Tool steel offers superior hardness and wear resistance, making it ideal for demanding applications, while nickel plating provides excellent corrosion resistance and a smooth finish to enhance durability. Selecting tool steel with nickel plating combines mechanical strength with protective surface properties for extended tool life.
Table of Comparison
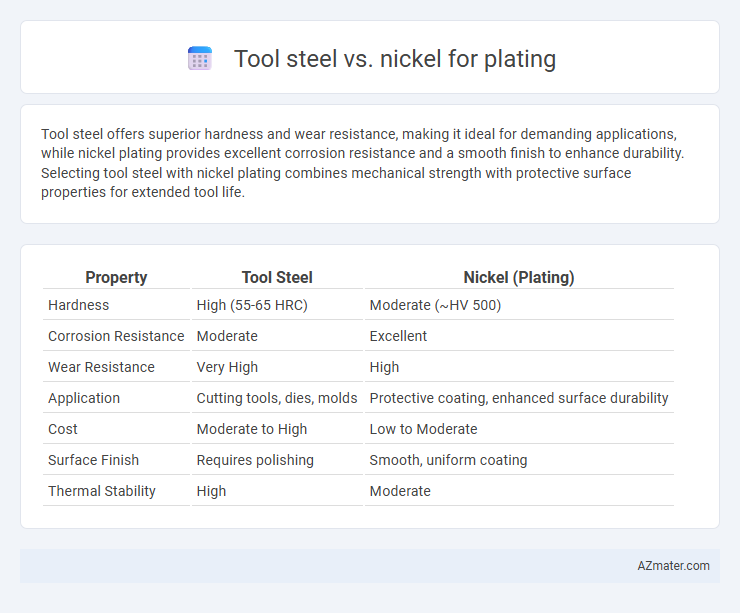
| Property | Tool Steel | Nickel (Plating) |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | High (55-65 HRC) | Moderate (~HV 500) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Wear Resistance | Very High | High |
| Application | Cutting tools, dies, molds | Protective coating, enhanced surface durability |
| Cost | Moderate to High | Low to Moderate |
| Surface Finish | Requires polishing | Smooth, uniform coating |
| Thermal Stability | High | Moderate |
Introduction to Tool Steel and Nickel Plating
Tool steel offers exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and durability, making it ideal for cutting, stamping, and forming applications. Nickel plating enhances corrosion resistance and surface hardness by depositing a uniform nickel layer, improving tool steel's lifespan in harsh environments. This combination of tool steel and nickel plating ensures superior performance and extended tool service life in industrial operations.
Chemical Composition and Material Properties
Tool steel contains high carbon and various alloying elements such as chromium, vanadium, and molybdenum, providing exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and toughness. Nickel plating offers excellent corrosion resistance, ductility, and a smooth finish due to its primarily nickel base with traces of other metals for enhanced adhesion. The chemical composition difference results in tool steel being ideal for mechanical strength applications, while nickel plating improves surface durability and corrosion protection.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Tool steel exhibits superior mechanical strength and hardness compared to nickel, making it ideal for high-stress applications where wear resistance is critical. Nickel plating enhances corrosion resistance and adds moderate hardness but does not match the inherent tensile strength and impact resistance of tool steel. The combination of tool steel substrate with nickel plating offers balanced durability with corrosion protection but relies primarily on the tool steel's mechanical properties for load-bearing performance.
Corrosion Resistance: Tool Steel vs Nickel
Tool steel exhibits moderate corrosion resistance but is prone to rust and oxidation when exposed to moisture and harsh environments. Nickel plating significantly enhances corrosion resistance by providing a dense, protective barrier that prevents oxidation and chemical damage. This makes nickel-coated tool steel ideal for applications requiring long-term durability and protection against rust.
Surface Hardness and Wear Resistance
Tool steel offers superior surface hardness and wear resistance compared to nickel plating, making it ideal for applications requiring heavy-duty cutting and molding. Nickel plating enhances corrosion resistance and provides moderate wear protection but typically underperforms against abrasion and impact stresses relative to tool steel. For extended durability in harsh mechanical environments, tool steel maintains structural integrity better due to its inherent alloy composition and heat treatment capabilities.
Plating Process Overview
Tool steel requires precise surface preparation before nickel plating to ensure strong adhesion and corrosion resistance. The plating process typically involves cleaning, etching, activation, and the application of a nickel layer using electroplating methods, which enhances hardness and wear resistance. Nickel plating on tool steel also improves surface smoothness and provides a protective barrier against oxidation and chemical exposure.
Adhesion Characteristics in Plating
Tool steel offers superior adhesion characteristics in plating due to its high hardness and surface stability, which promote strong mechanical interlocking with the plating layer. Nickel plating on tool steel exhibits excellent adhesion, enhancing corrosion resistance and wear properties, compared to direct plating on softer substrates. Conversely, nickel as a substrate for plating often requires pretreatment to achieve adequate adhesion, making tool steel the preferred choice for durable, well-adhered plating finishes.
Cost Analysis: Tool Steel vs Nickel Plating
Tool steel offers a lower initial material cost compared to nickel plating, which involves added expenses for surface preparation, plating process, and post-treatment. Nickel plating incurs ongoing maintenance costs due to wear and potential re-plating, increasing the long-term expense relative to solid tool steel components. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including durability and application-specific requirements, is critical when choosing between tool steel and nickel plating for industrial uses.
Industrial Applications and Suitability
Tool steel, known for its high hardness and wear resistance, is ideal for industrial applications requiring durable cutting, forming, and stamping tools. Nickel plating enhances corrosion resistance and surface hardness, making it suitable for components exposed to harsh environments and frequent mechanical stress. Combining tool steel substrates with nickel plating extends tool life, improves performance in manufacturing processes, and reduces maintenance costs.
Choosing the Right Material for Plating
Tool steel offers exceptional hardness and wear resistance ideal for high-stress applications, while nickel plating provides superior corrosion resistance and a uniform, aesthetically pleasing finish. Selecting the right material for plating depends on the desired balance between mechanical durability and surface protection, with nickel preferred for environmental shielding and tool steel chosen for structural strength. Understanding the specific operational conditions and performance requirements ensures optimal material compatibility and plating longevity.
Infographic: Tool steel vs Nickel for Plating
 azmater.com
azmater.com