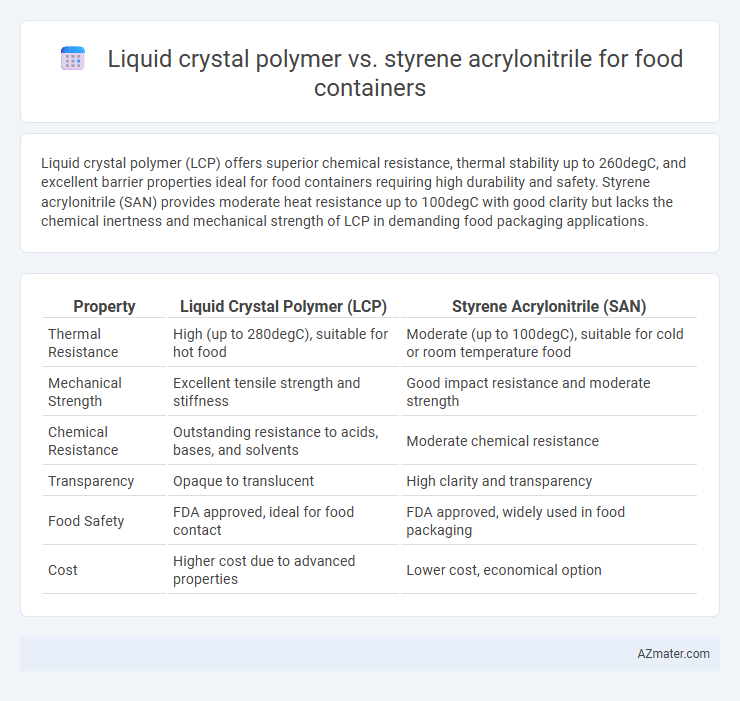
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior chemical resistance, thermal stability up to 260degC, and excellent barrier properties ideal for food containers requiring high durability and safety. Styrene acrylonitrile (SAN) provides moderate heat resistance up to 100degC with good clarity but lacks the chemical inertness and mechanical strength of LCP in demanding food packaging applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) | Styrene Acrylonitrile (SAN) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Resistance | High (up to 280degC), suitable for hot food | Moderate (up to 100degC), suitable for cold or room temperature food |
| Mechanical Strength | Excellent tensile strength and stiffness | Good impact resistance and moderate strength |
| Chemical Resistance | Outstanding resistance to acids, bases, and solvents | Moderate chemical resistance |
| Transparency | Opaque to translucent | High clarity and transparency |
| Food Safety | FDA approved, ideal for food contact | FDA approved, widely used in food packaging |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced properties | Lower cost, economical option |
Introduction to Liquid Crystal Polymer and Styrene Acrylonitrile
Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for exceptional chemical resistance, dimensional stability, and ability to withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for durable, long-lasting food containers. Styrene Acrylonitrile (SAN) is a transparent copolymer with good impact resistance, clarity, and moderate chemical resistance, commonly used for microwave-safe and recyclable food packaging. Comparing both, LCP offers superior mechanical strength and thermal stability while SAN provides clarity and cost-effectiveness for everyday food container applications.
Material Composition and Structural Properties
Liquid crystal polymers (LCP) consist of aromatic polyester chains that form highly ordered molecular structures, providing excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance, ideal for food container applications requiring durability and repeated sterilization. Styrene acrylonitrile (SAN) is a copolymer made from styrene and acrylonitrile monomers, offering good clarity and moderate heat resistance but lower mechanical strength compared to LCP. The superior structural rigidity and low moisture absorption of LCP make it preferable for high-performance food containers, while SAN is favored for transparent containers with less demanding thermal requirements.
Thermal Stability and Temperature Resistance
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) exhibits superior thermal stability and temperature resistance compared to styrene acrylonitrile (SAN), maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 260degC. SAN typically withstands temperatures up to 100degC, making it less suitable for high-heat food container applications like microwave or dishwasher use. The high melting point and low thermal expansion coefficient of LCP ensure durability and safety in environments involving repeated thermal cycling.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior mechanical strength and durability compared to styrene acrylonitrile (SAN) in food container applications, with high tensile strength and excellent resistance to impact and fatigue. LCP's molecular structure provides outstanding thermal stability and chemical resistance, ensuring long-lasting performance under repeated use and cleaning. SAN, while cost-effective and transparent, generally exhibits lower impact resistance and may degrade faster under harsh environmental conditions, reducing its overall lifespan in demanding food storage scenarios.
Chemical Resistance in Food Packaging
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to styrene acrylonitrile (SAN) in food packaging applications, effectively withstanding acids, bases, and organic solvents without degradation. SAN, while moderately resistant to chemicals, is more susceptible to swelling and leaching when exposed to harsh food additives or prolonged contact with oils and alcohols. This makes LCP a preferred choice for packaging that requires high durability and safety against chemical interaction with various food products.
Food Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior chemical resistance and thermal stability compared to styrene acrylonitrile (SAN), making it highly suitable for food containers requiring prolonged exposure to heat and acidic or alkaline foods. LCP meets stringent food safety standards such as FDA 21 CFR 177.2415 and EU Regulation No 10/2011, ensuring minimal migration of harmful substances into food products. In contrast, SAN, while approved under FDA and EU regulations, is more prone to chemical interaction and lower heat tolerance, which may affect long-term food safety and compliance in high-temperature applications.
Barrier Properties: Moisture and Gas Permeability
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) exhibits superior barrier properties compared to styrene acrylonitrile (SAN) for food containers, with significantly lower moisture and gas permeability rates. LCP's tightly ordered molecular structure effectively minimizes oxygen and water vapor transmission, enhancing food preservation and shelf life. In contrast, SAN, while offering moderate barrier performance, allows higher permeation of moisture and gases, making it less ideal for applications requiring stringent protection against contamination and spoilage.
Processability and Manufacturing Techniques
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior processability for food containers through high melt strength and excellent dimensional stability, enabling precise injection molding and thin-walled structures. Styrene acrylonitrile (SAN) provides easier processing with lower melting temperatures suitable for extrusion and thermoforming but exhibits less thermal and chemical resistance compared to LCP. Manufacturing techniques for LCP emphasize rapid cooling and shear control to maintain molecular orientation, while SAN benefits from flexible molding conditions and faster cycle times.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to Styrene Acrylonitrile (SAN), but its complex polymer structure limits recyclability and contributes to environmental challenges. Styrene Acrylonitrile, while less heat-resistant, is more widely accepted in recycling programs due to its simpler polymer composition and greater ease of mechanical recycling. Considering life cycle assessments, SAN-based food containers generally have a lower environmental footprint in terms of recycling and waste management compared to LCP containers.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior heat resistance and chemical stability for food containers but comes at a significantly higher cost compared to styrene acrylonitrile (SAN), making LCP less attractive for budget-sensitive applications. SAN provides a cost-effective alternative with good clarity and moderate heat resistance, widely available in the food packaging market due to its affordability and ease of processing. Market availability favors SAN because of its established production scale and distribution channels, while LCP remains niche, primarily used in high-performance or specialized food container applications where cost is less critical.
Infographic: Liquid crystal polymer vs Styrene acrylonitrile for Food container
 azmater.com
azmater.com