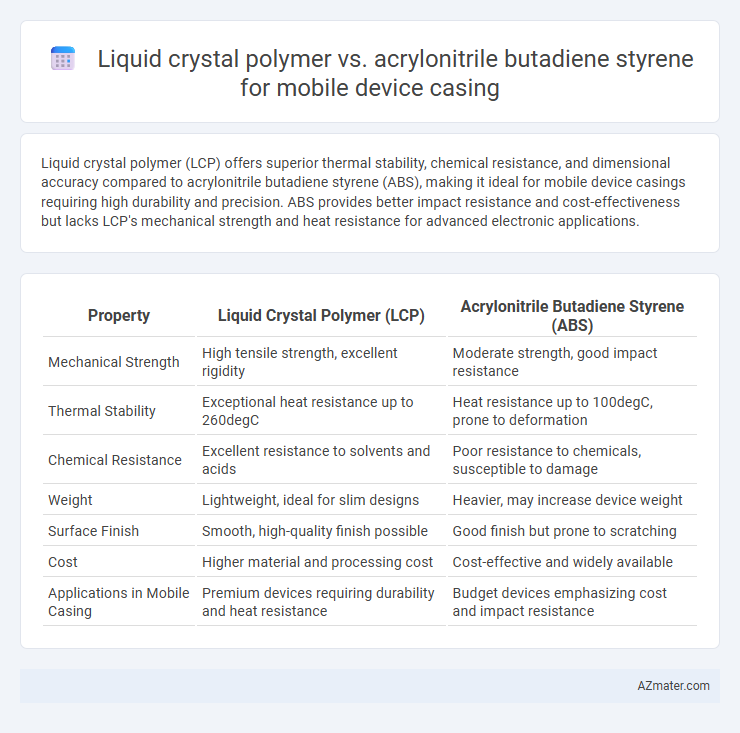
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and dimensional accuracy compared to acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), making it ideal for mobile device casings requiring high durability and precision. ABS provides better impact resistance and cost-effectiveness but lacks LCP's mechanical strength and heat resistance for advanced electronic applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength, excellent rigidity | Moderate strength, good impact resistance |
| Thermal Stability | Exceptional heat resistance up to 260degC | Heat resistance up to 100degC, prone to deformation |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to solvents and acids | Poor resistance to chemicals, susceptible to damage |
| Weight | Lightweight, ideal for slim designs | Heavier, may increase device weight |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, high-quality finish possible | Good finish but prone to scratching |
| Cost | Higher material and processing cost | Cost-effective and widely available |
| Applications in Mobile Casing | Premium devices requiring durability and heat resistance | Budget devices emphasizing cost and impact resistance |
Introduction to Liquid Crystal Polymer and ABS
Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for exceptional mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability, making it ideal for mobile device casings that require durability and precision. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a versatile, cost-effective polymer widely used in mobile device housings due to its impact resistance, ease of manufacturing, and good surface finish. Comparing LCP and ABS highlights LCP's superior thermal and mechanical properties against ABS's affordability and processability in electronic enclosure applications.
Key Properties of LCP and ABS
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior thermal stability up to 260degC and excellent chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-performance mobile device casings that require durability and heat endurance. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides impact resistance and ease of molding at lower costs but has lower thermal resistance, typically up to 100degC, which limits its use in devices exposed to higher temperatures. The low moisture absorption and high dimensional stability of LCP further enhance its suitability for precise, lightweight mobile device components compared to the more flexible and cost-effective ABS.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), offering higher tensile strength and excellent impact resistance, making it ideal for mobile device casing requiring durability and flexibility. LCP's stiffness and dimensional stability outperform ABS, especially under thermal stress and mechanical load, ensuring device protection against drops and bending. ABS, while cost-effective and easier to mold, lacks the long-term mechanical robustness of LCP, often resulting in lower resistance to wear and tear in demanding mobile environments.
Thermal Resistance and Stability
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior thermal resistance with a high melting point around 280degC, making it ideal for mobile device casings exposed to intense heat during operation and charging. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) has a lower thermal resistance, typically deforming at temperatures around 100degC, which limits its stability under prolonged high-temperature conditions. LCP's exceptional dimensional stability and resistance to thermal degradation enhance device durability, while ABS provides cost-effective molding but with reduced thermal performance.
Chemical Resistance Capabilities
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), with excellent stability against oils, solvents, acids, and alkalis, making it ideal for mobile device casings exposed to harsh environments. ABS is more susceptible to chemical degradation from prolonged exposure to organic solvents and strong acids, which can compromise device durability and aesthetics. The high chemical resistance of LCP ensures longer-lasting protection and maintains structural integrity in mobile device applications where exposure to chemicals is a concern.
Weight and Design Flexibility
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers significantly lower density compared to acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), resulting in lighter mobile device casings essential for portability and user comfort. LCP's unique molecular structure provides superior dimensional stability and design flexibility, enabling intricate, thin-walled, and high-precision components that enhance aesthetic appeal and functional performance. In contrast, ABS is heavier and less capable of supporting complex geometries, limiting innovative design possibilities for mobile devices.
Manufacturing Process and Cost
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior dimensional stability and high-temperature resistance, making it ideal for precision molding in mobile device casings, but its manufacturing process involves higher complexity and slower cycle times compared to acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS). ABS provides easier processability with faster injection molding and lower tooling costs, making it a more cost-effective option for large-scale production despite its lower thermal resistance and mechanical strength. The elevated cost of LCP stems from raw material expenses and specialized processing requirements, whereas ABS benefits from widespread availability and simpler manufacturing techniques.
Surface Finish and Aesthetics
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers a superior surface finish for mobile device casings due to its ability to produce smooth, high-gloss, and scratch-resistant exteriors that enhance aesthetic appeal. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides a more matte finish with decent texture but tends to show surface wear and scratches more easily over time. The choice between LCP and ABS impacts the visual quality and durability of the casing, with LCP favored for premium, sleek designs and ABS for cost-effective, versatile applications.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior environmental benefits over acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) in mobile device casing due to its higher thermal stability and lower environmental footprint during production, which results in reduced energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. LCP's recyclability is enhanced by its chemical resistance and ability to be reprocessed multiple times without significant degradation, whereas ABS often presents challenges in recycling due to the release of toxic compounds and mechanical property losses after multiple reprocessing cycles. Selecting LCP over ABS contributes to more sustainable mobile device manufacturing by minimizing hazardous waste and improving material lifecycle performance.
Best Choice for Mobile Device Casings
Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) offers superior chemical resistance, high tensile strength, and excellent thermal stability compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), making LCP the best choice for mobile device casings that require durability and heat resistance. LCP's low moisture absorption and exceptional dimensional stability ensure long-lasting performance and protection in various environmental conditions, whereas ABS is more prone to warping and degradation under prolonged heat exposure. Despite ABS being cost-effective and easier to process, LCP excels in providing premium structural integrity and reliability crucial for high-end mobile device applications.
Infographic: Liquid crystal polymer vs Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene for Mobile device casing
 azmater.com
azmater.com