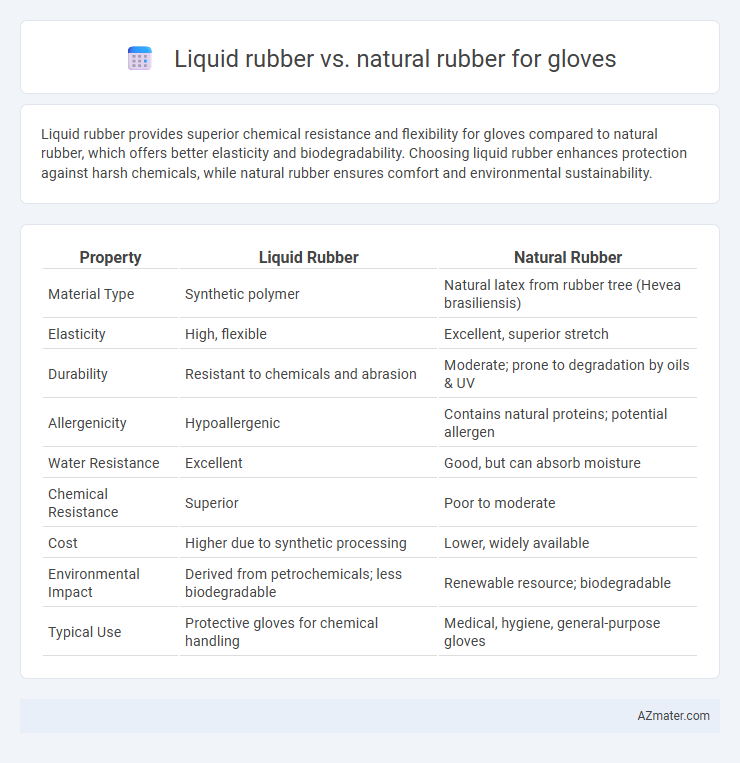
Liquid rubber provides superior chemical resistance and flexibility for gloves compared to natural rubber, which offers better elasticity and biodegradability. Choosing liquid rubber enhances protection against harsh chemicals, while natural rubber ensures comfort and environmental sustainability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Liquid Rubber | Natural Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic polymer | Natural latex from rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis) |
| Elasticity | High, flexible | Excellent, superior stretch |
| Durability | Resistant to chemicals and abrasion | Moderate; prone to degradation by oils & UV |
| Allergenicity | Hypoallergenic | Contains natural proteins; potential allergen |
| Water Resistance | Excellent | Good, but can absorb moisture |
| Chemical Resistance | Superior | Poor to moderate |
| Cost | Higher due to synthetic processing | Lower, widely available |
| Environmental Impact | Derived from petrochemicals; less biodegradable | Renewable resource; biodegradable |
| Typical Use | Protective gloves for chemical handling | Medical, hygiene, general-purpose gloves |
Introduction to Liquid Rubber and Natural Rubber Gloves
Liquid rubber gloves are made from a synthetic elastomer offering superior chemical resistance and durability, ideal for industrial and medical applications. Natural rubber gloves, derived from latex sap of rubber trees, provide excellent elasticity, comfort, and tactile sensitivity, making them preferred for medical and laboratory use. The choice between liquid rubber and natural rubber gloves depends on specific needs such as allergen concerns, flexibility, and resistance to chemicals or punctures.
Composition and Material Differences
Liquid rubber gloves are primarily made from synthetic polymers such as nitrile or liquid latex, featuring a uniform and customizable thickness that enhances durability and chemical resistance. Natural rubber gloves, derived from latex harvested from rubber trees, contain proteins that can cause allergic reactions but offer excellent flexibility and tactile sensitivity. The synthetic composition of liquid rubber provides superior resistance to oils, solvents, and punctures, while natural rubber maintains greater elasticity and biodegradability.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Liquid rubber gloves are produced using a dipping process where liquid latex or synthetic rubber is poured onto hand-shaped molds and cured, enabling precise control over thickness and uniformity. Natural rubber gloves typically involve latex harvested from rubber trees, undergoing coagulation, washing, and vulcanization, which can be more variable and labor-intensive. The liquid rubber manufacturing process allows for faster production cycles and greater flexibility in compound formulation compared to traditional natural rubber methods.
Physical Properties: Strength, Flexibility, and Comfort
Liquid rubber gloves offer superior strength and durability due to their enhanced polymer crosslinking, providing excellent resistance to tears and punctures compared to natural rubber gloves. Natural rubber gloves excel in flexibility and comfort, thanks to their inherent elasticity and breathability, which allow for better fit and tactile sensitivity. While liquid rubber gloves prioritize robustness for heavy-duty tasks, natural rubber gloves are preferred for prolonged wear due to their softness and reduced likelihood of causing skin irritation.
Chemical Resistance and Protection Levels
Liquid rubber gloves offer superior chemical resistance compared to natural rubber gloves due to their composition, which provides enhanced protection against acids, solvents, and oils. Natural rubber gloves, made from latex, exhibit excellent elasticity and comfort but are less effective against harsh chemicals and may degrade faster upon exposure. Choosing liquid rubber gloves ensures higher protection levels in industrial environments handling aggressive substances.
Allergic Reactions and Skin Sensitivity
Liquid rubber gloves, typically made from synthetic materials such as nitrile or neoprene, offer a hypoallergenic alternative to natural rubber gloves, reducing the risk of allergic reactions and skin sensitivity commonly associated with latex proteins. Natural rubber gloves, derived from latex, can trigger contact dermatitis and Type I hypersensitivity in individuals sensitive to latex allergens. Choosing liquid rubber gloves is beneficial for healthcare and industrial environments where minimizing allergic response and enhancing skin compatibility are critical.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Liquid rubber gloves typically offer greater environmental sustainability due to their potential for lower chemical additives and easier recycling processes compared to natural rubber gloves, which rely on latex harvested from rubber trees. Natural rubber gloves often involve deforestation and habitat disruption, raising concerns about biodiversity loss, whereas liquid rubber alternatives can be produced from synthetic or bio-based polymers with reduced ecological footprints. The biodegradability of natural rubber remains an advantage, but advancements in liquid rubber formulations are increasingly closing this gap while minimizing environmental impact during production and disposal.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Liquid rubber gloves generally offer a more cost-effective solution due to lower raw material expenses and simpler manufacturing processes compared to natural rubber gloves. The availability of liquid rubber, primarily derived from synthetic polymers, is less susceptible to seasonal fluctuations and geographical constraints that often impact natural rubber supplies. These factors contribute to more stable pricing and consistent stock levels for liquid rubber gloves in the global market.
Common Applications and Industry Preferences
Liquid rubber gloves offer superior chemical resistance and flexibility, making them ideal for industries such as automotive, electronics, and chemical manufacturing where exposure to oils and solvents is frequent. Natural rubber gloves excel in medical and food processing applications due to their excellent elasticity, comfort, and biodegradability, favored for tasks requiring tactile sensitivity. Industry preferences often hinge on specific protection needs and environmental considerations, with liquid rubber preferred for heavy-duty industrial use and natural rubber dominating healthcare and food safety sectors.
Choosing the Right Glove Material for Your Needs
Liquid rubber gloves offer excellent chemical resistance and flexibility, making them ideal for industrial or laboratory use where exposure to harsh substances is common. Natural rubber gloves provide superior elasticity and comfort, suitable for medical or everyday tasks requiring dexterity and tactile sensitivity. Selecting the right glove material depends on the specific application, exposure risk, and required durability to ensure optimal protection and performance.
Infographic: Liquid rubber vs Natural rubber for Glove
 azmater.com
azmater.com