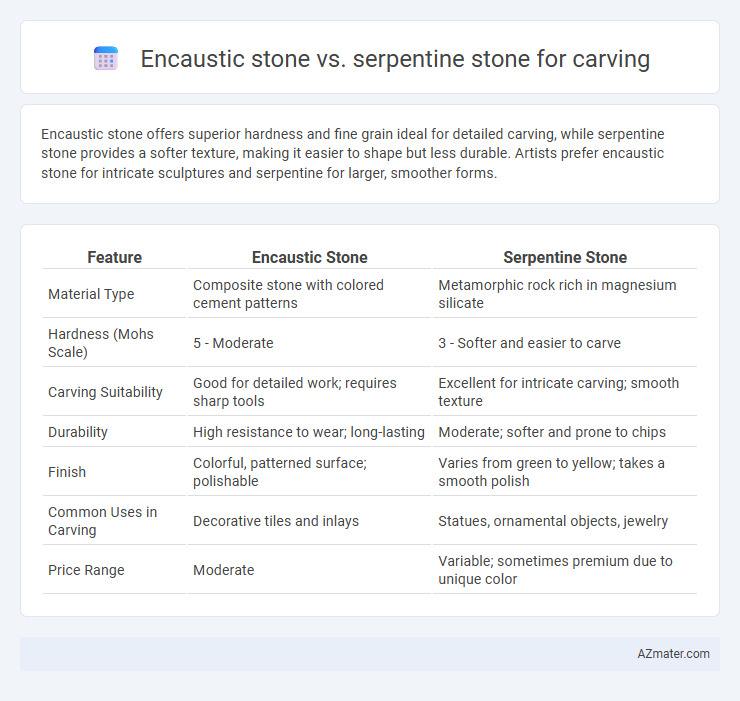
Encaustic stone offers superior hardness and fine grain ideal for detailed carving, while serpentine stone provides a softer texture, making it easier to shape but less durable. Artists prefer encaustic stone for intricate sculptures and serpentine for larger, smoother forms.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Encaustic Stone | Serpentine Stone |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Composite stone with colored cement patterns | Metamorphic rock rich in magnesium silicate |
| Hardness (Mohs Scale) | 5 - Moderate | 3 - Softer and easier to carve |
| Carving Suitability | Good for detailed work; requires sharp tools | Excellent for intricate carving; smooth texture |
| Durability | High resistance to wear; long-lasting | Moderate; softer and prone to chips |
| Finish | Colorful, patterned surface; polishable | Varies from green to yellow; takes a smooth polish |
| Common Uses in Carving | Decorative tiles and inlays | Statues, ornamental objects, jewelry |
| Price Range | Moderate | Variable; sometimes premium due to unique color |
Introduction to Encaustic Stone and Serpentine Stone
Encaustic stone, known for its fine-grained texture and ease of carving, provides artists with a durable medium that holds intricate details well, making it ideal for detailed sculptural work. Serpentine stone, often prized for its smooth finish and rich green hues, offers a softer composition that carvers find easier to shape but requires careful handling due to its relative fragility. Both stones serve distinct purposes in carving, with encaustic stone favored for precision and longevity, while serpentine stone is valued for its aesthetic appeal and tactile versatility.
Geological Origins and Composition
Encaustic stone, primarily formed from sedimentary processes, consists mainly of fine-grained calcite or dolomite, making it soft and ideal for detailed carving. Serpentine stone derives from ultramafic rocks undergoing metamorphism, characterized by its rich magnesium silicate composition, imparting a distinctive green hue and moderate hardness suitable for sculptural work. These geological origins influence their texture and durability, with encaustic stones offering smoother surfaces and serpentine providing resilience and natural variegation.
Physical Properties: Hardness and Density
Encaustic stone exhibits a hardness of approximately 3 on the Mohs scale, making it relatively soft and easier to carve for intricate details, with a density around 2.3 g/cm3 providing a lightweight feel. Serpentine stone is slightly harder, ranging from 3 to 5 on the Mohs scale, offering greater durability for carving, and has a higher density between 2.5 to 2.6 g/cm3, resulting in a more substantial finished piece. Both stones' physical properties influence their suitability for different carving techniques and final product aesthetics.
Color and Aesthetic Variations
Encaustic stone offers a wide color palette ranging from warm earth tones like reds, oranges, and yellows to softer hues such as cream and beige, giving carvings a vibrant and dynamic appearance. Serpentine stone is prized for its rich green shades, often veined with white, black, or yellow, providing a luxurious and natural aesthetic that emphasizes fluidity and texture. The distinct color variations of encaustic stone enhance bold, lively designs, while serpentine's elegant green hues lend themselves to more subtle, organic artistic expressions in carving projects.
Workability for Carving
Encaustic stone offers moderate workability for carving, characterized by its fine-grained texture that allows for detailed and smooth sculpting, making it suitable for intricate designs. Serpentine stone exhibits excellent workability due to its relatively soft and workable nature, which carvers favor for ease of shaping and fine detailing, often used in ornamental and artistic sculptures. Both stones provide good durability, but serpentine's softer composition makes it especially preferred for artists requiring greater flexibility in carving techniques.
Durability and Longevity of Carvings
Encaustic stone offers exceptional durability for carving projects due to its dense, fine-grained structure, which resists chipping and erosion over time. Serpentine stone, while valued for its workability and aesthetic appeal, is softer and more prone to weathering, making it less ideal for long-lasting carvings exposed to outdoor conditions. Carvings in encaustic stone typically exhibit greater longevity and maintain intricate details longer compared to serpentine stone sculptures.
Popular Uses in Art and Sculpture
Encaustic stone is highly favored for its smooth texture and ability to hold fine details, making it popular among artists for intricate reliefs and encaustic painting bases. Serpentine stone, known for its rich green hues and relative softness, is commonly used in sculpture for creating organic forms and decorative objects. Both stones offer unique aesthetic qualities, with encaustic stone preferred for detailed craftsmanship while serpentine excels in vibrant, naturalistic sculptures.
Maintenance and Preservation Requirements
Encaustic stone offers superior porosity and absorbs sealants more effectively, requiring regular reapplication every 6 to 12 months to maintain surface integrity and prevent staining. Serpentine stone is comparatively denser and naturally resistant to weathering, needing less frequent maintenance but benefits from occasional cleaning with mild, pH-neutral detergents to avoid surface degradation. Both stones require protection from acidic substances and harsh abrasives to preserve detailed carvings and extend their lifespan.
Cost and Availability
Encaustic stone, often derived from wax-infused materials, tends to be less costly and more readily available for carving due to widespread production and accessibility. Serpentine stone, valued for its rich green hues and smooth texture, is generally more expensive and less abundant, as it requires specific geological conditions to form. Carvers prioritizing budget and ease of sourcing commonly opt for encaustic stone, while those seeking unique aesthetic qualities may invest in the rarer serpentine stone despite higher costs.
Choosing the Right Stone for Your Carving Project
Encaustic stone offers hardness and durability, making it ideal for detailed and long-lasting carvings, while serpentine stone is softer and easier to carve, suitable for beginners or intricate work requiring delicate detail. Encaustic's fine grain supports precise designs but demands more advanced tools and techniques, whereas serpentine's smooth texture allows greater flexibility at a lower skill level. Selecting the right stone depends on your project's complexity, durability expectations, and carving experience.
Infographic: Encaustic stone vs Serpentine stone for Carving
 azmater.com
azmater.com