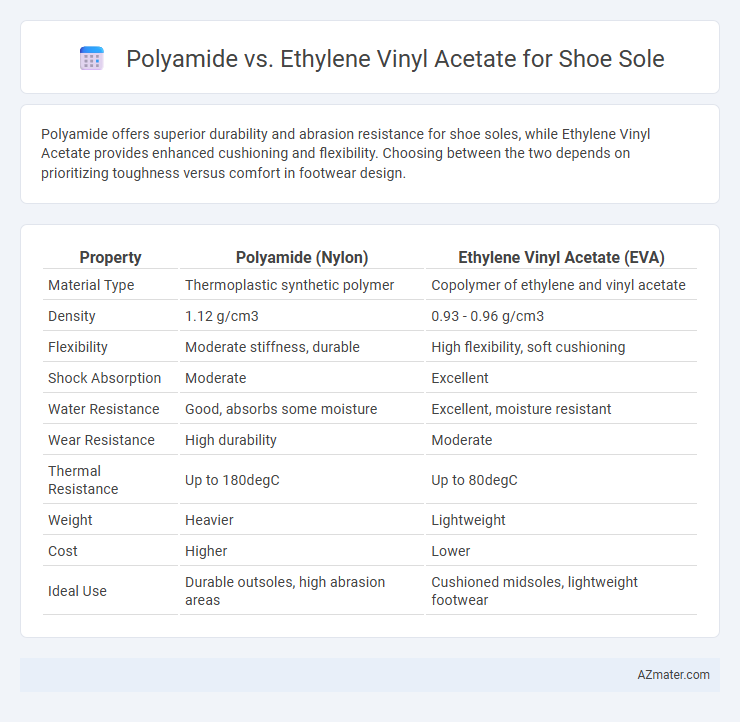
Polyamide offers superior durability and abrasion resistance for shoe soles, while Ethylene Vinyl Acetate provides enhanced cushioning and flexibility. Choosing between the two depends on prioritizing toughness versus comfort in footwear design.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyamide (Nylon) | Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic synthetic polymer | Copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate |
| Density | 1.12 g/cm3 | 0.93 - 0.96 g/cm3 |
| Flexibility | Moderate stiffness, durable | High flexibility, soft cushioning |
| Shock Absorption | Moderate | Excellent |
| Water Resistance | Good, absorbs some moisture | Excellent, moisture resistant |
| Wear Resistance | High durability | Moderate |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 180degC | Up to 80degC |
| Weight | Heavier | Lightweight |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Ideal Use | Durable outsoles, high abrasion areas | Cushioned midsoles, lightweight footwear |
Introduction to Shoe Sole Materials
Polyamide offers high durability, abrasion resistance, and excellent mechanical strength, making it ideal for shoe soles requiring long-lasting performance. Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) is lightweight, flexible, and provides superior cushioning and shock absorption, enhancing comfort during walking or running. Manufacturers often select between Polyamide and EVA based on the balance between durability and comfort needed for specific footwear applications.
Overview of Polyamide in Footwear
Polyamide, commonly known as nylon, is a durable and abrasion-resistant polymer widely used in footwear soles for its excellent mechanical strength and flexibility. It offers superior resilience to wear and tear, making it ideal for high-performance and athletic shoes requiring long-lasting support and cushioning. Polyamide's moisture-wicking properties and resistance to chemicals enhance comfort and longevity, positioning it as a preferred material for durable and reliable shoe soles compared to ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA).
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA): Key Features
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) stands out in shoe sole manufacturing due to its excellent cushioning, lightweight nature, and superior flexibility compared to polyamide. Its shock absorption capabilities enhance comfort and reduce fatigue during prolonged wear, making it ideal for athletic and casual footwear. EVA also offers good resistance to UV radiation and cracking, ensuring durability and maintaining sole integrity over time.
Durability Comparison: Polyamide vs EVA
Polyamide offers higher abrasion resistance and tensile strength compared to Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA), making it more durable for shoe soles exposed to rough terrains and heavy use. EVA provides superior cushioning and flexibility but tends to compress and degrade faster under continuous impact, reducing its lifespan. In durability-focused applications, polyamide outperforms EVA by maintaining structural integrity and resisting wear over extended periods.
Comfort and Cushioning Properties
Polyamide offers excellent durability and abrasion resistance but provides less cushioning compared to Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA), which excels in shock absorption and flexibility, making EVA a preferred material for enhanced comfort in shoe soles. EVA's lightweight and soft characteristics reduce foot fatigue by distributing pressure evenly during walking or running. Polyamide's rigidity supports structural integrity, but EVA soles deliver superior cushioning and energy return critical for athletic and casual footwear comfort.
Weight and Flexibility Analysis
Polyamide offers superior strength and abrasion resistance but tends to be heavier than Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA), which is known for its lightweight properties ideal for athletic footwear. EVA excels in flexibility and cushioning, providing enhanced comfort and shock absorption, whereas polyamide soles are stiffer and more durable, suitable for rugged use. Analyzing weight and flexibility, EVA is preferred for lightweight, flexible shoe soles, while polyamide is chosen for applications demanding durability and structural support.
Slip Resistance and Traction Differences
Polyamide shoe soles offer superior abrasion resistance and maintain slip resistance on wet surfaces due to their high tensile strength and durability. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) soles provide excellent cushioning and lightweight flexibility but typically exhibit lower slip resistance compared to polyamide in oily or uneven terrains. The chemical composition of polyamide enhances traction by increasing surface grip, whereas EVA's softer texture improves comfort but may reduce grip in challenging conditions.
Cost Efficiency and Production Considerations
Polyamide offers higher durability and abrasion resistance for shoe soles, resulting in longer-lasting performance but at a higher material cost compared to Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA). EVA provides greater flexibility, lightweight comfort, and ease of molding, which significantly reduces production time and energy consumption, enhancing overall cost efficiency. Choosing between polyamide and EVA depends on balancing upfront material expenses with manufacturing speed and desired sole properties.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyamide soles, derived from petroleum-based polymers, have a higher carbon footprint and lower biodegradability compared to Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA), which offers better recyclability and reduced environmental impact due to its partial bio-based content. EVA soles contribute to sustainability through lightweight design, enhancing energy efficiency in production and reducing fuel consumption during transport, while polyamide's durability extends product lifespan but challenges end-of-life disposal. Novel EVA formulations incorporating natural additives and recycled materials improve biodegradability, positioning EVA as a more eco-friendly sole material in sustainable footwear manufacturing.
Choosing the Right Material for Shoe Soles
Polyamide offers high durability, abrasion resistance, and excellent mechanical strength, making it ideal for heavy-duty shoe soles requiring long-lasting performance. Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) provides superior cushioning, flexibility, and lightweight comfort, preferred for athletic and casual footwear emphasizing shock absorption and comfort. Selecting the right material depends on balancing durability needs and user comfort, with polyamide suited for rugged use and EVA favored for cushioning and flexibility.
Infographic: Polyamide vs Ethylene Vinyl Acetate for Shoe Sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com