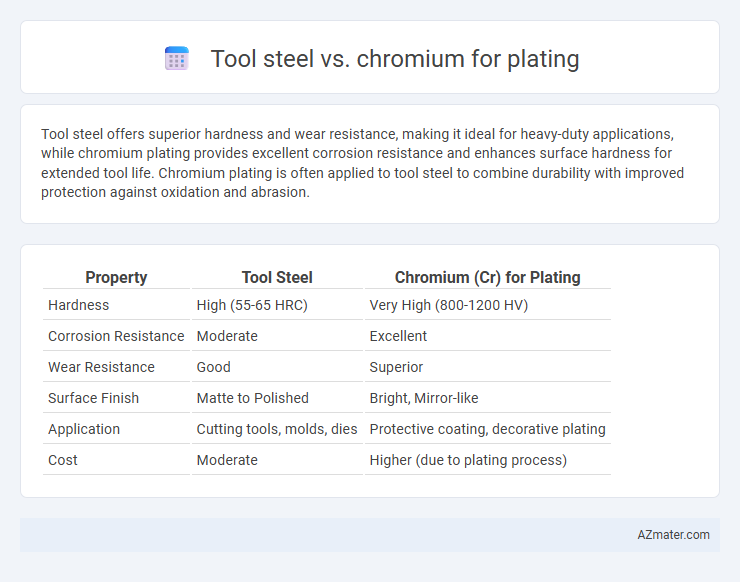
Tool steel offers superior hardness and wear resistance, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications, while chromium plating provides excellent corrosion resistance and enhances surface hardness for extended tool life. Chromium plating is often applied to tool steel to combine durability with improved protection against oxidation and abrasion.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tool Steel | Chromium (Cr) for Plating |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | High (55-65 HRC) | Very High (800-1200 HV) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Wear Resistance | Good | Superior |
| Surface Finish | Matte to Polished | Bright, Mirror-like |
| Application | Cutting tools, molds, dies | Protective coating, decorative plating |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher (due to plating process) |
Overview of Tool Steel and Chromium
Tool steel is a high-carbon steel known for its exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and ability to retain a sharp edge, making it ideal for cutting, molding, and stamping applications. Chromium, a hard, corrosion-resistant metal, is commonly used as a plating material to enhance surface durability, reduce friction, and prevent rust on tool steel components. The combination of tool steel substrates with chromium plating significantly improves tool longevity and performance in demanding industrial environments.
Chemical Composition Differences
Tool steel typically contains high carbon levels combined with elements like manganese, tungsten, and vanadium to enhance hardness and wear resistance, whereas chromium plating primarily consists of a thin layer of chromium metal known for its exceptional corrosion resistance and surface hardness. The chemical composition of tool steel is a bulk alloy designed for structural strength and toughness, while chromium plating provides a surface coating rich in chromium that enhances durability and reduces oxidation. Unlike tool steel's complex alloy matrix, chromium plating offers a pure metallic layer that significantly alters the surface chemistry without affecting the underlying material's core composition.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Tool steel exhibits superior hardness and wear resistance compared to chromium plating, making it ideal for high-impact and heavy-load applications. Chromium plating enhances surface hardness and corrosion resistance on softer substrates but lacks the bulk mechanical strength of solid tool steel. The ductility and toughness of tool steel surpass that of chromium coatings, which tend to be brittle and prone to cracking under stress.
Corrosion Resistance: Tool Steel vs Chromium
Tool steel offers moderate corrosion resistance but tends to oxidize and rust when exposed to moisture and harsh environments due to its iron content. Chromium plating significantly enhances corrosion resistance by forming a hard, non-reactive chromium oxide layer that protects underlying metals from rust, wear, and chemical damage. This protective chromium layer extends the lifespan of components in aggressive environments, making chromium plating a preferred choice over bare tool steel for corrosion resistance.
Hardness and Wear Resistance Analysis
Tool steel offers superior hardness ranging from 55 to 67 HRC, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring significant wear resistance and impact strength. Chromium plating, with hardness typically between 60 to 70 HRC, provides excellent surface wear resistance and corrosion protection but lacks the toughness of tool steel substrates. The combination of tool steel base materials with chromium plating enhances overall durability by leveraging the substrate's hardness and the coating's wear resistance properties.
Plating Process and Techniques
Tool steel offers robust mechanical properties, making it ideal for plating processes like electroplating and physical vapor deposition (PVD) to enhance surface hardness and wear resistance. Chromium plating on tool steel involves a multi-step process including cleaning, activation, and deposition to create a corrosion-resistant, low-friction surface ideal for industrial applications. Advanced techniques such as hard chromium plating use electrolytic baths to deposit thick, dense chromium layers that improve the longevity and performance of tool steel components.
Application Suitability in Industry
Tool steel exhibits superior hardness and wear resistance, making it ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications such as cutting, molding, and machining tools. Chromium plating offers enhanced corrosion resistance and surface hardness, suited for applications requiring protection against wear and oxidation in automotive and aerospace industries. Choosing between tool steel and chromium plating depends on whether the priority is structural integrity and toughness or surface durability and environmental protection.
Cost Efficiency and Longevity
Tool steel offers superior durability and wear resistance, making it a cost-efficient choice for applications requiring long service life. Chromium plating enhances surface hardness and corrosion resistance, extending the longevity of components while reducing maintenance costs. Balancing initial investment with operational lifespan, chromium-plated tool steel often delivers optimal cost efficiency in industrial settings.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Tool steel plating often involves hazardous chemicals and generates toxic waste, posing significant environmental and safety risks. Chromium plating, especially hexavalent chromium, is highly toxic and carcinogenic, requiring stringent controls to prevent soil and water contamination. Safer alternatives like trivalent chromium plating and improved waste treatment processes reduce environmental impact and enhance workplace safety.
Selecting the Right Material for Plating
Tool steel offers superior hardness and wear resistance essential for high-stress applications, making it ideal for components requiring durability after plating. Chromium plating on tool steel enhances corrosion resistance, surface hardness, and aesthetic appeal, providing a protective layer that extends the lifespan of the base material. Selecting the right material involves evaluating the tool steel grade for compatibility with chromium plating processes, balancing mechanical properties with plating adhesion requirements.
Infographic: Tool steel vs Chromium for Plating
 azmater.com
azmater.com