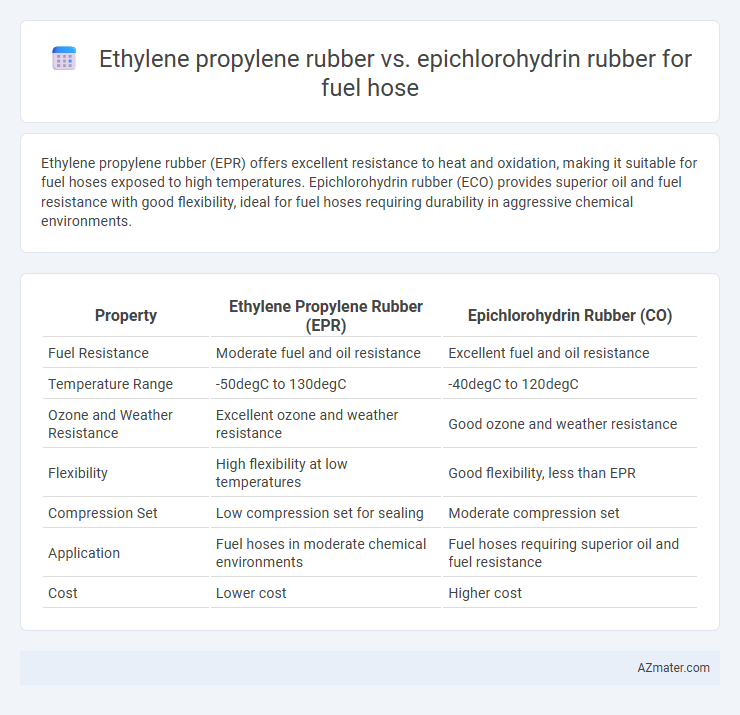
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers excellent resistance to heat and oxidation, making it suitable for fuel hoses exposed to high temperatures. Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) provides superior oil and fuel resistance with good flexibility, ideal for fuel hoses requiring durability in aggressive chemical environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR) | Epichlorohydrin Rubber (CO) |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Resistance | Moderate fuel and oil resistance | Excellent fuel and oil resistance |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 130degC | -40degC to 120degC |
| Ozone and Weather Resistance | Excellent ozone and weather resistance | Good ozone and weather resistance |
| Flexibility | High flexibility at low temperatures | Good flexibility, less than EPR |
| Compression Set | Low compression set for sealing | Moderate compression set |
| Application | Fuel hoses in moderate chemical environments | Fuel hoses requiring superior oil and fuel resistance |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Fuel Hose Materials
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) and epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) are widely used materials in fuel hose manufacturing due to their excellent chemical resistance and flexibility. EPR offers superior resistance to ozone, heat, and aging, making it ideal for long-term fuel exposure, while epichlorohydrin rubber provides excellent resistance to fuels, oils, and ozone with improved low-temperature flexibility. Selection between EPR and ECO depends on specific fuel types, temperature ranges, and environmental conditions to ensure optimal hose durability and performance.
Overview of Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR/EPM/EPDM)
Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR/EPM/EPDM) offers exceptional resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, making it highly suitable for fuel hose applications requiring durability and flexibility. Its excellent chemical resistance to a wide range of fuels and oils ensures long-lasting performance in automotive and industrial fuel delivery systems. Compared to Epichlorohydrin rubber, EPR exhibits superior elasticity and aging resistance, contributing to reduced maintenance and enhanced safety in fuel hose installations.
Overview of Epichlorohydrin Rubber (ECO)
Epichlorohydrin Rubber (ECO) offers exceptional resistance to fuels, oils, and ozone, making it ideal for fuel hose applications requiring durability under harsh chemical exposure. ECO exhibits superior low-temperature flexibility compared to Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR) and maintains excellent physical properties such as tensile strength and elongation in extreme environments. Its unique molecular structure provides enhanced fuel permeability resistance and reliable performance in automotive and industrial fuel delivery systems.
Chemical Compatibility with Fuels
Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR) offers excellent chemical resistance to a wide range of fuels, including gasoline, diesel, and alcohol-blended fuels, making it a preferred choice for fuel hoses in automotive and industrial applications. Epichlorohydrin Rubber (ECO) provides superior resistance to polar solvents, oils, and some aggressive fuels, offering enhanced durability against fuel additives and oxidative degradation. When selecting a fuel hose material, EPR excels in general hydrocarbon compatibility, while ECO is advantageous in environments with fuel formulations containing polar compounds or requiring increased fuel resistance.
Temperature Resistance Comparison
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers superior temperature resistance for fuel hoses, typically withstanding continuous exposure to temperatures ranging from -50degC to 130degC, making it suitable for high-temperature fuel systems. Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) generally tolerates temperatures between -40degC and 120degC but exhibits enhanced resistance to ozone and fuel additives, though with slightly lower heat endurance than EPR. For applications demanding higher thermal stability and prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures, EPR remains the preferred choice in fuel hose manufacturing.
Mechanical Properties and Durability
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) exhibits excellent mechanical properties such as high tensile strength, superior elasticity, and strong resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, making it highly durable for fuel hose applications. Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) is valued for its outstanding oil resistance, good mechanical strength, and resistance to fuel and chemicals, but typically shows moderate flexibility compared to EPR. While EPR offers better overall durability under harsh environmental conditions, ECO provides enhanced fuel resistance, making both suitable depending on specific mechanical and chemical exposure requirements.
Aging and Ozone Resistance
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers superior ozone and aging resistance compared to epichlorohydrin rubber, making it more durable for fuel hose applications exposed to environmental stressors. EPR's saturated hydrocarbon structure resists oxidative degradation and cracking, extending the hose's service life under heat and ozone exposure. In contrast, epichlorohydrin rubber, while resistant to fuels and oils, exhibits moderate ozone and aging resistance, which may limit its longevity in harsh outdoor conditions.
Fuel Permeation and Barrier Performance
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers moderate fuel permeation resistance but is generally less effective as a barrier compared to epichlorohydrin rubber (CO) in fuel hose applications. Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits superior barrier performance and lower fuel permeation rates due to its inherent chemical structure, making it ideal for fuel hoses requiring enhanced resistance to aggressive fuels and vapors. Consequently, epichlorohydrin rubber is preferred in environments where stringent fuel permeation standards and durability against fuel degradation are critical.
Cost and Availability Factors
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) generally offers lower cost and wider availability compared to epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO), making it a more economical choice for fuel hose applications. ECO provides superior resistance to fuel permeation and oil but tends to be pricier and less readily available due to its specialized production processes. Manufacturers often select EPR for cost-sensitive projects with standard fuel resistance requirements, while ECO is reserved for demanding environments where enhanced chemical compatibility is critical despite higher expenditures.
Application Recommendations and Industry Standards
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) is preferred for fuel hoses requiring excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, making it suitable for gasoline and diesel applications in automotive and industrial sectors. Epichlorohydrin rubber (CO) offers superior resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, recommended for hoses exposed to aggressive fuels and hydraulic fluids in aviation and heavy machinery industries. Both materials comply with SAE J30 and ISO 3821 standards, but EPR aligns more with general fuel delivery systems while epichlorohydrin meets stringent chemical resistance requirements.
Infographic: Ethylene propylene rubber vs Epichlorohydrin rubber for Fuel hose
 azmater.com
azmater.com