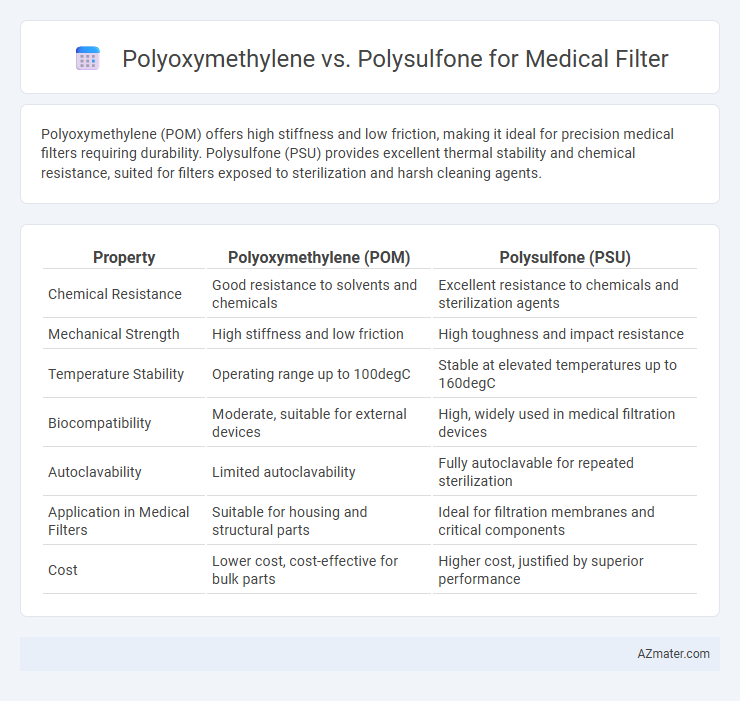
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers high stiffness and low friction, making it ideal for precision medical filters requiring durability. Polysulfone (PSU) provides excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance, suited for filters exposed to sterilization and harsh cleaning agents.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyoxymethylene (POM) | Polysulfone (PSU) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to solvents and chemicals | Excellent resistance to chemicals and sterilization agents |
| Mechanical Strength | High stiffness and low friction | High toughness and impact resistance |
| Temperature Stability | Operating range up to 100degC | Stable at elevated temperatures up to 160degC |
| Biocompatibility | Moderate, suitable for external devices | High, widely used in medical filtration devices |
| Autoclavability | Limited autoclavability | Fully autoclavable for repeated sterilization |
| Application in Medical Filters | Suitable for housing and structural parts | Ideal for filtration membranes and critical components |
| Cost | Lower cost, cost-effective for bulk parts | Higher cost, justified by superior performance |
Introduction to Polyoxymethylene and Polysulfone in Medical Filters
Polyoxymethylene (POM) is a highly crystalline thermoplastic known for its excellent mechanical strength, low friction, and chemical resistance, making it ideal for precision components in medical filters that require durability and dimensional stability. Polysulfone (PSU) offers superior thermal stability, excellent chemical resistance, and biocompatibility, which are critical for medical filters used in sterilization processes and high-temperature applications. Both polymers are widely applied in medical filtration due to their unique material properties that ensure reliability, safety, and performance in demanding healthcare environments.
Chemical Structure and Properties Comparison
Polyoxymethylene (POM) features a linear, highly crystalline structure composed of repeating -CH2-O- units, resulting in excellent mechanical strength, low friction, and chemical resistance, ideal for precision medical filters. Polysulfone (PSU) possesses an amorphous structure with aromatic rings and sulfone groups (-SO2-), providing superior thermal stability, hydrolytic resistance, and dimensional stability under steam sterilization. The choice between POM and PSU in medical filtration depends on the need for mechanical durability versus resistance to high-temperature sterilization and chemical exposure.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Analysis
Polyoxymethylene (POM) exhibits superior mechanical strength with high tensile modulus and excellent fatigue resistance, making it ideal for medical filter components subjected to repetitive stress. Polysulfone (PSU) offers exceptional durability due to its high thermal stability and chemical resistance, maintaining performance in sterilization processes and harsh environments. Comparative analysis shows POM excels in structural rigidity while PSU ensures long-term reliability under mechanical and chemical exposure in medical filtration applications.
Biocompatibility and Safety for Medical Applications
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers excellent mechanical strength and chemical resistance but demonstrates lower biocompatibility compared to polysulfone (PSU), which is renowned for its superior blood compatibility and minimal cytotoxicity. Polysulfone is widely favored in medical filter applications due to its high thermal stability, resistance to sterilization processes, and proven inertness, ensuring patient safety and reducing the risk of inflammatory responses. While POM can be used in specific non-implantable medical components, polysulfone's established safety profile makes it the preferred choice for critical filtration systems requiring stringent biocompatibility standards.
Filtration Efficiency and Performance in Medical Use
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers excellent dimensional stability and low moisture absorption, enhancing filtration efficiency in medical filters by maintaining consistent pore structure and preventing clogging during fluid passage. Polysulfone (PSU) exhibits superior thermal and chemical resistance, ensuring high-performance filtration under sterilization conditions without compromising membrane integrity or filter longevity. Both materials provide biocompatibility, but Polysulfone's enhanced durability and chemical resilience make it preferable for demanding medical filtration applications requiring repeated sterilization and reliable performance.
Resistance to Chemicals and Sterilization Methods
Polyoxymethylene (POM) exhibits excellent resistance to many chemicals, including solvents and fuels, but can degrade when exposed to strong acids or bases, limiting its application in aggressive chemical environments for medical filters. Polysulfone (PSU) offers superior chemical resistance, particularly against acids, alkalis, and oxidative sterilization methods such as autoclaving and gamma radiation, making it more suitable for repeated sterilization cycles in medical filtration. PSU's thermal stability up to 160-180degC supports sterilization techniques like steam autoclaving, whereas POM's lower thermal resistance restricts it to less aggressive sterilization processes.
Cost-Effectiveness in Medical Filter Manufacturing
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers a lower material cost compared to polysulfone, making it a more cost-effective choice for manufacturing medical filters where budget constraints are critical. Polysulfone provides superior thermal stability and chemical resistance but comes with a higher price point, impacting overall production expenses. Selecting POM can reduce cost without significantly compromising performance in applications requiring moderate chemical resistance and mechanical strength.
Regulatory Approvals and Industry Standards
Polyoxymethylene (POM) and Polysulfone (PSU) are widely used in medical filter applications due to their compliance with stringent regulatory approvals such as FDA and ISO 13485 certifications. Polysulfone exhibits superior biocompatibility and thermal stability, meeting USP Class VI standards more frequently than Polyoxymethylene, which is often selected for cost-effective, FDA-cleared components in less demanding filtration scenarios. Both materials conform to industry standards for sterility and cytotoxicity, but Polysulfone's enhanced chemical resistance and ability to endure sterilization processes like autoclaving make it the preferred choice in critical medical filtration devices.
Application Case Studies: POM vs. PSU in Medical Filters
Polyoxymethylene (POM) demonstrates superior dimensional stability and chemical resistance in medical filter housings, making it ideal for precision applications requiring tight tolerances and low friction. In contrast, Polysulfone (PSU) offers excellent thermal stability and biocompatibility, which is critical for high-temperature sterilization processes used in blood and intravenous filters. Case studies reveal POM excels in applications demanding mechanical strength and durability, while PSU is preferred in scenarios where repeated sterilization and exposure to aggressive chemicals are necessary.
Final Recommendation: Choosing the Right Material for Medical Filters
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers excellent dimensional stability, chemical resistance, and low friction, making it ideal for precise medical filter components requiring durability and smooth operation. Polysulfone (PSU) provides superior thermal stability, biocompatibility, and resistance to sterilization processes, ensuring reliability in high-temperature and sterilization-demanding medical filter applications. For final selection, choose polysulfone when high heat resistance and repeated sterilization are critical, while polyoxymethylene is preferable for applications demanding tight tolerances and mechanical robustness.
Infographic: Polyoxymethylene vs Polysulfone for Medical filter
 azmater.com
azmater.com