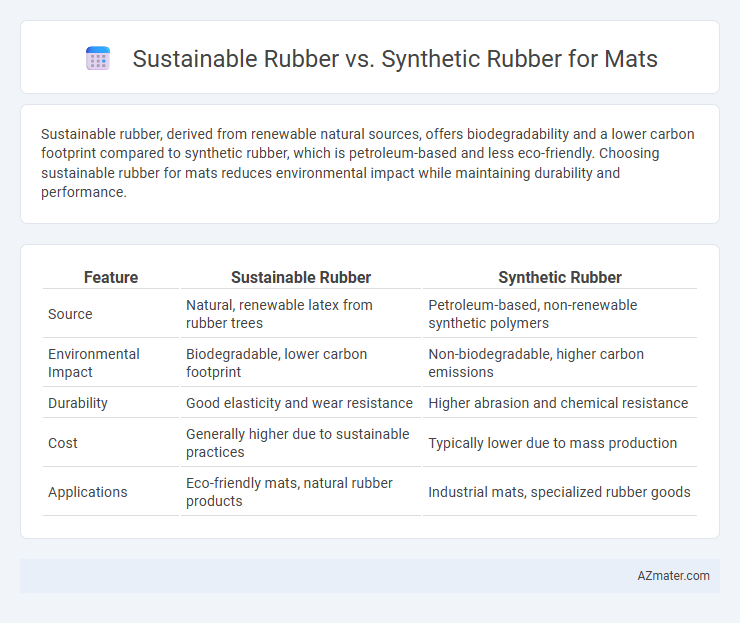
Sustainable rubber, derived from renewable natural sources, offers biodegradability and a lower carbon footprint compared to synthetic rubber, which is petroleum-based and less eco-friendly. Choosing sustainable rubber for mats reduces environmental impact while maintaining durability and performance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sustainable Rubber | Synthetic Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural, renewable latex from rubber trees | Petroleum-based, non-renewable synthetic polymers |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, lower carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, higher carbon emissions |
| Durability | Good elasticity and wear resistance | Higher abrasion and chemical resistance |
| Cost | Generally higher due to sustainable practices | Typically lower due to mass production |
| Applications | Eco-friendly mats, natural rubber products | Industrial mats, specialized rubber goods |
Introduction to Rubber Mats: Sustainability Matters
Sustainable rubber mats offer an eco-friendly alternative to synthetic rubber mats by utilizing natural, biodegradable latex sourced from rubber trees, reducing carbon footprint and environmental impact. Synthetic rubber mats, derived from petroleum-based polymers, provide durability but contribute to non-renewable resource depletion and increased pollution. Prioritizing sustainable rubber mats supports circular economy practices and promotes responsible material sourcing in everyday products.
What Is Sustainable Rubber?
Sustainable rubber is natural rubber derived from rubber trees cultivated using eco-friendly practices that promote biodiversity, reduce deforestation, and minimize chemical usage. This type of rubber emphasizes renewable resources and carbon sequestration, making it an environmentally responsible alternative to conventional synthetic rubber derived from petroleum. Sustainable rubber mats offer durability and flexibility while reducing the ecological footprint associated with synthetic rubber production.
Understanding Synthetic Rubber: Composition and Impact
Synthetic rubber, primarily derived from petrochemicals such as styrene and butadiene, offers consistent elasticity and durability ideal for mat production. Its manufacturing process involves polymerization, which enables customization of physical properties but relies heavily on non-renewable fossil fuels, contributing to environmental concerns. The impact of synthetic rubber includes high carbon emissions and limited biodegradability, prompting increased interest in sustainable alternatives that reduce ecological footprint.
Environmental Impact: Sustainable vs Synthetic Rubber
Sustainable rubber, derived from natural latex sources like Hevea brasiliensis trees, offers a lower carbon footprint and enhanced biodegradability compared to synthetic rubber, which is petroleum-based and contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions. The production of sustainable rubber supports carbon sequestration while reducing dependence on fossil fuels, whereas synthetic rubber manufacturing involves energy-intensive processes and generates non-biodegradable waste. Utilizing sustainable rubber for mats promotes environmental conservation through renewable resources and reduced ecological harm, aligning with eco-friendly product development goals.
Durability and Performance Comparison
Sustainable rubber, derived from natural sources like Hevea brasiliensis, offers superior elasticity and resilience compared to synthetic rubber, enhancing mat durability in dynamic environments. Synthetic rubber, typically made from petroleum-based polymers such as styrene-butadiene, provides consistent resistance to abrasion and chemical exposure but may degrade faster under UV light and extreme temperatures. Performance evaluations show sustainable rubber mats excel in tensile strength and eco-friendly decomposition, while synthetic mats offer stable mechanical properties and cost-effective production for high-traffic applications.
Health & Safety Considerations for Both Rubber Types
Sustainable rubber, often natural rubber sourced from Hevea brasiliensis trees, offers fewer chemical additives, reducing potential skin irritation and allergic reactions compared to synthetic rubber derived from petrochemicals. Synthetic rubber mats, such as those made from styrene-butadiene or nitrile, may emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during manufacturing and use, posing respiratory risks in poorly ventilated areas. Both rubber types require thorough testing for toxicity, flammability, and durability to ensure user safety, but sustainable rubber's biodegradability offers environmental health benefits not present in synthetic alternatives.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Long-Term Value
Sustainable rubber mats typically require a higher initial investment due to eco-friendly sourcing and processing methods, but they offer long-term value through biodegradability and reduced environmental impact. Synthetic rubber mats often have lower upfront costs and consistent material properties, yet they may involve higher lifecycle expenses linked to disposal and less sustainable manufacturing. Evaluating total cost of ownership favors sustainable rubber when factoring in regulatory compliance, brand reputation, and end-of-life environmental benefits.
Applications: Where Each Rubber Type Excels
Sustainable rubber excels in eco-friendly applications such as yoga mats, automotive seals, and footwear soles where biodegradability and reduced environmental impact are crucial. Synthetic rubber dominates in industrial mats, heavy-duty anti-fatigue mats, and medical mats due to its superior resistance to chemicals, abrasion, and extreme temperatures. Each rubber type's unique properties determine optimal use, with sustainable rubber favored for green products and synthetic rubber preferred for durability and performance-intensive environments.
End-of-Life: Recycling and Decomposition
Sustainable rubber mats, derived from natural latex, offer superior biodegradability and can decompose within 5 to 10 years in composting conditions, reducing landfill impact compared to synthetic rubber which may take over 50 years to break down. Natural rubber recycling involves devulcanization processes that allow material reuse, whereas synthetic rubber, made from petroleum-based polymers, faces complex recycling challenges due to chemical stability and mixed polymer compositions. Choosing sustainable rubber mats supports circular economy initiatives by promoting easier end-of-life material recovery and minimizing environmental pollution.
Making an Informed Choice: Sustainable or Synthetic Rubber Mats?
Choosing between sustainable rubber and synthetic rubber mats involves evaluating environmental impact, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Sustainable rubber, sourced from natural latex trees, offers biodegradability and reduced carbon footprint, making it eco-friendly, while synthetic rubber, derived from petrochemicals, provides superior resistance to wear and chemicals but contributes to pollution. An informed choice balances the need for longevity and performance with commitment to environmental sustainability, considering factors such as product lifecycle, recyclability, and manufacturing processes.
Infographic: Sustainable rubber vs Synthetic rubber for Mat
 azmater.com
azmater.com