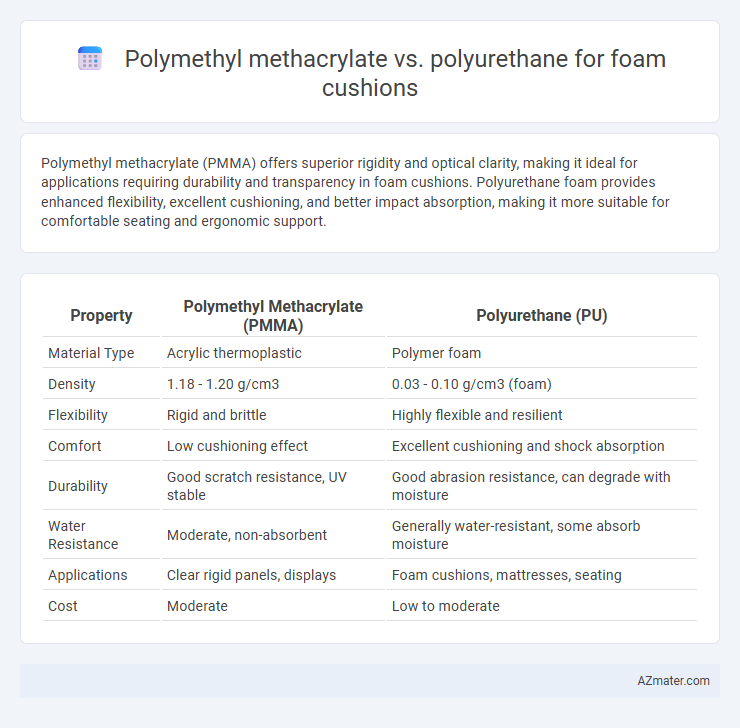
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior rigidity and optical clarity, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and transparency in foam cushions. Polyurethane foam provides enhanced flexibility, excellent cushioning, and better impact absorption, making it more suitable for comfortable seating and ergonomic support.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) | Polyurethane (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Acrylic thermoplastic | Polymer foam |
| Density | 1.18 - 1.20 g/cm3 | 0.03 - 0.10 g/cm3 (foam) |
| Flexibility | Rigid and brittle | Highly flexible and resilient |
| Comfort | Low cushioning effect | Excellent cushioning and shock absorption |
| Durability | Good scratch resistance, UV stable | Good abrasion resistance, can degrade with moisture |
| Water Resistance | Moderate, non-absorbent | Generally water-resistant, some absorb moisture |
| Applications | Clear rigid panels, displays | Foam cushions, mattresses, seating |
| Cost | Moderate | Low to moderate |
Introduction to Foam Cushion Materials
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) and polyurethane are two prominent materials used in foam cushions, with distinct properties influencing comfort and durability. PMMA foam is known for its rigidity, transparency, and resistance to UV light, making it suitable for applications where structural support and longevity are critical. Polyurethane foam excels in flexibility, cushioning, and impact absorption, often preferred in furniture and automotive seating due to its superior comfort and adaptability.
Overview of Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA)
Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) is a transparent thermoplastic often used as a lightweight and shatter-resistant alternative to glass in foam cushion applications. Known for its excellent rigidity, weather resistance, and clarity, PMMA provides enhanced durability and aesthetic appeal in cushioning materials. Its low moisture absorption and high UV resistance make it suitable for both indoor and outdoor foam cushion uses.
Overview of Polyurethane (PU)
Polyurethane (PU) foam is widely used in cushion applications due to its excellent resilience, durability, and cushioning properties. Its open-cell structure allows for breathability and moisture resistance, enhancing comfort and longevity compared to Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA). PU foam also offers better flexibility and impact absorption, making it ideal for furniture, automotive seating, and bedding uses.
Material Properties Comparison: PMMA vs Polyurethane
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) exhibits high rigidity, excellent optical clarity, and strong resistance to UV light, making it less flexible compared to polyurethane foams, which offer superior elasticity, cushioning, and durability under repeated compression. Polyurethane foam demonstrates enhanced shock absorption and resilience due to its cellular structure, whereas PMMA is brittle and prone to cracking under impact. Thermal insulation and moisture resistance are significantly better in polyurethane foam, supporting its widespread use in cushioning applications over rigid PMMA sheets.
Comfort and Support Analysis
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) foam cushions offer superior support due to their high rigidity and excellent load distribution, making them ideal for applications requiring firm cushioning. Polyurethane foam cushions provide enhanced comfort with their flexible, resilient structure that conforms closely to body contours, reducing pressure points effectively. By balancing the stiffness of PMMA with the softness of polyurethane, manufacturers optimize both comfort and support for various cushion applications.
Durability and Longevity
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers excellent rigidity and resistance to environmental factors, resulting in moderate durability in foam cushions but limited flexibility and cushioning lifespan. Polyurethane foam cushions exhibit superior durability and longevity due to their high resilience, excellent tear resistance, and ability to maintain shape over extended use under various conditions. For applications requiring long-lasting comfort and wear resistance, polyurethane outperforms PMMA in foam cushion materials.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) foam cushions exhibit lower biodegradability and higher environmental persistence compared to polyurethane foams, which often contain petrochemical-based polyols and isocyanates contributing to significant carbon emissions. Polyurethane foams can be engineered for improved recyclability and incorporate bio-based polyols, enhancing their sustainability profile, while PMMA foams typically lack this adaptability. Life cycle assessments reveal polyurethane cushions have greater potential for environmental optimization through advances in green chemistry and waste management, whereas PMMA remains less favorable due to its chemical stability and disposal challenges.
Cost-Effectiveness and Affordability
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) foam cushions typically offer higher initial costs compared to polyurethane foams but provide superior durability and resistance to wear, making them more cost-effective over long-term use. Polyurethane foam cushions are generally more affordable upfront and widely available, though they may require more frequent replacement due to lower resilience and susceptibility to compression set. When balancing budget with lifespan, polyurethane is preferred for short-term or budget-conscious applications, while PMMA is a better investment for extended use and enhanced performance.
Applications in Foam Cushion Manufacturing
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers high transparency and rigidity, making it suitable for foam cushions requiring enhanced structural support and aesthetic appeal, especially in medical and automotive seating applications. Polyurethane (PU) foam cushions provide superior elasticity, resilience, and comfort, widely used in furniture, bedding, and automotive interiors for impact absorption and long-lasting durability. Foam cushion manufacturing favors PU for flexible cushioning needs, while PMMA is incorporated for rigid inserts or transparent cushioning layers in specialized applications.
Choosing the Best Material for Foam Cushions
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers high rigidity and transparency, making it ideal for foam cushions requiring structural support and aesthetic clarity. Polyurethane provides superior flexibility, cushioning, and durability, resulting in enhanced comfort and long-lasting performance in foam cushions. Selecting the best material depends on whether rigidity and visual appeal (PMMA) or flexibility and comfort (Polyurethane) are the primary priorities.
Infographic: Polymethyl methacrylate vs Polyurethane for Foam cushion
 azmater.com
azmater.com