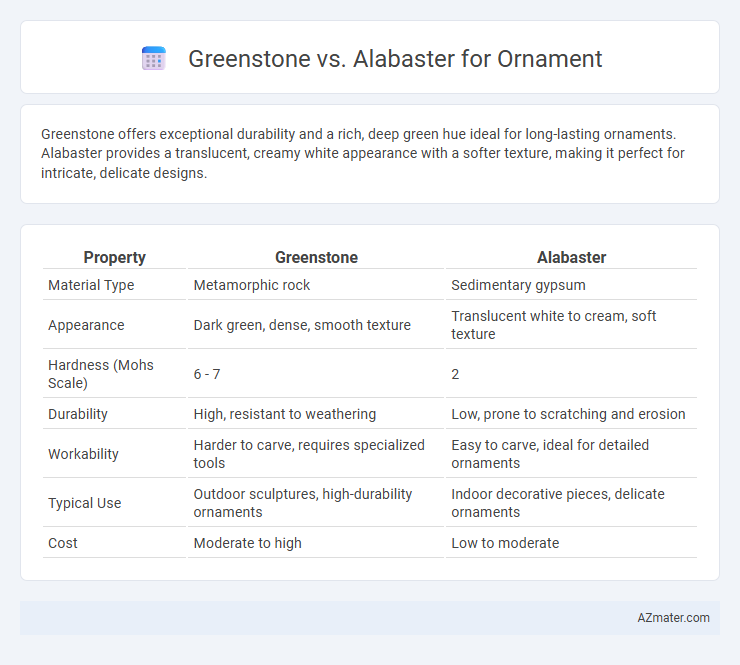
Greenstone offers exceptional durability and a rich, deep green hue ideal for long-lasting ornaments. Alabaster provides a translucent, creamy white appearance with a softer texture, making it perfect for intricate, delicate designs.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Greenstone | Alabaster |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Metamorphic rock | Sedimentary gypsum |
| Appearance | Dark green, dense, smooth texture | Translucent white to cream, soft texture |
| Hardness (Mohs Scale) | 6 - 7 | 2 |
| Durability | High, resistant to weathering | Low, prone to scratching and erosion |
| Workability | Harder to carve, requires specialized tools | Easy to carve, ideal for detailed ornaments |
| Typical Use | Outdoor sculptures, high-durability ornaments | Indoor decorative pieces, delicate ornaments |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
Introduction to Greenstone and Alabaster
Greenstone, a durable and dense metamorphic rock with a distinct green hue, is prized for its toughness and ability to be finely carved, making it ideal for intricate ornaments. Alabaster, a soft, translucent mineral often white or cream-colored, is favored for its smooth texture and ability to diffuse light, creating elegant and delicate decorative pieces. Both materials hold significant cultural and artistic value, but Greenstone's hardness contrasts with alabaster's softness, influencing their use in ornamental craftsmanship.
Origin and Formation of Greenstone
Greenstone, primarily formed through the metamorphism of basaltic rocks in ancient volcanic arcs, originates from regions such as the Canadian Shield and parts of New Zealand, making it prized for its durability and rich green hues in ornamental use. Alabaster, a softer, sedimentary gypsum or calcite mineral, is often quarried in areas like Italy, Egypt, and the United States, valued for its creamy, translucent appearance. The distinct geological formation of greenstone results in a tougher and more resilient material compared to alabaster's more delicate and easily carved texture.
Origin and Formation of Alabaster
Alabaster is a translucent, fine-grained form of gypsum or calcite primarily formed through the evaporation of mineral-rich waters in sedimentary basins, prevalent in regions like Egypt and Italy. Unlike greenstone, which is an igneous rock commonly formed under high-pressure conditions within the Earth's crust, alabaster's sedimentary origin contributes to its smooth texture and ease of carving, making it highly favored for ornamental work. The gentle formation process of alabaster results in its characteristic soft, warm tones, contrasting with the dense, often darker hues of greenstone used in jewelry and sculptures.
Physical Characteristics Comparison
Greenstone exhibits a dense, fine-grained texture with a predominantly dark green hue and subtle veining, making it highly durable and suitable for intricate ornament designs. Alabaster features a softer, translucent quality with a creamy white to pale yellow coloration, characterized by its fine grain and ease of carving but lower durability compared to Greenstone. The physical hardness and resistance to weathering make Greenstone ideal for long-lasting outdoor ornaments, while Alabaster's delicate nature suits detailed indoor decorative pieces.
Color and Aesthetic Appeal
Greenstone exhibits a rich, earthy green hue that evokes natural serenity, making it highly desirable for ornamental carvings and jewelry. Alabaster, with its creamy white to translucent appearance, offers a smooth, elegant aesthetic that enhances light diffusion and softens interior decor. The distinct color contrast between Greenstone's vibrant green and Alabaster's subtle tones allows artisans to select based on desired visual impact and complementary design schemes.
Durability and Maintenance
Greenstone offers superior durability for ornaments due to its dense composition and resistance to chipping, making it ideal for long-lasting decorative pieces. Alabaster, while prized for its smooth texture and translucent beauty, is softer and more susceptible to scratches and discoloration from moisture exposure. Maintenance of greenstone ornaments is minimal, requiring only occasional polishing, whereas alabaster demands careful cleaning with non-abrasive materials and protection from prolonged water contact to preserve its appearance.
Ease of Carving and Artistic Flexibility
Greenstone offers moderate ease of carving due to its fine-grained texture, providing artists with durable material that holds intricate details well. Alabaster is notably softer and easier to carve, allowing for smoother, more delicate shapes and faster work, enhancing artistic flexibility. The choice between these stones depends on the desired balance between carving detail precision in greenstone and the versatile softness in alabaster.
Popular Uses in Ornamentation
Greenstone is widely favored in ornamentation for its durable texture and rich green hues, commonly used in intricate carvings, jewelry, and traditional Maori taonga, symbolizing strength and prosperity. Alabaster, prized for its smooth, translucent appearance, is popular in sculptural art, decorative vases, and inlays, lending a soft, luminous quality to ornamental designs. Both materials hold cultural significance and are selected for their aesthetic appeal and ease of carving, particularly in bespoke and heritage-inspired ornaments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Greenstone and alabaster differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability; greenstone, a durable and naturally abundant metamorphic rock, tends to have a lower carbon footprint due to minimal processing requirements. Alabaster, a soft, fine-grained mineral, often involves intensive quarrying and chemical stabilization, increasing ecological disruption and carbon emissions. Choosing greenstone for ornamental purposes promotes longevity and reduces resource depletion, supporting more sustainable environmental practices.
Cost and Market Availability
Greenstone typically commands a higher price due to its rarity and cultural significance, making it a premium choice for ornaments. Alabaster, being more abundant and easier to work with, offers a cost-effective alternative with broader market availability. The preference between greenstone and alabaster often depends on budget constraints and the desired aesthetic or symbolic value for ornamental pieces.
Infographic: Greenstone vs Alabaster for Ornament
 azmater.com
azmater.com