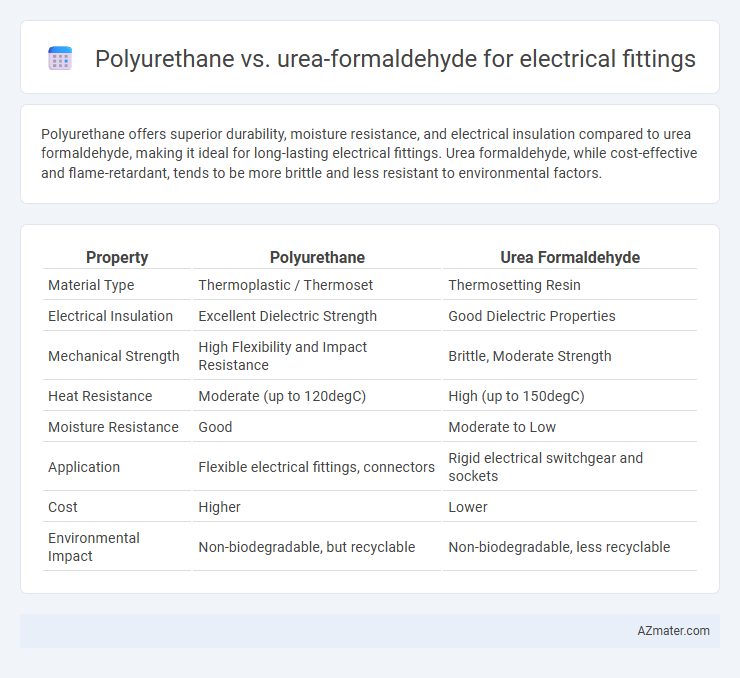
Polyurethane offers superior durability, moisture resistance, and electrical insulation compared to urea formaldehyde, making it ideal for long-lasting electrical fittings. Urea formaldehyde, while cost-effective and flame-retardant, tends to be more brittle and less resistant to environmental factors.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyurethane | Urea Formaldehyde |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic / Thermoset | Thermosetting Resin |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent Dielectric Strength | Good Dielectric Properties |
| Mechanical Strength | High Flexibility and Impact Resistance | Brittle, Moderate Strength |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate (up to 120degC) | High (up to 150degC) |
| Moisture Resistance | Good | Moderate to Low |
| Application | Flexible electrical fittings, connectors | Rigid electrical switchgear and sockets |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, but recyclable | Non-biodegradable, less recyclable |
Introduction: Comparing Polyurethane and Urea Formaldehyde
Polyurethane and urea formaldehyde are widely used materials in electrical fittings due to their insulating and mechanical properties. Polyurethane offers superior flexibility, chemical resistance, and durability, making it ideal for applications requiring impact resistance and moisture protection. Urea formaldehyde provides excellent hardness, high heat resistance, and cost-effectiveness, commonly favored for rigid components with precise dimensional stability.
Material Properties Overview
Polyurethane offers excellent electrical insulation, superior chemical resistance, and high durability, making it ideal for electrical fittings exposed to harsh environments. Urea formaldehyde provides good mechanical strength and high heat resistance but tends to be more brittle and less moisture-resistant compared to polyurethane. The choice between these materials depends on specific application needs, including thermal stability, moisture exposure, and mechanical stress tolerance.
Electrical Insulation Performance
Polyurethane offers superior electrical insulation performance compared to urea formaldehyde due to its high dielectric strength and excellent resistance to moisture and chemicals, making it ideal for durable electrical fittings. Urea formaldehyde provides good insulation properties but tends to be more brittle and less resistant to thermal and mechanical stresses, which can compromise long-term reliability. The enhanced flexibility and stability of polyurethane ensure safer and more consistent insulation in demanding electrical applications.
Thermal Resistance and Stability
Polyurethane offers superior thermal resistance withstanding continuous temperatures up to 120degC, making it ideal for electrical fittings exposed to heat. In contrast, urea formaldehyde typically degrades at lower temperatures around 80-100degC, reducing its thermal stability under high-heat conditions. The enhanced thermal stability of polyurethane ensures longer-lasting insulation and durability in electrical components subjected to extreme thermal environments.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polyurethane offers superior mechanical strength and high impact resistance compared to urea formaldehyde, making it ideal for electrical fittings subjected to physical stress. Its excellent durability resists moisture, chemicals, and temperature variations, ensuring long-term performance in harsh environments. Urea formaldehyde, while cost-effective, tends to be more brittle and less resistant to environmental degradation, limiting its use in demanding electrical applications.
Chemical and Moisture Resistance
Polyurethane offers superior chemical resistance compared to urea formaldehyde, making it ideal for electrical fittings exposed to harsh environments or corrosive substances. Its enhanced moisture resistance prevents degradation and maintains insulation integrity under high humidity or wet conditions. Urea formaldehyde, while cost-effective, tends to absorb moisture and degrade faster, limiting its durability in chemically aggressive or moist settings.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyurethane coatings offer superior environmental benefits over urea formaldehyde in electrical fittings due to their lower formaldehyde emissions and enhanced durability, reducing the need for frequent replacements and waste. Urea formaldehyde, a phenol-based resin, releases formaldehyde gas during curing and degradation, posing significant indoor air quality and health concerns, impacting sustainability negatively. Polyurethane's formulation with fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs) leads to improved environmental compliance and supports sustainable manufacturing practices for electrical components.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Polyurethane offers superior durability and moisture resistance compared to urea formaldehyde, making it ideal for electrical fittings exposed to harsh environments, although it generally incurs higher raw material and processing costs. Urea formaldehyde is more cost-effective and easier to mold with shorter curing times, resulting in faster production cycles but less impact and heat resistance. Manufacturing with polyurethane demands advanced equipment and controlled conditions, while urea formaldehyde benefits from simpler manufacturing processes that reduce overall production expenses.
Common Applications in Electrical Fittings
Polyurethane is widely used in electrical fittings for insulation, sealing, and protective coatings due to its excellent mechanical strength, flexibility, and resistance to moisture and chemicals. Urea formaldehyde, known for its high electrical insulation properties and heat resistance, is commonly used in switchgear components, lamp holders, and socket outlets. Polyurethane suits applications requiring durability and environmental resistance, while urea formaldehyde excels in rigid, heat-resistant electrical parts.
Summary: Which Material is Better for Electrical Fittings?
Polyurethane offers superior moisture resistance, flexibility, and durability compared to urea formaldehyde, making it more suitable for electrical fittings exposed to varying environmental conditions. Urea formaldehyde is more cost-effective and provides excellent hardness and electrical insulation but is brittle and less resistant to moisture, limiting its application in high-stress or damp environments. For electrical fittings requiring longevity, environmental resistance, and mechanical strength, polyurethane is generally the better choice.
Infographic: Polyurethane vs Urea formaldehyde for Electrical fitting
 azmater.com
azmater.com