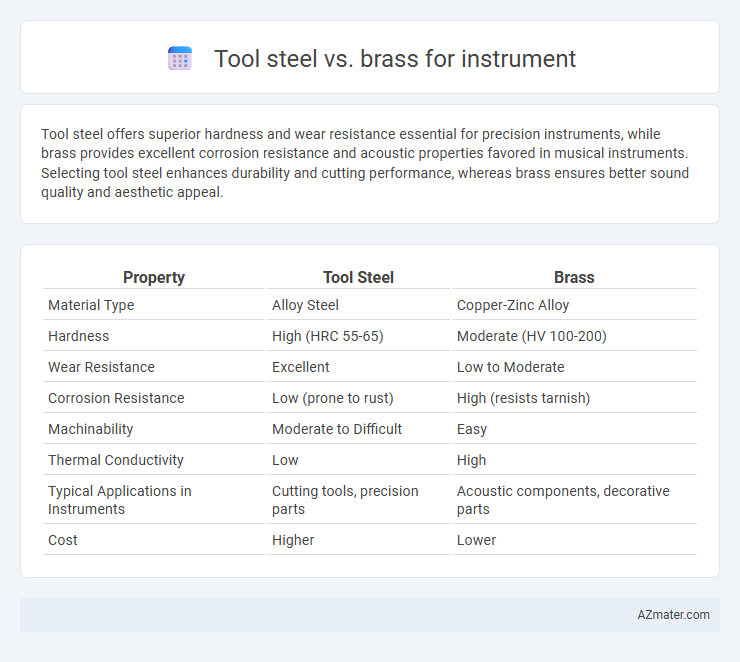
Tool steel offers superior hardness and wear resistance essential for precision instruments, while brass provides excellent corrosion resistance and acoustic properties favored in musical instruments. Selecting tool steel enhances durability and cutting performance, whereas brass ensures better sound quality and aesthetic appeal.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tool Steel | Brass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Alloy Steel | Copper-Zinc Alloy |
| Hardness | High (HRC 55-65) | Moderate (HV 100-200) |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent | Low to Moderate |
| Corrosion Resistance | Low (prone to rust) | High (resists tarnish) |
| Machinability | Moderate to Difficult | Easy |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low | High |
| Typical Applications in Instruments | Cutting tools, precision parts | Acoustic components, decorative parts |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction: Understanding Instrument Materials
Tool steel offers exceptional hardness and wear resistance, making it ideal for precision instrument components requiring durability and rigidity. Brass provides excellent corrosion resistance and acoustic properties, favored in musical instruments and decorative parts for its malleability and warm tonal quality. Selecting between tool steel and brass depends on balancing mechanical strength with aesthetic and acoustic performance in instrument design.
Tool Steel vs Brass: Core Material Properties
Tool steel offers superior hardness, wear resistance, and tensile strength compared to brass, making it ideal for instruments requiring durability and precision. Brass exhibits excellent corrosion resistance, electrical conductivity, and machinability but lacks the strength and hardness found in tool steel. The choice between tool steel and brass core materials ultimately depends on the specific performance needs, with tool steel favored for high-stress applications and brass preferred for environments demanding corrosion resistance and ease of fabrication.
Durability and Longevity in Instrument Construction
Tool steel exhibits superior durability and longevity in instrument construction compared to brass, owing to its high hardness, abrasion resistance, and exceptional tensile strength. Brass offers moderate corrosion resistance and ease of machining but is softer and more prone to wear and deformation under stress over time. Instruments crafted with tool steel components maintain structural integrity and precise performance for extended periods, making it ideal for high-impact and precision applications.
Sound Quality and Acoustic Performance
Tool steel offers superior durability and hardness, resulting in consistent tonal quality and enhanced resonance for musical instruments requiring precision and brightness. Brass provides warmer, richer harmonics with excellent resonance, making it ideal for brasswind instruments where a mellow and full-bodied sound is essential. The choice between tool steel and brass significantly impacts acoustic performance, with tool steel favoring clarity and projection while brass excels in tonal warmth and sustain.
Resistance to Corrosion and Maintenance Needs
Tool steel exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to brass, making it highly suitable for instruments exposed to harsh or humid environments. Its low susceptibility to rust and minimal maintenance requirements ensure long-term durability and consistent performance. Brass, while easier to machine, requires regular polishing and protective coatings to prevent tarnishing and corrosion over time.
Workability: Crafting Precision Instruments
Tool steel offers superior hardness and wear resistance, making it ideal for precision instrument components requiring durability and sharp edges. Brass, with its excellent machinability and corrosion resistance, allows for smooth shaping and fine detailing during crafting, enhancing workability for intricate parts. Both materials serve specific roles in instrument making, balancing toughness with ease of machining based on the application's precision demands.
Weight and Playability: User Experience
Tool steel offers significantly higher density than brass, resulting in a heavier instrument that may affect long-term playing comfort and fatigue. Brass, being lighter, provides enhanced playability and maneuverability, which is preferred by musicians seeking ease of handling during extended sessions. The weight difference influences balance and responsiveness, directly impacting user experience and performance quality.
Cost Comparison: Tool Steel vs Brass
Tool steel typically incurs higher costs than brass due to its enhanced durability, wear resistance, and heat tolerance, which are critical for precision instruments exposed to stress and friction. Brass offers a more economical option with good machinability and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for less demanding instrument components. Cost efficiency in instrument manufacturing depends on balancing the material's initial price with its performance and longevity benefits.
Common Instrument Applications for Each Material
Tool steel is favored in musical instruments for components requiring high durability and wear resistance, such as piano action parts and woodwind key mechanisms. Brass is extensively used in wind instruments, including trumpets, trombones, and saxophones, due to its excellent acoustic properties and corrosion resistance. The choice between tool steel and brass depends on the instrument's functional demands, with tool steel supporting mechanical strength and brass enhancing sound quality.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Material for Instruments
Tool steel offers exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and durability, making it ideal for instruments requiring high precision and long-lasting performance. Brass provides excellent corrosion resistance, machinability, and a warm tonal quality, preferred for instruments where acoustic properties and ease of fabrication are priorities. Selecting between tool steel and brass depends on the instrument's functional demands, balancing mechanical strength with desired sound characteristics.
Infographic: Tool steel vs Brass for Instrument
 azmater.com
azmater.com