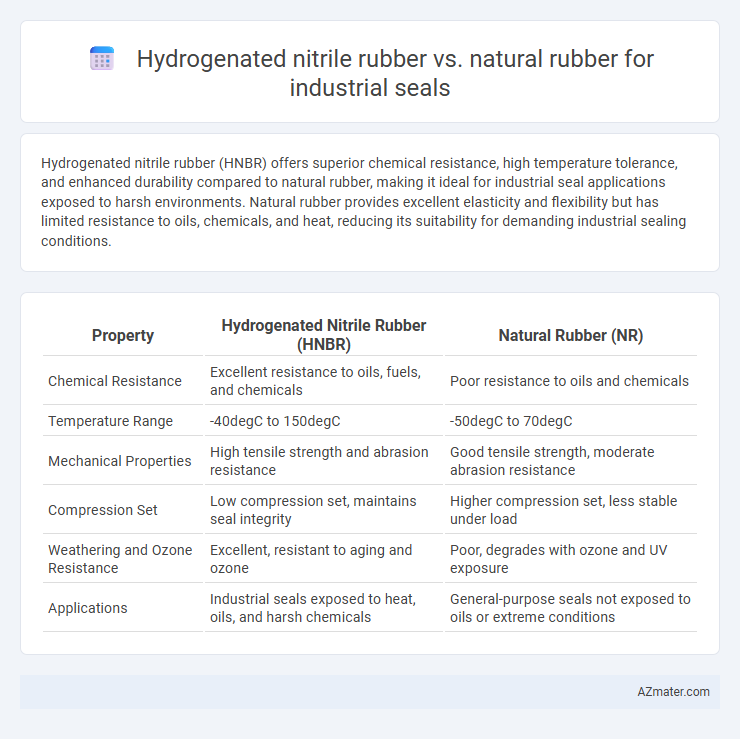
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical resistance, high temperature tolerance, and enhanced durability compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for industrial seal applications exposed to harsh environments. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity and flexibility but has limited resistance to oils, chemicals, and heat, reducing its suitability for demanding industrial sealing conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) | Natural Rubber (NR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals | Poor resistance to oils and chemicals |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 150degC | -50degC to 70degC |
| Mechanical Properties | High tensile strength and abrasion resistance | Good tensile strength, moderate abrasion resistance |
| Compression Set | Low compression set, maintains seal integrity | Higher compression set, less stable under load |
| Weathering and Ozone Resistance | Excellent, resistant to aging and ozone | Poor, degrades with ozone and UV exposure |
| Applications | Industrial seals exposed to heat, oils, and harsh chemicals | General-purpose seals not exposed to oils or extreme conditions |
Introduction to Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber and Natural Rubber
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers enhanced resistance to heat, oil, and chemicals compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for demanding industrial sealing applications. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity and mechanical properties but is less effective in high-temperature and chemical environments. Selecting between HNBR and natural rubber depends on specific industrial requirements such as temperature range, chemical exposure, and durability needs.
Chemical Structure and Properties Comparison
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) features a saturated polymer backbone with nitrile groups, offering superior resistance to heat, oil, and chemicals compared to natural rubber, which consists of cis-1,4-polyisoprene with unsaturated bonds prone to oxidation and degradation. HNBR's enhanced chemical stability and mechanical strength enable it to withstand harsh industrial environments, while natural rubber provides excellent elasticity and abrasion resistance but suffers from limited chemical and temperature resistance. The presence of hydrogenation in HNBR significantly reduces unsaturation, improving aging performance and ozone resistance crucial for industrial sealing applications.
Resistance to Oils, Fuels, and Chemicals
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for demanding industrial seal applications exposed to harsh substances. Its enhanced molecular structure provides excellent swelling resistance and durability against petroleum-based fluids, hydraulic oils, and aggressive chemicals. Natural rubber, while flexible and resilient, tends to degrade and swell when exposed to hydrocarbons and many chemical agents, limiting its effectiveness in industrial environments requiring robust chemical resistance.
Temperature Tolerance and Thermal Stability
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) outperforms natural rubber in temperature tolerance and thermal stability, operating effectively in temperatures ranging from -40degC to 150degC, compared to natural rubber's limit of approximately -50degC to 70degC. HNBR exhibits superior resistance to heat aging and oxidation, maintaining mechanical properties in harsh industrial environments, while natural rubber tends to degrade faster under prolonged thermal exposure. This enhanced thermal stability makes HNBR the preferred choice for industrial seals in high-temperature applications requiring durability and reliability.
Mechanical Strength and Durability in Sealing Applications
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior mechanical strength and enhanced resistance to abrasion, heat, and chemicals compared to natural rubber, making it highly effective in demanding industrial sealing applications. Its increased tensile strength and excellent aging properties ensure long-lasting durability under high pressure and temperature conditions, reducing the frequency of seal replacements. Natural rubber, while flexible and cost-effective, typically offers lower resistance to oils and chemicals, resulting in faster degradation and limited durability in harsh industrial environments.
Aging, Ozone, and Weather Resistance
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior aging, ozone, and weather resistance compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for demanding industrial seal applications exposed to harsh environments. HNBR maintains flexibility and mechanical properties after prolonged exposure to heat, oil, and oxidative conditions, while natural rubber tends to degrade, crack, and lose elasticity under similar stressors. This enhanced durability of HNBR translates into longer service life and reduced maintenance costs for seals in industries such as automotive, oil and gas, and chemical processing.
Cost Effectiveness and Economic Considerations
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical resistance, heat tolerance, and durability compared to natural rubber, making it cost-effective for industrial seals requiring long service life and reduced maintenance. Although HNBR has a higher initial price than natural rubber, its extended lifespan and lower replacement frequency result in better overall economic value. Natural rubber remains a budget-friendly option for low-demand sealing applications but may incur higher lifecycle costs due to wear and environmental susceptibility.
Common Industrial Seal Applications
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) excels in industrial seal applications requiring superior resistance to heat, oil, and chemical exposure, making it ideal for automotive, aerospace, and oilfield equipment seals. Natural rubber offers excellent elasticity and abrasion resistance, frequently used in water and air seals, conveyor belts, and agricultural machinery where flexibility is prioritized over chemical resistance. The choice between HNBR and natural rubber depends on the operational environment, with HNBR preferred for harsh chemical and temperature conditions, while natural rubber suits dynamic sealing applications with moderate exposure.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to oils, heat, and chemicals, extending seal life and reducing waste compared to natural rubber, which biodegrades more readily but has limited chemical resistance leading to more frequent replacements. Natural rubber is derived from renewable sources and is biodegradable, presenting a lower environmental footprint during disposal, whereas HNBR, synthesized from petroleum-based materials, poses challenges in recyclability and environmental degradation. Industrial seals made from HNBR contribute to reduced resource consumption through durability but require advanced recycling processes to mitigate environmental impact, contrasting with the simpler disposal of natural rubber seals.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Industrial Seals
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to heat, oils, and chemicals, making it ideal for industrial seals exposed to harsh environments and high temperatures. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity and abrasion resistance but tends to degrade quickly when exposed to oils, ozone, and extreme temperatures. Selecting the right rubber for industrial seals depends on operational conditions, with HNBR preferred for durability in aggressive media and natural rubber suited for applications requiring flexibility and wear resistance.
Infographic: Hydrogenated nitrile rubber vs Natural rubber for Industrial seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com