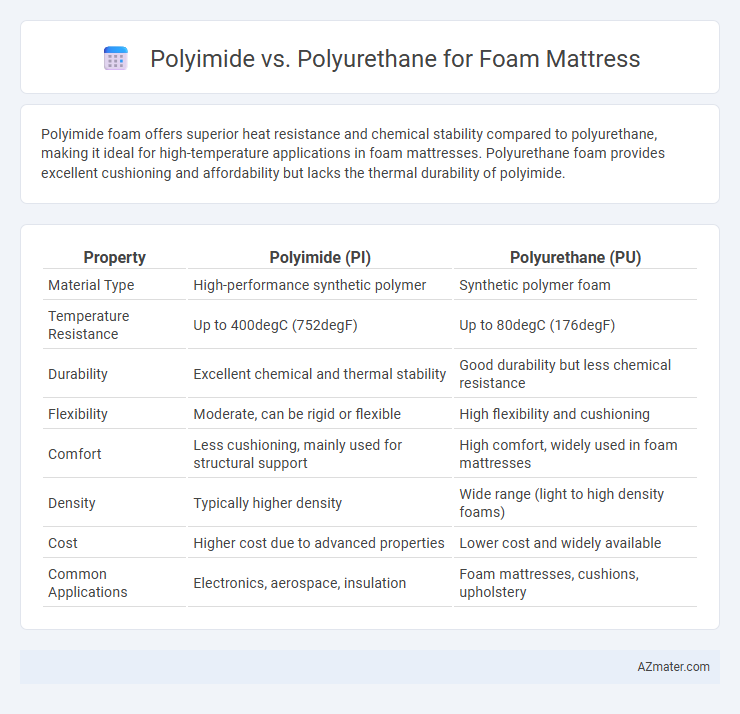
Polyimide foam offers superior heat resistance and chemical stability compared to polyurethane, making it ideal for high-temperature applications in foam mattresses. Polyurethane foam provides excellent cushioning and affordability but lacks the thermal durability of polyimide.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyimide (PI) | Polyurethane (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | High-performance synthetic polymer | Synthetic polymer foam |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 400degC (752degF) | Up to 80degC (176degF) |
| Durability | Excellent chemical and thermal stability | Good durability but less chemical resistance |
| Flexibility | Moderate, can be rigid or flexible | High flexibility and cushioning |
| Comfort | Less cushioning, mainly used for structural support | High comfort, widely used in foam mattresses |
| Density | Typically higher density | Wide range (light to high density foams) |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced properties | Lower cost and widely available |
| Common Applications | Electronics, aerospace, insulation | Foam mattresses, cushions, upholstery |
Introduction to Foam Mattress Materials
Polyimide and polyurethane represent two distinct materials used in foam mattresses, each with unique chemical structures and performance characteristics. Polyurethane foam, widely popular for its affordability and versatile comfort levels, is composed of polymer chains formed by reacting diisocyanates with polyols, offering varying densities and firmness. Polyimide foam, known for its exceptional thermal stability and durability, is a high-performance polymer often chosen for specialized mattress applications requiring enhanced resilience and long-term shape retention.
What is Polyimide Foam?
Polyimide foam is a high-performance, heat-resistant material known for its exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and low thermal conductivity, making it ideal for demanding applications such as aerospace and insulation. Unlike polyurethane foam, which is commonly used in mattress applications for its cushioning and flexibility, polyimide foam offers superior durability and resilience in extreme environments. Its unique molecular structure allows polyimide foam to maintain shape and integrity over a wide temperature range, providing enhanced support and longevity in specialized foam mattress designs.
What is Polyurethane Foam?
Polyurethane foam is a versatile, synthetic material widely used in foam mattresses due to its excellent cushioning and support properties. It is created through the chemical reaction of polyols and diisocyanates, resulting in a flexible, lightweight foam that offers good pressure relief and durability. Polyurethane foam mattresses are cost-effective and available in various densities and firmness levels, making them a popular choice for comfort and affordability.
Key Differences Between Polyimide and Polyurethane
Polyimide foam offers exceptional thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature applications, whereas polyurethane foam is known for its flexibility, softness, and affordability, commonly used in everyday mattresses. Polyimide's dense structure provides superior durability and dimensional stability compared to polyurethane's open-cell design, which delivers better breathability and pressure relief. Cost differences are significant; polyimide foam tends to be more expensive due to its advanced properties, while polyurethane foam is widely available and budget-friendly.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Polyimide foam exhibits superior durability compared to polyurethane foam due to its high thermal stability and resistance to chemical degradation, making it ideal for long-term mattress use. Polyurethane foam typically has a shorter lifespan, averaging 5 to 10 years, as it is more prone to wear, sagging, and breakdown under repeated weight and pressure. Investing in polyimide foam mattresses ensures extended longevity and consistent support, significantly outperforming standard polyurethane options in durability and lifespan.
Comfort and Support Performance
Polyimide foam mattresses offer superior support and high-temperature resistance, maintaining consistent comfort and durability over prolonged use. Polyurethane foam mattresses provide excellent initial comfort and pressure relief, adapting well to body contours but may degrade faster under heavy use. For optimal comfort and support performance, polyimide foam excels in longevity and resilience, while polyurethane foam delivers softer cushioning and may require more frequent replacement.
Thermal and Fire Resistance Attributes
Polyimide foam mattresses offer superior thermal stability, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures above 300degC, making them ideal for high-temperature environments. Polyurethane foam, while widely used, has a lower heat resistance, typically degrading around 200degC, and often requires chemical additives to enhance fire retardancy. The inherent flame retardant properties of polyimide provide better fire resistance without heavy reliance on additives, ensuring safer performance in applications demanding rigorous thermal and fire resistance standards.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyimide foam mattresses exhibit superior environmental stability and resist degradation, resulting in longer lifespan and reduced waste compared to polyurethane foams, which often contain petrochemical-based compounds and emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Polyurethane foams typically have higher carbon footprints due to energy-intensive manufacturing processes and limited recyclability, whereas polyimide foams incorporate advanced synthetic polymers that can be engineered for enhanced recyclability and lower ecological toxicity. Choosing polyimide over polyurethane for mattress foam supports sustainability goals by minimizing resource consumption, decreasing landfill contributions, and promoting environmentally responsible material innovations.
Cost Considerations
Polyimide foam mattresses generally carry a higher price due to their superior thermal stability and durability, making them suitable for long-term investment despite the initial cost. Polyurethane foam mattresses are more budget-friendly and widely available, offering decent comfort and support for everyday use but with a shorter lifespan. Cost considerations should weigh the balance between long-term performance of polyimide and the immediate affordability of polyurethane options.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Mattress
Polyurethane foam offers versatility and cost-effectiveness, featuring good support and durability suitable for a wide range of mattress types. Polyimide foam, known for its exceptional heat resistance and superior mechanical strength, provides enhanced longevity and performance in high-stress environments. Selecting the right foam depends on priorities like budget, durability, temperature regulation, and specific comfort preferences, with polyurethane excelling in affordability and polyimide in resilience.
Infographic: Polyimide vs Polyurethane for Foam Mattress
 azmater.com
azmater.com