Tuff offers lightweight and porous properties ideal for drainage in pavement, whereas sandstone provides higher durability and abrasion resistance suitable for heavy traffic areas. Choosing between tuff and sandstone for pavement depends on specific load requirements and environmental conditions.
Table of Comparison
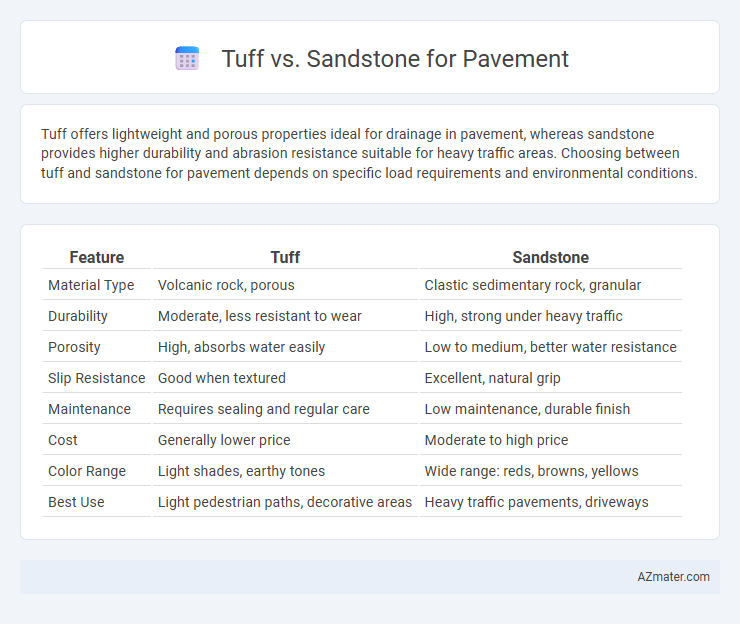
| Feature | Tuff | Sandstone |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Volcanic rock, porous | Clastic sedimentary rock, granular |
| Durability | Moderate, less resistant to wear | High, strong under heavy traffic |
| Porosity | High, absorbs water easily | Low to medium, better water resistance |
| Slip Resistance | Good when textured | Excellent, natural grip |
| Maintenance | Requires sealing and regular care | Low maintenance, durable finish |
| Cost | Generally lower price | Moderate to high price |
| Color Range | Light shades, earthy tones | Wide range: reds, browns, yellows |
| Best Use | Light pedestrian paths, decorative areas | Heavy traffic pavements, driveways |
Introduction: Tuff vs Sandstone in Pavement Construction
Tuff and sandstone are both popular natural stones used in pavement construction, each offering unique properties that influence durability and aesthetic appeal. Tuff, a volcanic rock, is lightweight and porous, providing excellent insulation and easy workability, while sandstone, composed of compacted sand grains, boasts superior hardness and resistance to weathering. Selecting between tuff and sandstone depends on project requirements such as load-bearing capacity, environmental conditions, and desired architectural style.
Geological Formation and Composition
Tuff, formed from consolidated volcanic ash, contains high silica content and fine volcanic fragments, making it relatively porous and lightweight compared to sandstone. Sandstone originates from cemented sand-sized mineral grains, primarily quartz and feldspar, resulting in a denser and more abrasion-resistant material. The geological formation of tuff involves pyroclastic deposits from volcanic eruptions, whereas sandstone forms through sedimentary processes in ancient riverbeds, beaches, or deserts.
Physical Properties Comparison
Tuff and sandstone differ significantly in their physical properties impacting pavement performance; tuff is a volcanic rock with lower density and higher porosity, which affects its durability under heavy traffic loads. Sandstone, composed primarily of compacted sand grains, offers higher compressive strength and better abrasion resistance, making it more suitable for high-traffic pavements. Moisture absorption rates are typically higher in tuff, leading to increased weathering compared to the more moisture-resistant sandstone.
Strength and Durability Factors
Tuff offers moderate strength but lower durability compared to sandstone, making it more prone to weathering and erosion in pavement applications. Sandstone exhibits higher compressive strength and superior resistance to abrasion and freeze-thaw cycles, resulting in longer-lasting pavement surfaces. Choosing sandstone enhances pavement longevity and reduces maintenance costs due to its robust structural properties.
Weather Resistance and Longevity
Tuff demonstrates superior weather resistance compared to sandstone due to its volcanic origin, making it less prone to erosion and chemical degradation in harsh climates. Sandstone, while aesthetically versatile, is more susceptible to weathering effects such as freeze-thaw cycles and acid rain, reducing its longevity in pavement applications. Consequently, tuff pavements typically offer extended durability, requiring less maintenance over time in variable weather conditions.
Aesthetic Appeal and Color Variations
Tuff offers a wide range of earthy tones such as soft yellows, rich browns, and warm reds that create a natural and rustic aesthetic for pavements. Sandstone provides a smooth texture with diverse color variations including creamy beiges, golden yellows, and subtle pinks, delivering a more uniform yet elegant appearance. Both materials enhance outdoor spaces differently, with tuff emphasizing rugged charm and sandstone showcasing refined warmth.
Workability and Installation Methods
Tuff offers superior workability for pavement due to its lightweight and softer texture, allowing easier cutting and shaping during installation. In contrast, sandstone's denser and harder composition requires specialized tools for cutting and longer installation times, impacting overall project efficiency. Workability differences influence installation methods, with tuff enabling more flexible designs and quicker placement, while sandstone demands precision and skilled labor for a durable finish.
Cost Analysis and Budget Considerations
Tuff offers a more cost-effective solution compared to sandstone for pavement due to its lower extraction and processing expenses, making it suitable for budget-conscious projects. Sandstone, while generally pricier, provides greater durability and aesthetic appeal, potentially reducing long-term maintenance costs despite a higher initial investment. Careful evaluation of upfront costs versus lifecycle expenses is essential for optimal budget allocation in pavement construction.
Maintenance Requirements and Challenges
Tuff pavement requires regular sealing and crack repair due to its relatively porous nature, which can absorb water and lead to surface degradation. Sandstone, while more durable and less porous, demands attention to prevent surface erosion and moss buildup, especially in humid environments. Both materials face challenges such as weathering effects and potential for surface wear, but sandstone generally offers lower long-term maintenance costs compared to tuff.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Tuff offers a more sustainable choice for pavement due to its lower carbon footprint and natural abundance, reducing the need for extensive quarrying and processing compared to sandstone. Sandstone extraction often results in significant habitat disruption and higher energy consumption during cutting and finishing. Tuff's porous nature also improves water permeability, enhancing stormwater management and reducing urban runoff impacts.
Infographic: Tuff vs Sandstone for Pavement
 azmater.com
azmater.com