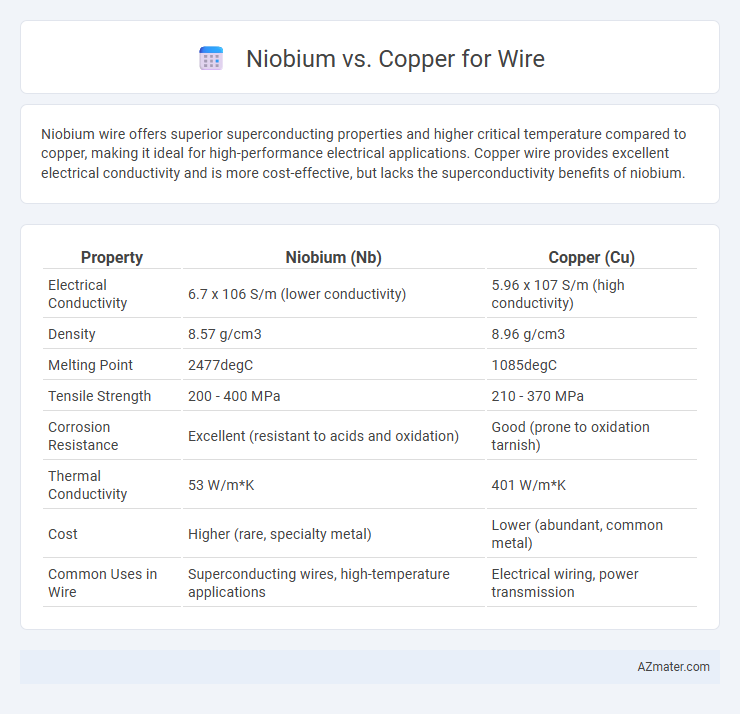
Niobium wire offers superior superconducting properties and higher critical temperature compared to copper, making it ideal for high-performance electrical applications. Copper wire provides excellent electrical conductivity and is more cost-effective, but lacks the superconductivity benefits of niobium.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Niobium (Nb) | Copper (Cu) |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | 6.7 x 106 S/m (lower conductivity) | 5.96 x 107 S/m (high conductivity) |
| Density | 8.57 g/cm3 | 8.96 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 2477degC | 1085degC |
| Tensile Strength | 200 - 400 MPa | 210 - 370 MPa |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent (resistant to acids and oxidation) | Good (prone to oxidation tarnish) |
| Thermal Conductivity | 53 W/m*K | 401 W/m*K |
| Cost | Higher (rare, specialty metal) | Lower (abundant, common metal) |
| Common Uses in Wire | Superconducting wires, high-temperature applications | Electrical wiring, power transmission |
Introduction to Niobium and Copper Wires
Niobium wire offers exceptional strength, corrosion resistance, and superconducting properties, making it ideal for specialized applications such as aerospace, medical devices, and high-performance electronics. Copper wire, renowned for its superior electrical conductivity and affordability, is widely used in electrical wiring, telecommunications, and power generation. When comparing niobium vs copper wires, factors like conductivity, mechanical strength, and cost efficiency determine their suitability for specific industrial and technological uses.
Physical and Chemical Properties Comparison
Niobium exhibits a higher melting point of about 2,468degC compared to copper's 1,085degC, enhancing its thermal stability for wire applications in extreme environments. Chemically, niobium is more corrosion-resistant due to its passive oxide layer, while copper offers superior electrical conductivity around 5.96 x 10^7 S/m, surpassing niobium's lower conductivity of approximately 6.7 x 10^6 S/m. Niobium's flexibility and strength under cryogenic conditions make it ideal for specialized superconducting wire, whereas copper's ductility and excellent conductivity suit general electrical wiring.
Electrical Conductivity: Niobium vs Copper
Copper exhibits superior electrical conductivity, approximately 5.96 x 10^7 Siemens per meter (S/m), making it the preferred choice for electrical wiring in most applications. Niobium's electrical conductivity is significantly lower, about 1.5 x 10^7 S/m, limiting its efficiency in conducting electricity compared to copper. Despite niobium's lower conductivity, its properties such as corrosion resistance and superconductivity under specific conditions make it valuable in specialized wire applications beyond standard electrical use.
Thermal Conductivity and Heat Resistance
Niobium exhibits significantly higher heat resistance compared to copper, maintaining mechanical stability at temperatures exceeding 2,000degC, making it ideal for high-temperature wire applications. Copper offers superior thermal conductivity, approximately 400 W/m*K, which enhances efficient heat dissipation but has a lower melting point around 1,085degC. Choosing niobium wire is advantageous in environments demanding corrosion resistance and thermal endurance, whereas copper wire excels in electrical applications requiring rapid heat transfer.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Niobium wire exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to copper, with a tensile strength often exceeding 200 MPa, making it ideal for applications requiring high durability under stress. Its corrosion resistance and ability to maintain strength at cryogenic temperatures enhance its longevity in harsh environments. Copper, while highly conductive, typically shows lower mechanical strength around 210 MPa and is more prone to deformation and oxidation over time.
Corrosion Resistance and Longevity
Niobium exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to copper, making it highly suitable for harsh environments and applications requiring long service life. Its ability to endure oxidation and chemical exposure without significant degradation extends the longevity of wires made from niobium. Copper, while highly conductive, tends to oxidize and corrode over time, reducing its durability in corrosive conditions.
Weight and Flexibility Considerations
Niobium offers a significant weight advantage over copper due to its lower density, making it ideal for applications where reducing mass is critical. Its excellent flexibility allows niobium wire to withstand repeated bending and deformation without breaking, outperforming copper in durability. Copper remains heavier and less flexible, which can limit its use in lightweight or highly flexible wiring applications.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Niobium wire typically costs more than copper due to its rarity and complex extraction process, making it less economically feasible for large-scale electrical applications. Copper remains widely available and affordable, benefiting from extensive mining operations and established recycling infrastructures. The cost-effectiveness and abundant supply of copper make it the preferred choice for most wiring needs despite niobium's superior superconducting properties.
Common Applications in Industry
Niobium wire is preferred in superconducting magnets, aerospace, and nuclear reactors due to its high melting point, corrosion resistance, and excellent superconducting properties. Copper wire dominates in electrical wiring, power transmission, and electronics because of its superior electrical conductivity, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. Industries select niobium for high-performance, high-temperature environments, while copper serves standard electrical and thermal conduction needs in consumer and industrial applications.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Project
Niobium offers superior corrosion resistance, higher melting point, and excellent superconducting properties compared to copper, making it ideal for specialized applications like aerospace or medical wiring. Copper remains the preferred choice for general electrical wiring due to its outstanding electrical conductivity, affordability, and ease of installation. Selecting between niobium and copper should consider project requirements such as conductivity needs, environmental conditions, and budget constraints to ensure optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
Infographic: Niobium vs Copper for Wire
 azmater.com
azmater.com