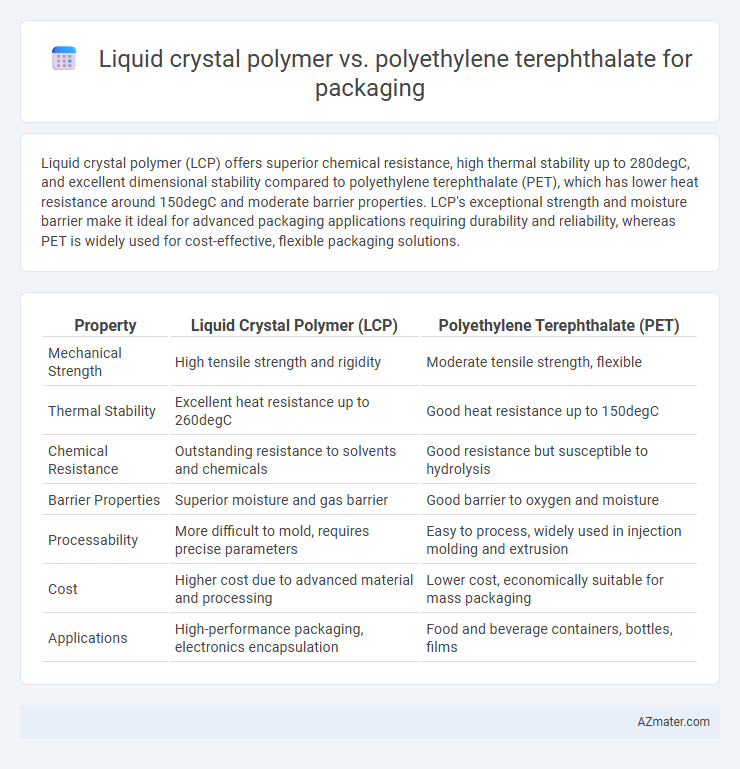
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior chemical resistance, high thermal stability up to 280degC, and excellent dimensional stability compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET), which has lower heat resistance around 150degC and moderate barrier properties. LCP's exceptional strength and moisture barrier make it ideal for advanced packaging applications requiring durability and reliability, whereas PET is widely used for cost-effective, flexible packaging solutions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) | Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and rigidity | Moderate tensile strength, flexible |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent heat resistance up to 260degC | Good heat resistance up to 150degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Outstanding resistance to solvents and chemicals | Good resistance but susceptible to hydrolysis |
| Barrier Properties | Superior moisture and gas barrier | Good barrier to oxygen and moisture |
| Processability | More difficult to mold, requires precise parameters | Easy to process, widely used in injection molding and extrusion |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced material and processing | Lower cost, economically suitable for mass packaging |
| Applications | High-performance packaging, electronics encapsulation | Food and beverage containers, bottles, films |
Introduction to Liquid Crystal Polymer and Polyethylene Terephthalate
Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its exceptional mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, making it ideal for specialized packaging applications requiring durability under extreme conditions. Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) is a widely used polyester polymer recognized for its clarity, barrier properties, and recyclability, commonly employed in food and beverage packaging to maintain freshness and extend shelf life. Both materials offer distinct advantages: LCP excels in high-temperature and chemically aggressive environments, while PET provides cost-effective, lightweight packaging with excellent gas and moisture resistance.
Chemical Structure and Material Properties
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) features a highly ordered molecular structure with rigid rod-like polymer chains, resulting in exceptional chemical resistance, thermal stability exceeding 260degC, and superior mechanical strength ideal for packaging requiring high performance. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET), a semi-crystalline polyester composed of repeating ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid units, offers good clarity, moderate thermal resistance around 230degC, and excellent barrier properties against moisture and gases. The anisotropic molecular alignment in LCP imparts enhanced dimensional stability and lower gas permeability compared to PET, making LCP suitable for specialized packaging applications demanding greater durability and chemical inertness.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Liquid crystal polymers (LCPs) exhibit superior mechanical strength compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET), with higher tensile strength and enhanced dimensional stability under stress. LCPs demonstrate exceptional rigidity and resistance to deformation, making them ideal for high-performance packaging requiring durability and impact resistance. PET offers good strength but is more prone to creep and deformation under sustained loads, limiting its use in applications demanding long-term mechanical integrity.
Barrier Properties: Moisture and Gas Permeability
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) exhibits superior barrier properties compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET), with significantly lower moisture and gas permeability rates crucial for high-performance packaging applications. LCP's highly ordered molecular structure provides enhanced resistance to oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water vapor transmission, extending product shelf life and maintaining freshness. PET, while effective as a general packaging material, shows higher permeability levels, making it less suitable for products requiring stringent moisture and gas barrier performance.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Liquid crystal polymers (LCPs) exhibit superior thermal stability and heat resistance compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET), with melting points typically above 300degC versus PET's melting point around 260degC. LCPs maintain structural integrity and dimensional stability under prolonged exposure to high temperatures, making them ideal for high-temperature packaging applications. PET, while widely used for packaging due to its good mechanical properties and transparency, tends to deform and lose strength at temperatures above 150degC, limiting its use in heat-intensive environments.
Processing Techniques and Manufacturability
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers advanced melt processability with exceptional thermal stability and dimensional accuracy, enabling high-speed injection molding and extrusion for precision packaging applications. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) excels in conventional blow molding and thermoforming, providing cost-effective, scalable manufacturing with excellent barrier properties and clarity. LCP's superior chemical resistance and mechanical strength support complex, high-performance packaging, while PET remains the standard for mass-produced, consumer-friendly containers due to its ease of processing and recyclability.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior chemical resistance and thermal stability compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET), but its complex molecular structure limits recyclability and increases environmental persistence. PET is widely recycled through established collection and processing systems, making it more sustainable for packaging applications despite its lower thermal resistance and chemical durability. The environmental impact of PET is mitigated by efficient recycling streams, whereas LCP packaging often ends up in landfills or incineration due to technical barriers in recycling.
Cost Analysis and Commercial Availability
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior chemical resistance and mechanical strength but comes with a higher cost compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET), which is significantly more affordable and widely used in packaging applications. PET benefits from extensive commercial availability due to its mass production, making it the preferred choice for cost-sensitive packaging solutions. Market demand and supply chain infrastructures strongly favor PET, whereas LCP remains niche, limiting its cost efficiency and accessibility for large-scale packaging.
Application Suitability in Packaging
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior heat resistance and mechanical strength, making it ideal for high-performance packaging applications requiring durability and dimensional stability. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) excels in food and beverage packaging due to its excellent barrier properties, transparency, and recyclability. LCP is suited for specialty packaging where chemical resistance and thermal endurance are critical, while PET remains the preferred choice for everyday packaging with a balance of cost-effectiveness and functional performance.
Future Trends and Innovations in Polymer Packaging
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET), positioning it as a prime candidate for advanced packaging applications in electronics and high-performance sectors. Emerging trends emphasize the integration of LCP with sustainable processes and biodegradable additives to enhance environmental compatibility without compromising durability. Innovations focus on smart packaging solutions incorporating LCP composites for improved barrier properties, sensor integration, and recyclability, driving the evolution of next-generation polymer packaging materials.
Infographic: Liquid crystal polymer vs Polyethylene terephthalate for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com