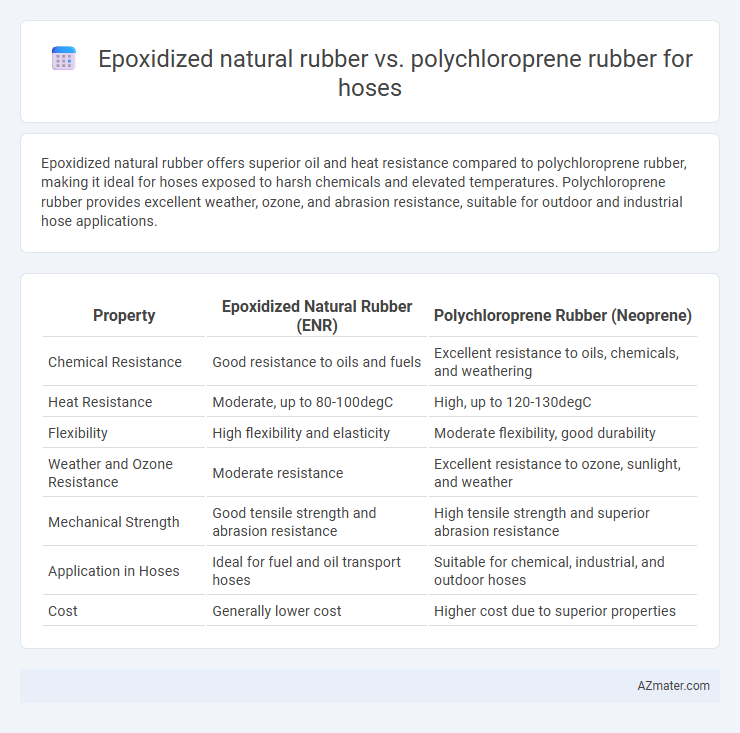
Epoxidized natural rubber offers superior oil and heat resistance compared to polychloroprene rubber, making it ideal for hoses exposed to harsh chemicals and elevated temperatures. Polychloroprene rubber provides excellent weather, ozone, and abrasion resistance, suitable for outdoor and industrial hose applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR) | Polychloroprene Rubber (Neoprene) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils and fuels | Excellent resistance to oils, chemicals, and weathering |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate, up to 80-100degC | High, up to 120-130degC |
| Flexibility | High flexibility and elasticity | Moderate flexibility, good durability |
| Weather and Ozone Resistance | Moderate resistance | Excellent resistance to ozone, sunlight, and weather |
| Mechanical Strength | Good tensile strength and abrasion resistance | High tensile strength and superior abrasion resistance |
| Application in Hoses | Ideal for fuel and oil transport hoses | Suitable for chemical, industrial, and outdoor hoses |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to superior properties |
Introduction to Hose Materials: ENR vs Polychloroprene
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) exhibits enhanced oil resistance and mechanical strength, making it suitable for hoses exposed to harsh environments and chemicals. Polychloroprene rubber, known for its excellent weather, ozone, and abrasion resistance, provides durability and flexibility in industrial hose applications. Hose materials selection between ENR and polychloroprene depends on operational demands such as chemical exposure, temperature range, and mechanical stress.
Chemical Structure and Composition Differences
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) contains oxirane rings introduced into the polyisoprene backbone, enhancing polarity and chemical resistance compared to natural rubber's purely hydrocarbon structure. Polychloroprene rubber (CR), synthesized through polymerization of chloroprene monomers, incorporates chlorine atoms directly into its polymer chain, imparting inherent flame resistance and superior oil resistance. The presence of chlorinated sites in CR leads to distinct thermal and chemical stability profiles, while the epoxide groups in ENR improve adhesive properties and oxygen barrier performance in hose applications.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) exhibits superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to polychloroprene rubber, making it ideal for high-performance hose applications requiring durability under mechanical stress. Polychloroprene rubber offers excellent flexibility, excellent compression set resistance, and good weatherability, but generally falls short of ENR's enhanced elasticity and resilience. ENR's improved mechanical properties stem from its polar epoxy groups, which enhance intermolecular bonding and contribute to greater wear resistance and tensile modulus in hose assemblies.
Resistance to Oils, Chemicals, and Fuels
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) exhibits superior resistance to oils, chemicals, and fuels due to its enhanced polarity and cross-linked structure, making it suitable for applications requiring exposure to aggressive substances. Polychloroprene rubber (Neoprene) offers excellent resistance to oils, moderate chemicals, and fuels, with particularly strong performance against ozone, weathering, and moderate chemical environments. ENR outperforms Polychloroprene in fuel and aromatic hydrocarbon resistance, while Polychloroprene provides better general chemical stability and aging resistance for hose applications.
Heat and Weathering Resistance
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior heat resistance due to its chemical modification, which enhances thermal stability compared to conventional natural rubber. Polychloroprene rubber (Neoprene) exhibits excellent weathering resistance, including ozone, UV, and oxidative degradation, making it highly durable for outdoor hose applications. ENR provides moderate weathering resistance but excels in flexibility and oil resistance, while Polychloroprene balances heat resistance with outstanding environmental durability.
Flexibility and Elasticity Under Pressure
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior flexibility and enhanced elasticity under pressure compared to polychloroprene rubber, making it ideal for hoses requiring significant deformation without losing shape. The polar epoxide groups in ENR improve interaction with filler materials, resulting in better tensile strength and resilience during repeated pressure cycles. Polychloroprene rubber provides moderate elasticity but typically exhibits less flexibility, which can limit hose performance in high-flex or dynamic pressure applications.
Aging and Ozone Resistance
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) exhibits superior aging and ozone resistance compared to polychloroprene rubber, due to the presence of epoxy groups that enhance its resistance to oxidative degradation and ozone attack. Polychloroprene rubber, while inherently ozone resistant because of its saturated backbone, can still experience surface cracking under prolonged exposure. ENR's enhanced durability in harsh environmental conditions makes it particularly advantageous for hose applications requiring long-term reliability.
Processing and Manufacturing Considerations
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior compatibility with polar fillers, enhancing processing efficiency and vulcanization speed, which is beneficial for manufacturing hoses requiring flexibility and oil resistance. Polychloroprene rubber (CR) exhibits excellent resilience and weather resistance but demands precise control of heat and mixing conditions due to its sensitivity to scorch and the need for specific curing agents. Processing ENR typically involves conventional mixing and vulcanization techniques, whereas CR requires specialized handling to maintain its mechanical properties and durability in hose applications.
Cost-Effectiveness and Sustainability
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior sustainability due to its renewable origin and enhanced biodegradability compared to polychloroprene rubber (CR), which is petroleum-based and less eco-friendly. In terms of cost-effectiveness, ENR generally presents lower production costs linked to natural raw materials, while polychloroprene provides better chemical resistance and durability but at a higher manufacturing expense. Choosing between ENR and CR for hoses depends on prioritizing eco-conscious material use with competitive costs or opting for premium performance with increased investment.
Application Suitability: Choosing the Right Rubber for Hoses
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior resistance to oils, chemicals, and weathering, making it ideal for hoses handling fuels, lubricants, and harsh environments. Polychloroprene rubber (Neoprene) provides excellent abrasion resistance, flexibility, and moderate chemical resistance, suitable for general-purpose hoses in air, water, and mild chemical applications. Selecting ENR enhances durability in aggressive media, while Polychloroprene ensures versatility and mechanical strength for standard industrial hose needs.
Infographic: Epoxidized natural rubber vs Polychloroprene rubber for Hose
 azmater.com
azmater.com