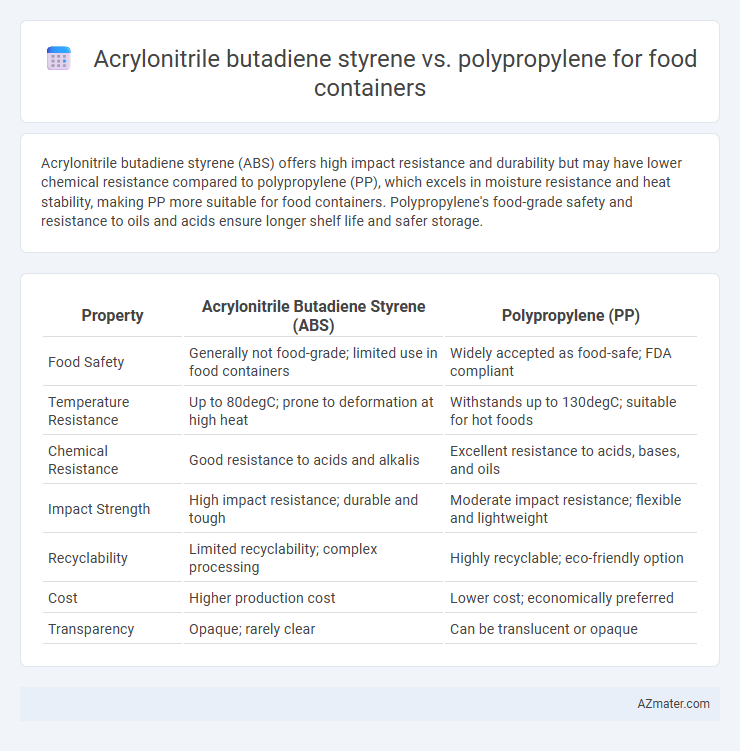
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers high impact resistance and durability but may have lower chemical resistance compared to polypropylene (PP), which excels in moisture resistance and heat stability, making PP more suitable for food containers. Polypropylene's food-grade safety and resistance to oils and acids ensure longer shelf life and safer storage.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Polypropylene (PP) |
|---|---|---|
| Food Safety | Generally not food-grade; limited use in food containers | Widely accepted as food-safe; FDA compliant |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 80degC; prone to deformation at high heat | Withstands up to 130degC; suitable for hot foods |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to acids and alkalis | Excellent resistance to acids, bases, and oils |
| Impact Strength | High impact resistance; durable and tough | Moderate impact resistance; flexible and lightweight |
| Recyclability | Limited recyclability; complex processing | Highly recyclable; eco-friendly option |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Lower cost; economically preferred |
| Transparency | Opaque; rarely clear | Can be translucent or opaque |
Introduction to Food-Safe Plastics
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) and polypropylene (PP) are commonly used plastics in food container manufacturing, with polypropylene being widely recognized for its superior food-safe properties due to its high resistance to chemicals and heat. Polypropylene is FDA-approved and BPA-free, making it suitable for repeated food contact and microwave use, whereas ABS is less frequently used for direct food contact because it may contain additives that could leach. Understanding the chemical stability and regulatory compliance of these materials is essential when selecting safe plastics for food storage applications.
Overview of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a thermoplastic polymer known for its toughness, impact resistance, and glossy surface, making it a popular choice for food containers requiring durable and rigid packaging. ABS offers excellent heat resistance up to 80degC and strong chemical resistance, but it is less resistant to prolonged exposure to acids and oils compared to polypropylene. Its ability to be easily molded and printed on makes ABS ideal for reusable food containers where structural integrity and aesthetic appeal are critical.
Overview of Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene (PP) is a versatile, thermoplastic polymer widely used in food containers due to its excellent chemical resistance, high melting point, and non-toxic nature, making it safe for food contact applications. Its low moisture absorption and resistance to fats and oils contribute to maintaining food freshness and container durability. PP also offers superior flexibility and impact resistance compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), enhancing its suitability for microwave-safe and reusable food packaging solutions.
Safety and Food Contact Regulations
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is generally not recommended for food containers due to potential migration of styrene and other additives, raising safety concerns under FDA and EFSA food contact regulations. Polypropylene (PP) offers superior chemical resistance, is BPA-free, and complies with global food safety standards, making it a preferred choice for food containers. PP's heat tolerance and inertness minimize leaching risks, ensuring better protection against contamination in food storage applications.
Temperature Resistance: ABS vs. PP
Polypropylene (PP) offers superior temperature resistance for food containers, withstanding heat up to 100-120degC, making it ideal for microwave and dishwasher use. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), however, has a lower heat tolerance, generally up to 80-90degC, limiting its suitability for high-temperature food storage or reheating. PP's enhanced thermal stability and chemical resistance ensure safer and more durable containers for varied food applications.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers excellent resistance to acids and alkalis but tends to degrade when exposed to strong solvents and oils, limiting its use in some food container applications. Polypropylene (PP) exhibits superior chemical resistance to a wider range of food-related substances, including oils, fats, and many acids, making it more suitable for long-term food storage. The inherent chemical stability of polypropylene under high temperatures and exposure to various cleaning agents ensures enhanced durability and safety in food contact applications compared to ABS.
Durability and Longevity
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior impact resistance and toughness compared to polypropylene (PP), making it more durable under rough handling conditions in food containers. Polypropylene excels in chemical resistance and thermal stability, providing longevity by resisting degradation from repeated washing and exposure to food acids. Both materials tolerate varying temperatures, but ABS maintains structural integrity better under mechanical stress, while polypropylene's lightweight nature contributes to extended usability through flexibility and resistance to cracking.
Ease of Cleaning and Maintenance
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers moderate ease of cleaning due to its smooth surface but can absorb oils and stains, requiring regular maintenance to prevent discoloration. Polypropylene (PP) is highly favored for food containers because of its excellent chemical resistance and non-porous texture, enabling quick and thorough cleaning while resisting stains and odors. Maintenance for PP is generally low, as it withstands repeated washing without degrading, making it superior to ABS in both ease of cleaning and long-term upkeep.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is less environmentally sustainable than polypropylene (PP) due to its lower recyclability and higher energy consumption during production. Polypropylene boasts greater biodegradability and can be more efficiently recycled, reducing landfill waste and environmental pollution associated with food containers. PP's lower carbon footprint and resistance to chemical leaching make it a preferable choice for eco-friendly, sustainable food packaging solutions.
Which Material is Better for Food Containers?
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers excellent impact resistance and durability but has lower chemical resistance compared to polypropylene (PP), making PP safer for food contact due to its inert nature and higher resistance to moisture and chemicals. Polypropylene is also preferred for its superior heat resistance, allowing it to withstand microwave and dishwasher use without leaching harmful substances. For food containers, polypropylene's FDA approval and better barrier properties against odor and stains make it the superior choice over ABS.
Infographic: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene vs Polypropylene for Food container
 azmater.com
azmater.com