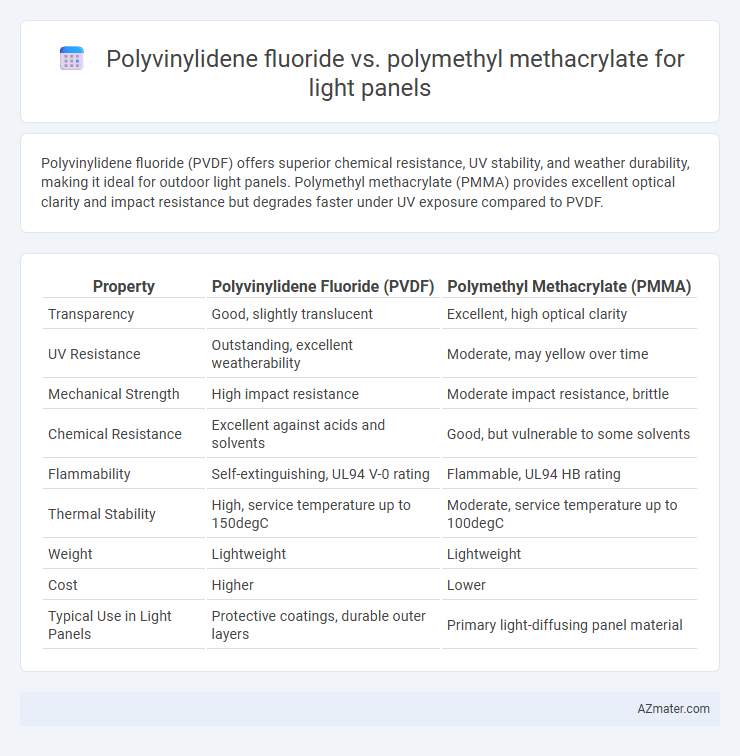
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance, UV stability, and weather durability, making it ideal for outdoor light panels. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) provides excellent optical clarity and impact resistance but degrades faster under UV exposure compared to PVDF.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) | Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) |
|---|---|---|
| Transparency | Good, slightly translucent | Excellent, high optical clarity |
| UV Resistance | Outstanding, excellent weatherability | Moderate, may yellow over time |
| Mechanical Strength | High impact resistance | Moderate impact resistance, brittle |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent against acids and solvents | Good, but vulnerable to some solvents |
| Flammability | Self-extinguishing, UL94 V-0 rating | Flammable, UL94 HB rating |
| Thermal Stability | High, service temperature up to 150degC | Moderate, service temperature up to 100degC |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Typical Use in Light Panels | Protective coatings, durable outer layers | Primary light-diffusing panel material |
Introduction to Light Panels and Material Choice
Light panels require materials with high optical clarity and durability. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and UV stability, making it ideal for outdoor light panels exposed to harsh environments. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) provides excellent transparency and impact resistance, commonly used for indoor applications where light diffusion and aesthetic appeal are crucial.
Overview of Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF)
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) is a highly durable fluoropolymer known for its exceptional chemical resistance, UV stability, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for light panel applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions. PVDF offers superior weathering properties and maintains clarity over time, outperforming polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) in terms of impact resistance and long-term stability. This material's low surface energy also enhances its self-cleaning abilities, reducing maintenance and preserving the optical quality of light panels.
Overview of Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA)
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) is a transparent thermoplastic known for its superior optical clarity, UV resistance, and excellent weatherability, making it ideal for light panels and glazing applications. It offers high light transmittance, typically around 92%, outperforming many plastics including polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) in optical performance. PMMA is also lightweight, impact-resistant, and easy to fabricate, which contributes to its widespread use in architectural and lighting panel industries.
Optical Clarity and Light Transmission Comparison
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance but lower optical clarity compared to Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), which is renowned for its high transparency and excellent light transmission, exceeding 90%. PMMA's light panels provide clearer, sharper visibility due to their minimal light scattering properties, while PVDF panels typically exhibit a slight haze affecting visual performance. For applications prioritizing maximum light transmission and optical clarity, PMMA remains the preferred choice in light panel manufacturing.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior durability and weather resistance compared to Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) for light panels, with excellent resistance to UV radiation, chemical exposure, and extreme temperatures. PVDF coatings maintain color stability and structural integrity over extended outdoor exposure, making them ideal for harsh environments. PMMA, while lightweight and optically clear, tends to yellow and degrade faster under prolonged UV and weather stress.
Chemical Resistance and Stability
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior chemical resistance to acids, bases, and solvents, making it highly stable for use in light panels exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), while offering excellent optical clarity, has lower chemical resistance, especially to strong solvents and UV exposure, leading to potential degradation over time. PVDF's exceptional thermal and weather stability ensures longer-lasting light panels in industrial and outdoor applications compared to PMMA.
Weight and Structural Considerations
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and lightweight properties compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), making it ideal for light panel applications demanding corrosion resistance and durability without added weight. PMMA, while heavier than PVDF, provides excellent clarity and higher impact resistance, but its increased density can affect the overall structural load and installation requirements. Selecting between PVDF and PMMA hinges on balancing the need for lightweight construction versus optical performance and mechanical strength in light panel systems.
Cost Analysis and Economic Factors
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and UV stability, making it more durable but generally more expensive than Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) for light panel applications. PMMA provides a cost-effective solution with excellent optical clarity and ease of fabrication, reducing installation and maintenance expenses over time. Balancing initial material costs against longevity and performance, PVDF may be more economical for long-term projects, while PMMA suits budget-sensitive, short to medium-term uses.
Application Suitability in Light Panels
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior weather resistance and chemical stability, making it highly suitable for outdoor light panels exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) excels in light transmission and optical clarity, ensuring bright and uniform illumination in indoor light panel applications. For long-term durability combined with UV resistance, PVDF is preferred, while PMMA is favored for its lightweight properties and high visual clarity in protected environments.
Conclusion: Choosing the Optimal Material
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) excels in durability, UV resistance, and chemical stability, making it ideal for long-lasting outdoor light panels exposed to harsh environments. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior optical clarity and light transmission, enhancing brightness and color fidelity for indoor or less demanding applications. Selecting the optimal material depends on environmental exposure, desired optical performance, and durability requirements, with PVDF favored for robust protection and PMMA preferred for visual quality.
Infographic: Polyvinylidene fluoride vs Polymethyl methacrylate for Light panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com