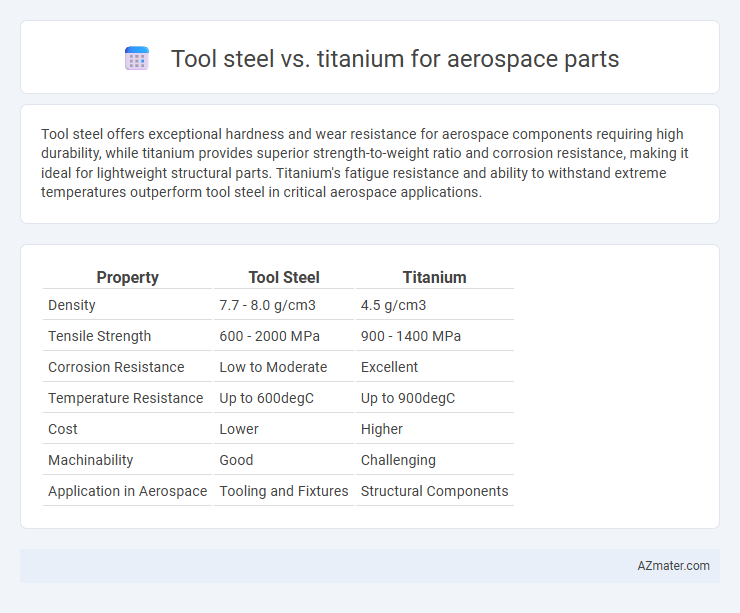
Tool steel offers exceptional hardness and wear resistance for aerospace components requiring high durability, while titanium provides superior strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for lightweight structural parts. Titanium's fatigue resistance and ability to withstand extreme temperatures outperform tool steel in critical aerospace applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tool Steel | Titanium |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 7.7 - 8.0 g/cm3 | 4.5 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 600 - 2000 MPa | 900 - 1400 MPa |
| Corrosion Resistance | Low to Moderate | Excellent |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 600degC | Up to 900degC |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Machinability | Good | Challenging |
| Application in Aerospace | Tooling and Fixtures | Structural Components |
Introduction to Tool Steel and Titanium in Aerospace
Tool steel, known for its high hardness, wear resistance, and ability to retain shape under stress, is commonly utilized in aerospace applications requiring precision tooling and forming dies. Titanium offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability, making it ideal for critical aerospace components such as airframe structures and engine parts. The choice between tool steel and titanium depends on specific aerospace requirements, balancing durability, weight reduction, and mechanical performance.
Key Material Properties: Tool Steel vs Titanium
Tool steel offers high hardness and wear resistance essential for aerospace tooling applications, while titanium provides a superior strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance crucial for aerospace structural parts. Titanium's excellent fatigue resistance and ability to perform well under extreme temperatures make it preferred for critical aerospace components, whereas tool steel excels in applications requiring durability and machinability. The choice between tool steel and titanium depends on balancing aerospace demands for weight reduction, mechanical strength, and environmental resilience.
Strength and Weight Comparison
Tool steel offers exceptional tensile strength and hardness, making it ideal for aerospace parts subjected to high stress and wear; however, it is significantly heavier, with a density around 7.85 g/cm3. Titanium alloys provide an excellent strength-to-weight ratio, combining high tensile strength with low density approximately 4.5 g/cm3, resulting in substantial weight savings crucial for aerospace efficiency. Despite being lighter, titanium retains corrosion resistance and fatigue strength superior to most tool steels, making it preferable for weight-sensitive aerospace components.
Corrosion Resistance and Durability
Titanium offers superior corrosion resistance compared to most tool steels, making it ideal for aerospace parts exposed to harsh environments such as saltwater or high humidity. Tool steel, while highly durable and wear-resistant, typically requires protective coatings to prevent rust and corrosion in aerospace applications. The superior durability of titanium under cyclic stress and its ability to maintain strength at elevated temperatures further enhance its performance in critical aerospace components.
Machinability and Fabrication Challenges
Tool steel offers excellent wear resistance and hardness but presents significant machinability challenges due to its high toughness and tendency to cause tool wear, increasing fabrication time and costs in aerospace parts. Titanium provides superior strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, yet its poor thermal conductivity and reactivity at high temperatures complicate machining processes, requiring specialized tooling and techniques. Both materials necessitate tailored fabrication strategies to balance performance requirements with machining efficiency in aerospace applications.
Cost Analysis: Tool Steel vs Titanium
Tool steel offers a significantly lower initial cost compared to titanium, making it a cost-effective choice for aerospace parts with moderate performance requirements. Titanium's higher material cost is offset by its superior strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, which reduce maintenance and fuel expenses over the aircraft's lifespan. Considering lifecycle costs, titanium often provides better long-term value despite its premium price.
Performance in High-Temperature Environments
Tool steel demonstrates excellent hardness and wear resistance but experiences significant strength reduction and oxidation at temperatures exceeding 500degC. Titanium alloys maintain superior strength-to-weight ratios and corrosion resistance while sustaining mechanical properties up to approximately 600degC, making them more suitable for high-temperature aerospace applications. The choice between tool steel and titanium hinges on balancing temperature resilience, weight constraints, and structural integrity for specific aerospace component requirements.
Typical Aerospace Applications for Each Material
Tool steel excels in aerospace applications requiring high wear resistance and dimensional stability, such as cutting tools, dies, and molds used in manufacturing aircraft components. Titanium is preferred for structural aerospace parts, like airframe components, turbine blades, and fasteners, due to its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and fatigue performance. Each material's unique properties cater to specific aerospace requirements, with tool steel dominating in tool-making and titanium in lightweight structural applications.
Advances in Material Technology
Advances in material technology have significantly enhanced the performance of aerospace components by optimizing the use of tool steel and titanium. Tool steel offers exceptional hardness and wear resistance, making it ideal for high-stress aerospace tooling applications, while titanium's superior strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance improve fuel efficiency and durability in critical aircraft parts. Innovations in alloy composition and processing techniques, such as powder metallurgy and additive manufacturing, are driving the next generation of aerospace materials that balance strength, weight, and longevity.
Choosing the Right Material for Aerospace Parts
Tool steel offers exceptional hardness and wear resistance, ideal for aerospace parts requiring high durability under stress. Titanium provides superior strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance, making it preferable for components exposed to extreme environments and weight-sensitive applications. Selecting the right material depends on balancing factors such as mechanical performance, weight constraints, and environmental conditions for optimal aerospace part functionality.
Infographic: Tool steel vs Titanium for Aerospace part
 azmater.com
azmater.com