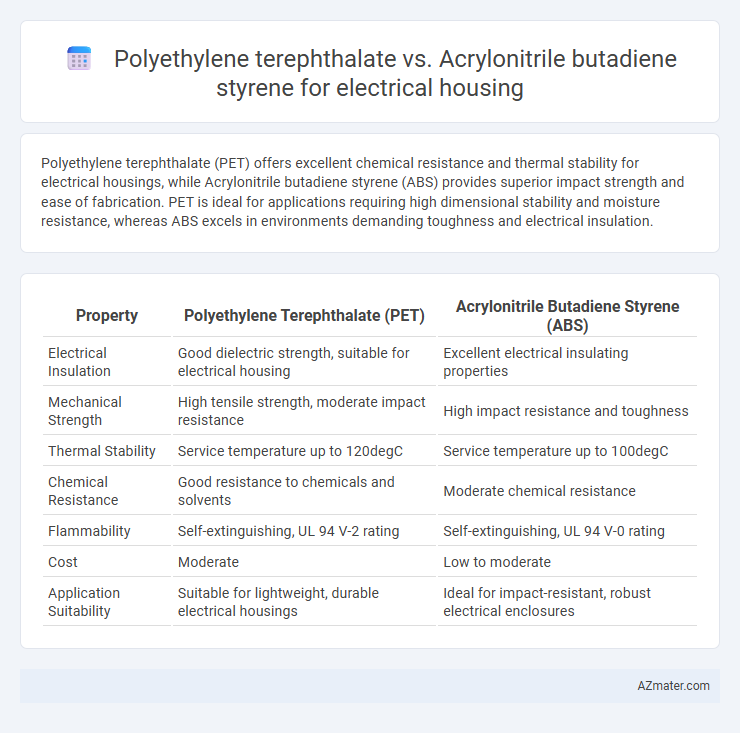
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers excellent chemical resistance and thermal stability for electrical housings, while Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides superior impact strength and ease of fabrication. PET is ideal for applications requiring high dimensional stability and moisture resistance, whereas ABS excels in environments demanding toughness and electrical insulation.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Insulation | Good dielectric strength, suitable for electrical housing | Excellent electrical insulating properties |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength, moderate impact resistance | High impact resistance and toughness |
| Thermal Stability | Service temperature up to 120degC | Service temperature up to 100degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to chemicals and solvents | Moderate chemical resistance |
| Flammability | Self-extinguishing, UL 94 V-2 rating | Self-extinguishing, UL 94 V-0 rating |
| Cost | Moderate | Low to moderate |
| Application Suitability | Suitable for lightweight, durable electrical housings | Ideal for impact-resistant, robust electrical enclosures |
Introduction to Electrical Housing Materials
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) are two commonly used materials for electrical housing due to their distinct properties. PET offers high chemical resistance, excellent dimensional stability, and good electrical insulation, making it suitable for protecting sensitive electronic components. ABS provides superior impact resistance, heat resistance, and ease of fabrication, which is ideal for durable and robust electrical enclosures.
Overview of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is a thermoplastic polymer known for its excellent electrical insulation properties, high mechanical strength, and resistance to moisture and chemicals, making it suitable for electrical housing applications. PET offers superior thermal stability compared to acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), with a higher melting point around 255degC, enabling it to endure elevated operating temperatures in electronic components. Its dimensional stability and resistance to wear and impact ensure reliable protection and longevity for electrical enclosures in various industrial environments.
Overview of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a thermoplastic polymer known for its high impact resistance, toughness, and excellent electrical insulating properties, making it a preferred material for electrical housing. Compared to Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET), ABS offers greater dimensional stability and better resistance to heat, which is critical for protecting sensitive electrical components. Its ease of molding and superior surface finish contribute to enhanced durability and aesthetic appeal in electrical housings used in consumer electronics and industrial applications.
Mechanical Strength Comparison: PET vs ABS
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior mechanical strength and stiffness compared to acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), making PET more resistant to deformation under mechanical stress in electrical housing applications. PET exhibits higher tensile strength, typically around 50-75 MPa, while ABS ranges from 40-60 MPa, providing enhanced durability and impact resistance for protective enclosures. The dimensional stability and chemical resistance of PET also contribute to its preference in environments demanding robust mechanical performance.
Thermal Resistance and Stability
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers higher thermal resistance with a melting point around 260degC, making it suitable for electrical housing applications requiring stability under prolonged heat exposure. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) has a lower thermal resistance, typically softening around 105degC, which limits its performance in high-temperature environments but provides better impact resistance. PET maintains dimensional stability and mechanical strength at elevated temperatures, whereas ABS may deform or degrade faster under thermal stress, impacting long-term reliability in electrical enclosures.
Electrical Insulating Properties
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers excellent electrical insulating properties with a high dielectric strength, making it suitable for electrical housing applications requiring reliable insulation. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides good insulating characteristics but generally has lower dielectric strength compared to PET, which may limit its use in high-voltage environments. PET's superior thermal stability and moisture resistance further enhance its electrical insulation performance in demanding electrical housing contexts.
Chemical Resistance and Durability
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior chemical resistance against acids, oils, and solvents, making it highly suitable for electrical housing exposed to harsh environments. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides excellent impact resistance and durability but is more susceptible to degradation when exposed to chemicals like hydrocarbons and strong acids. For applications requiring both long-term chemical resistance and mechanical strength, PET is generally preferred over ABS in electrical housing solutions.
Ease of Manufacturing and Processing
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers excellent ease of manufacturing for electrical housings due to its high thermal stability and good flow characteristics during injection molding, enabling precise and complex geometries. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is favored for its superior impact resistance and lower melting point, allowing faster cycle times and reduced energy consumption in processing. Both materials provide robust options, but PET's crystalline structure often demands higher processing temperatures compared to the more easily molded amorphous ABS.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior recyclability and a lower carbon footprint compared to acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), making it a more environmentally sustainable choice for electrical housing. PET's ability to be efficiently recycled into new products reduces landfill waste and conserves fossil fuel resources. In contrast, ABS production involves higher energy consumption and emits more greenhouse gases, contributing to greater environmental impact over its lifecycle.
Conclusion: Selecting the Optimal Material for Electrical Housing
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior chemical resistance and clarity, making it ideal for transparent electrical housings requiring durability against solvents and impact. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides excellent mechanical strength, thermal stability, and cost-effectiveness, suitable for robust, opaque housings in high-impact environments. Selecting the optimal material depends on specific application needs: choose PET for chemical resilience and aesthetic clarity, while ABS is preferred for strength, heat resistance, and economical production.
Infographic: Polyethylene terephthalate vs Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene for Electrical Housing
 azmater.com
azmater.com