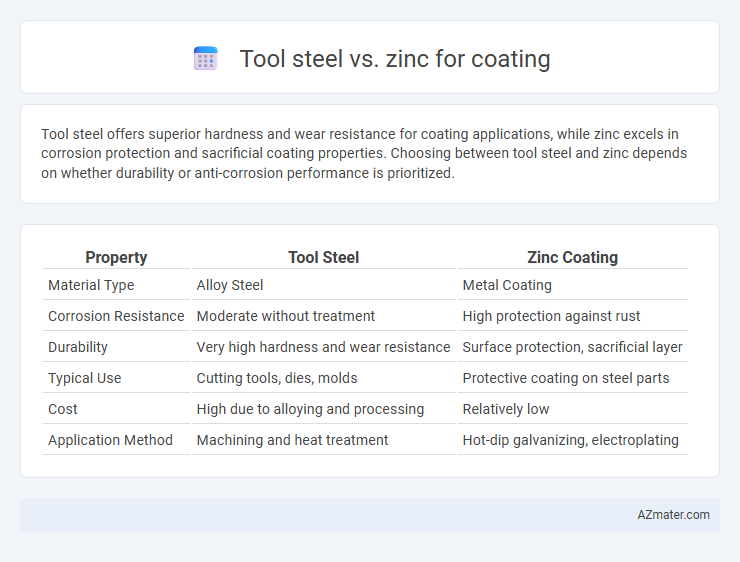
Tool steel offers superior hardness and wear resistance for coating applications, while zinc excels in corrosion protection and sacrificial coating properties. Choosing between tool steel and zinc depends on whether durability or anti-corrosion performance is prioritized.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tool Steel | Zinc Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Alloy Steel | Metal Coating |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate without treatment | High protection against rust |
| Durability | Very high hardness and wear resistance | Surface protection, sacrificial layer |
| Typical Use | Cutting tools, dies, molds | Protective coating on steel parts |
| Cost | High due to alloying and processing | Relatively low |
| Application Method | Machining and heat treatment | Hot-dip galvanizing, electroplating |
Introduction to Tool Steel and Zinc Coating
Tool steel, known for its high hardness and resistance to abrasion, is widely used in manufacturing cutting tools, dies, and molds, where durability and strength are critical. Zinc coating, primarily applied through galvanization, provides a protective layer that prevents corrosion and extends the lifespan of steel products in harsh environments. Comparing the intrinsic properties of tool steel with the protective benefits of zinc coating highlights the balance between mechanical performance and corrosion resistance in industrial applications.
Composition and Properties of Tool Steel
Tool steel is primarily composed of carbon, chromium, vanadium, molybdenum, and tungsten, which provide exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and toughness essential for cutting and shaping applications. These alloys undergo heat treatment to achieve a balance of strength and durability, making tool steel ideal for high-stress environments, unlike zinc coatings that mainly offer corrosion resistance. Zinc coatings serve as sacrificial layers protecting underlying metals from oxidation, whereas tool steel's intrinsic composition ensures mechanical performance without relying on protective layers.
Characteristics and Uses of Zinc Coatings
Zinc coatings provide exceptional corrosion resistance by forming a protective barrier and sacrificing itself through galvanic action, making it ideal for steel protection in outdoor and marine environments. Unlike tool steel, which offers high hardness and wear resistance for cutting and shaping tools, zinc coatings are primarily used to extend the lifespan of steel components by preventing rust formation. Common applications of zinc coatings include automotive parts, construction materials, and electrical appliances where durability and weather resistance are crucial.
Corrosion Resistance: Tool Steel vs Zinc
Tool steel offers superior mechanical strength but has limited inherent corrosion resistance compared to zinc coatings. Zinc provides excellent corrosion resistance through sacrificial galvanic protection, effectively preventing rust formation on steel substrates. In environments prone to moisture and oxidation, zinc coatings significantly extend the lifespan of steel tools by acting as a protective barrier against corrosive elements.
Surface Hardness and Wear Performance
Tool steel coatings exhibit significantly higher surface hardness compared to zinc coatings, typically ranging from 55 to 65 HRC, enhancing resistance to abrasive wear. Zinc coatings, with a softer surface hardness around 2.5 to 3.5 on the Mohs scale, provide sacrificial corrosion protection but offer limited wear resistance. In high-wear applications, tool steel coatings outperform zinc by maintaining dimensional stability and reducing material loss under mechanical stress.
Application Methods and Processes
Tool steel typically undergoes coating processes such as PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition), CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition), or electroplating to enhance hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion protection in cutting, molding, and industrial tooling applications. Zinc coatings, commonly applied through hot-dip galvanizing, electro-galvanizing, or zinc thermal spray, primarily serve to prevent rust and corrosion on steel structures, automotive parts, and construction materials. The application of zinc coatings is generally more cost-effective and suited for large surface areas, while tool steel coatings require precise, controlled environments for uniform deposition and durability in high-stress conditions.
Cost Comparison: Tool Steel vs Zinc Coating
Tool steel typically incurs higher initial costs compared to zinc coatings due to its material hardness and manufacturing complexity. Zinc coating provides a cost-effective corrosion-resistant solution with lower application expenses and maintenance requirements. Long-term cost analysis favors zinc coating for protective purposes, while tool steel offers durability that may justify higher upfront investments in specialized applications.
Durability and Longevity Analysis
Tool steel offers superior durability and longevity compared to zinc coatings due to its high hardness, wear resistance, and ability to maintain structural integrity under extreme stress. Zinc coatings primarily provide corrosion protection through sacrificial anode action but are less effective against mechanical abrasion and wear over time. The longevity of tool steel in demanding applications surpasses zinc-coated materials, especially where mechanical strength and surface resilience are critical factors.
Maintenance and Repair Considerations
Tool steel coatings offer superior durability and resistance to wear, reducing the frequency of maintenance and repair compared to zinc coatings that are prone to corrosion over time. Zinc coatings require regular inspections and touch-ups to prevent rust and degradation, especially in harsh environments. Repair of tool steel coatings tends to be more complex and costly but less frequent, while zinc coatings are easier and cheaper to reapply but demand more frequent upkeep.
Best Use Cases: Choosing Between Tool Steel and Zinc Coating
Tool steel offers superior hardness and wear resistance, making it ideal for cutting, stamping, and molding applications that demand durability and precision. Zinc coating excels in corrosion resistance, providing a protective barrier on steel components exposed to moisture and environmental elements, such as automotive parts and outdoor structures. Selecting between tool steel and zinc coating depends on whether the primary requirement is mechanical strength or enhanced weather resistance.
Infographic: Tool steel vs Zinc for Coating
 azmater.com
azmater.com