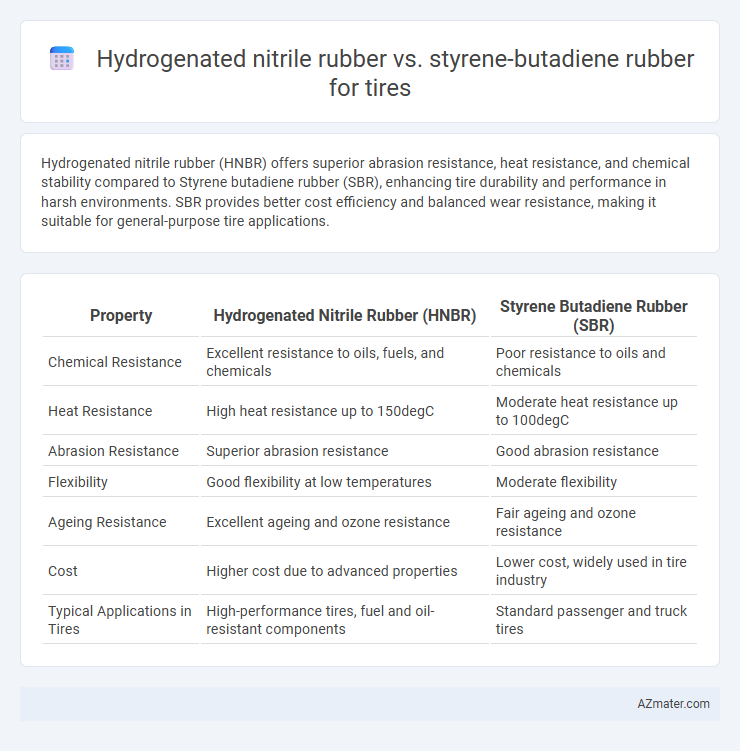
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior abrasion resistance, heat resistance, and chemical stability compared to Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), enhancing tire durability and performance in harsh environments. SBR provides better cost efficiency and balanced wear resistance, making it suitable for general-purpose tire applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) | Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals | Poor resistance to oils and chemicals |
| Heat Resistance | High heat resistance up to 150degC | Moderate heat resistance up to 100degC |
| Abrasion Resistance | Superior abrasion resistance | Good abrasion resistance |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility at low temperatures | Moderate flexibility |
| Ageing Resistance | Excellent ageing and ozone resistance | Fair ageing and ozone resistance |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced properties | Lower cost, widely used in tire industry |
| Typical Applications in Tires | High-performance tires, fuel and oil-resistant components | Standard passenger and truck tires |
Introduction to Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) and Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR)
Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) is a high-performance elastomer known for exceptional resistance to heat, oil, and chemicals, making it ideal for demanding tire applications requiring durability and longevity. Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) is a widely used synthetic rubber in tire manufacturing, recognized for its good abrasion resistance, aging stability, and cost-effectiveness in providing balanced performance in passenger and commercial vehicle tires. The key difference lies in HNBR's superior thermal and chemical resistance compared to SBR's more economical and versatile properties tailored for mass production.
Key Properties of HNBR and SBR in Tire Manufacturing
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior heat resistance, oil resistance, and mechanical strength compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), making it ideal for high-performance tire components exposed to harsh conditions. SBR provides excellent abrasion resistance, good aging stability, and cost-effective manufacturing, commonly used in tread compounds for enhanced grip and wear life. The enhanced thermal stability and chemical resistance of HNBR contribute to longer tire durability and performance, while SBR supports flexibility and traction under typical driving conditions.
Comparative Durability: HNBR vs SBR Tires
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to heat, oil, and abrasion compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), making HNBR tires significantly more durable under harsh driving conditions. SBR tires, while offering good wear resistance and traction on wet surfaces, typically degrade faster when exposed to high temperatures and oil contaminants. The enhanced chemical stability of HNBR contributes to longer tire life, reduced cracking, and improved performance in demanding environments.
Heat and Chemical Resistance: Performance Under Extreme Conditions
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior heat and chemical resistance compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), maintaining performance at temperatures up to 150degC, while SBR typically withstands temperatures only up to 100degC. HNBR's enhanced resistance to oils, fuels, and oxidative environments makes it ideal for tires operating under extreme heat and exposure to automotive fluids. SBR offers good abrasion resistance but lacks the chemical stability and heat endurance required for high-performance or heavy-duty tire applications.
Rolling Resistance and Fuel Efficiency Implications
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior rolling resistance characteristics compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) due to its enhanced thermal stability and lower hysteresis losses, resulting in improved fuel efficiency for vehicles. The reduced energy dissipation in HNBR compounds directly correlates to decreased rolling resistance, which can significantly lower fuel consumption and CO2 emissions over the tire's lifespan. In contrast, SBR, while cost-effective and widely used, exhibits higher rolling resistance that diminishes its contribution to fuel economy and overall vehicle performance.
Tread Wear and Longevity Analysis
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior tread wear resistance and enhanced longevity compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) due to its exceptional abrasion resistance and thermal stability. HNBR's molecular structure allows it to endure higher temperatures and oxidative environments, significantly reducing tread degradation over time. In contrast, SBR generally shows faster wear rates under similar conditions, resulting in shorter tire lifespan and more frequent replacement cycles.
Cost Considerations: HNBR vs SBR in Tire Production
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) incurs higher initial costs compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) due to its complex hydrogenation process and superior chemical resistance. SBR remains the cost-effective choice for tire production, balancing performance with affordable raw material expenses and large-scale availability. Manufacturers favor SBR in budget-sensitive applications while opting for HNBR when enhanced durability and heat resistance justify the increased investment.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Factors
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to ozone, heat, and chemicals compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), contributing to longer tire lifespans and reduced environmental waste. While SBR is widely used due to cost-effectiveness, its production relies heavily on petroleum-based feedstocks, resulting in higher carbon emissions and lower sustainability. HNBR's enhanced durability supports tire longevity and resource efficiency, making it a more sustainable choice in tire manufacturing with reduced ecological impact over the product lifecycle.
Application Suitability: Passenger Cars vs Commercial Vehicles
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior heat, oil, and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for commercial vehicle tires that demand high durability under heavy loads and harsh conditions. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) provides excellent wear resistance and good aging properties, which suits passenger car tires designed for regular road use and balanced performance. HNBR's enhanced mechanical strength benefits commercial vehicles, while SBR's cost-effectiveness and adequate performance align well with passenger car tire requirements.
Final Verdict: Choosing Between HNBR and SBR for Tires
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior heat resistance, oil resistance, and durability compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), making it ideal for high-performance tire applications exposed to extreme conditions. SBR remains cost-effective with good abrasion resistance and flexibility, suitable for standard passenger tire tread compounds. Selecting HNBR ensures enhanced longevity and performance in demanding environments, while SBR provides reliable performance at a lower cost for conventional tire uses.
Infographic: Hydrogenated nitrile rubber vs Styrene butadiene rubber for Tire
 azmater.com
azmater.com