Zirconium pipes offer superior corrosion resistance and high-temperature strength compared to steel pipes, making them ideal for aggressive chemical environments. Steel pipes provide greater cost efficiency and mechanical strength but are more prone to corrosion and require protective coatings in harsh conditions.
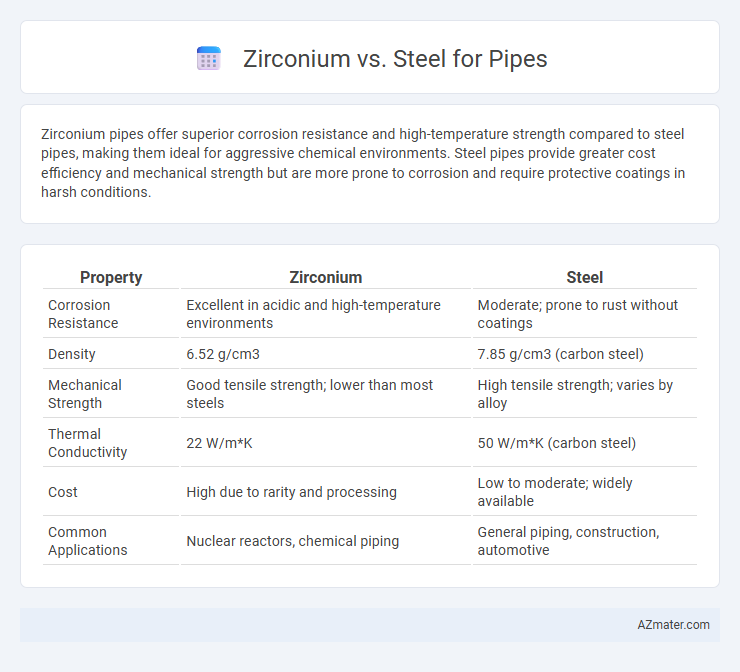
Table of Comparison
| Property | Zirconium | Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent in acidic and high-temperature environments | Moderate; prone to rust without coatings |
| Density | 6.52 g/cm3 | 7.85 g/cm3 (carbon steel) |
| Mechanical Strength | Good tensile strength; lower than most steels | High tensile strength; varies by alloy |
| Thermal Conductivity | 22 W/m*K | 50 W/m*K (carbon steel) |
| Cost | High due to rarity and processing | Low to moderate; widely available |
| Common Applications | Nuclear reactors, chemical piping | General piping, construction, automotive |
Introduction to Zirconium and Steel Pipes
Zirconium pipes offer exceptional corrosion resistance and high strength, making them ideal for aggressive chemical environments and high-temperature applications in nuclear reactors and chemical processing plants. Steel pipes, particularly carbon and stainless steel variants, provide versatile mechanical strength, cost-effectiveness, and ease of fabrication for a wide range of industrial uses including water transport, oil and gas, and construction. While steel excels in structural applications due to its durability and availability, zirconium is preferred in specialized settings requiring superior resistance to corrosion and heat.
Chemical Composition and Material Properties
Zirconium pipes, with a primary composition of zirconium (Zr), offer exceptional corrosion resistance, especially in aggressive chemical environments, due to their stable oxide layer, making them ideal for nuclear and chemical industries. Steel pipes, mainly composed of iron (Fe) with varying carbon content, provide high tensile strength and durability but are more susceptible to corrosion and chemical degradation without protective coatings or alloys. The choice between zirconium and steel pipes depends on the operational environment, balancing zirconium's chemical inertness and steel's mechanical robustness.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Zirconium pipes exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to steel, especially in highly aggressive environments such as chemical processing and nuclear reactors. Zirconium forms a stable, protective oxide layer that prevents corrosion from acids and chloride ions, whereas steel is prone to rust and pitting without specialized coatings. This makes zirconium an ideal choice for applications requiring long-term durability in corrosive media.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Zirconium pipes exhibit superior corrosion resistance and maintain mechanical strength at high temperatures, making them ideal for harsh chemical environments compared to steel. Steel pipes, while offering excellent tensile strength and cost-effectiveness, are prone to corrosion and reduced durability in aggressive conditions. Zirconium's enhanced durability and resistance to stress corrosion cracking significantly extend the lifespan of piping systems in nuclear and chemical industries.
Temperature and Pressure Performance
Zirconium pipes exhibit superior corrosion resistance and maintain structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 1000degC, outperforming steel in high-temperature environments commonly found in chemical processing and nuclear industries. Steel pipes, while strong under moderate temperatures up to 600degC, tend to weaken and corrode faster under extreme heat and aggressive chemical exposure. Pressure-wise, zirconium sustains high pressure without deformation due to its excellent tensile strength and creep resistance, making it ideal for high-pressure applications where steel may fail prematurely.
Applications in Various Industries
Zirconium pipes are highly valued in the chemical and nuclear industries due to their exceptional corrosion resistance and ability to withstand high temperatures, making them ideal for handling aggressive fluids and radioactive materials. Steel pipes, particularly stainless steel, dominate in construction, oil and gas, and water supply systems owing to their strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness. While zirconium excels in specialized environments requiring superior chemical stability, steel's versatility supports broad industrial applications including automotive, manufacturing, and infrastructure projects.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Zirconium pipes typically present a higher upfront cost compared to steel due to the rarity and complexity of zirconium extraction and processing. Despite the initial expense, zirconium's superior corrosion resistance and longer lifespan can result in lower total lifecycle costs, especially in industries such as chemical processing or nuclear power. Steel pipes, while more affordable initially, may incur higher maintenance and replacement expenses over time due to susceptibility to corrosion and wear.
Maintenance and Longevity
Zirconium pipes offer superior corrosion resistance compared to steel, significantly reducing maintenance frequency and costs in aggressive chemical environments. The longevity of zirconium pipes often surpasses steel due to their enhanced resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion, making them ideal for long-term use in harsh industrial applications. Steel pipes require more frequent inspections and protective coatings to prevent rust and degradation, increasing overall maintenance efforts over time.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Zirconium pipes exhibit superior corrosion resistance, significantly reducing the risk of environmental contamination compared to steel pipes, which are prone to rust and require frequent replacements. The production of zirconium, although energy-intensive, results in longer-lasting pipes, lessening the overall resource consumption and waste generation over time. Steel pipes, while recyclable, often involve higher carbon emissions during manufacturing and maintenance, making zirconium a more sustainable option for critical applications where durability and environmental safety are paramount.
Final Recommendation: Choosing Between Zirconium and Steel Pipes
Zirconium pipes offer superior corrosion resistance and high-temperature strength, making them ideal for aggressive chemical environments and nuclear applications, whereas steel pipes provide greater cost-effectiveness and mechanical strength suitable for general industrial use and water transport. When selecting between zirconium and steel pipes, prioritize zirconium for critical corrosion-prone systems requiring longevity and minimal maintenance, while steel remains the preferred choice for structural applications demanding high tensile strength at a lower cost. Final recommendation depends on balancing budget constraints with the specific environmental and operational demands of the piping system.
Infographic: Zirconium vs Steel for Pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com